|
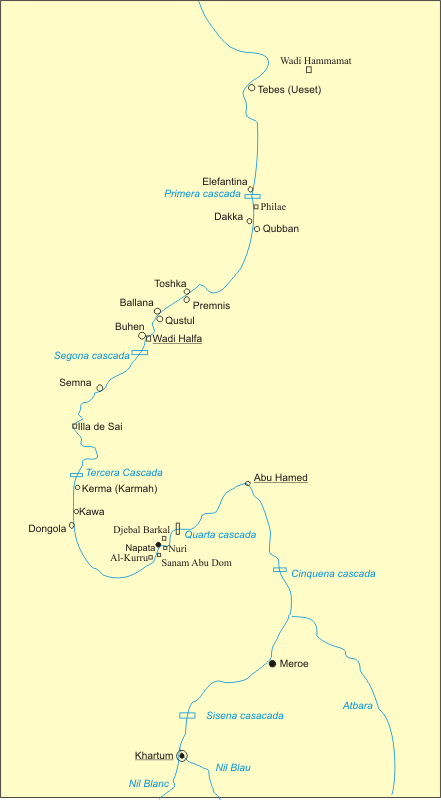
Semna (Nubia) , Semna
The region of Semna is 15 miles south of Wadi Halfa and is situated where rocks cross the Nile narrowing its flow—the Semna Cataract. Semna was a fortified area established in the reign of Senusret I (1965–1920 BC) on the west bank of the Nile at the southern end of a series of Middle Kingdom fortresses founded during the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt (1985–1795 BC) in the Second-Cataract area of Lower Nubia. There are three forts at Semna: Semna West (Semna Gharb), Semna East (Semna Sherq, also called Kummeh or Kumma), and Semna South (Semna Gubli). The forts to the east and west of the Semna Cataract are Semna East and West, respectively; Semna South is approximately one kilometer south of Semna West on the west bank of the Nile. The Semna gorge, at the southern edge of ancient Egypt, was the narrowest part of the Nile valley. It was here, at this strategic location, that the 12th Dynasty pharaohs built a cluster of four mud-brick fortresses: Semna, Kumma, Semna South an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Soil
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined '' alluvion'' (the French term for alluvium) as new land formed by deposition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinized name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time. The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons ( Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic) of the geologic time scale. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance. Overview Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of the Earth's history, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dike (geology), dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF diagram, QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batn-El-Hajar
Batn-El-Hajar or ''Belly of Stones'' is a reach of approximately 160 km in length stretching from the Dal Cataract of the Nile downriver to the now under Lake Nubia submerged Second Cataract in present-day Sudan. History ''Batn-El-Hajar'' is a barren and granite-rich landscape limiting arable soil and, thus, sparsely inhabited. It was the traditional border between Upper Nubia and Lower Nubia. In this area are a number of important A-Group The A-Group was the first powerful society in Nubia, located in modern northern Sudan and southern Egypt and flourished between the First and Second Cataracts of the Nile in Lower Nubia. It lasted from the 4th millennium BC, reached its climax ... and Meroitics archeological sites.D. N. Edwards and A. J. Mills; 'Pharaonic' Sites in the Batn el-Hajar - the 'Archaeological Survey of Sudanese Nubia' Revisited; in: ''Sudan & Nubia'' No 17, published by The Sudan Archaeological Research Society; 2013. References {{coord, 21, 01, 0, N, 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Oriental Institute
The Institute for the Study of Ancient Cultures, West Asia & North Africa (ISAC), formerly known as the Oriental Institute, is the University of Chicago's interdisciplinary research center for ancient Near Eastern studies and archaeology museum. Established in 1919, it was founded for the university by Egyptology and ancient history professor James Henry Breasted with funds donated by John D. Rockefeller Jr. It conducts research on ancient civilizations throughout the Near East, including at its facility, Chicago House, in Luxor, Egypt. The institute also publicly exhibits an extensive collection of artifacts related to ancient civilizations and archaeological discoveries at its on-campus building in Hyde Park, Chicago. According to anthropologist William Parkinson of the Field Museum, the ISAC's highly focused "near Eastern, or southwest Asian and Egyptian" collection is one of the finest in the world. History In the early 20th century, James Henry Breasted built up the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public university, public research university in Tempe, Arizona, United States. Founded in 1885 as Territorial Normal School by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, the university is one of the List of United States university campuses by enrollment, largest public universities by enrollment in the United States. It was one of about 180 "normal schools" founded in the late 19th century to train teachers for the rapidly growing public common schools. Some closed, but most steadily expanded their role and became state colleges in the early 20th century, then state universities in the late 20th century. One of three universities governed by the Arizona Board of Regents, Arizona State University is a member of the Association of American Universities (AAU) and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity". ASU has over 183,000 st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Vico Žabkar
Louis Vico Žabkar (7 December 1914 – 15 September 1994)''Social Security Death Index, 1935-2014''. Social Security Administration. was an American Egyptologist who published a number of academic works and who participated in the 1960s in the UNESCO campaign to salvage the monuments threatened by the building of the Aswan Dam. Louis Žabkar was born on the Dalmatian island of Lastovo, which was then part of Italy. He was born to a Slovenian father, Lieutenant Louis Franz Žabkar, who was stationed on the island, and Italian mother, Maria Carminatti. He immigrated to the United States in 1948. He had eight years of classical studies at the classical gymnasium of Split, Yugoslavia and obtained master's degrees in Oriental history and languages from the Pontifical Biblical and Oriental Institute in Rome. He had mastery of German, French, Italian, Serbo-Croatian, ancient Greek and Latin, Egyptian, Coptic and Hebrew. He received his Ph.D. in 1958 from the University of Chicago. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Vercoutter
Jean Vercoutter (20 January 1911 – 16 July 2000) was a French Egyptologist. One of the pioneers of archaeological research into Sudan from 1953, he was Director of the Institut Français d'Archéologie Orientale from 1977 to 1981. Biography Born in Lambersart, Nord, Vercoutter attended the Académie Julian to learn about painting, but soon turned to Egyptology. In 1939, he graduated from the IVe section of the École Pratique des Hautes Études with a thesis on ancient Egyptian funerary objects and was appointed resident of the French Institute of Oriental Archaeology of Cairo (IFAO). He participated in excavations in Karnak and directed an excavation in El-Tod. Upon his return to France, he joined CNRS (1949–1955). During all these years, he pursued research on the relationship between Egyptians and pre-Hellenes, providing some firm conclusions on the relationship between these two great civilizations and the history of the ancient Aegean world. He was appointed profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |