|
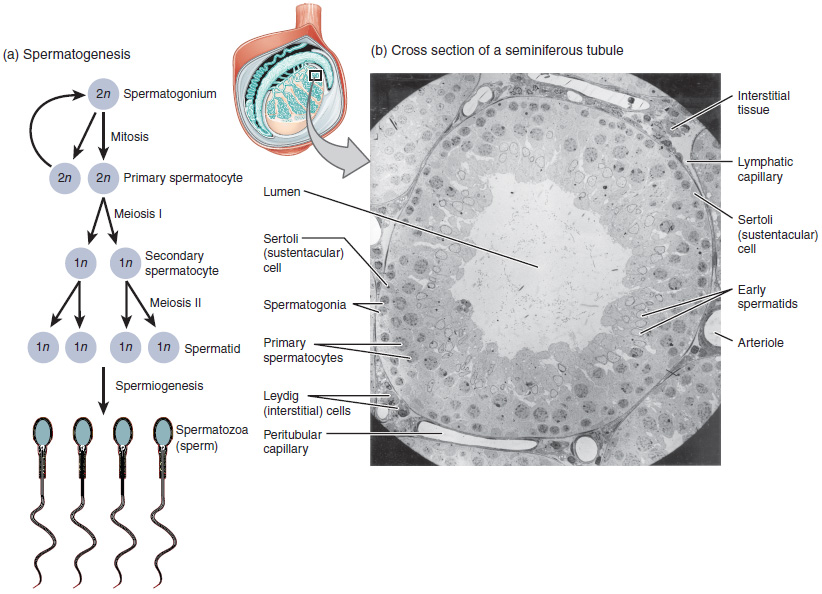
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa. Structure The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells known as Sertoli cells, which are tall, columnar type cells that line the tubule. In between the Sertoli cells are spermatogenic cells, which differentiate through meiosis to sperm cells. Sertoli cells function to nourish the developing sperm cells. They secrete androgen-binding protein, a binding protein which increases the concentration of testosterone. There are two types: convoluted and straight, convoluted toward the lateral side, and straight as the tubule comes medially to form ducts that will exit the testis. The seminiferous tubules are formed from the testis cords that develop from the primitive gonadal cords, formed from the gonadal ridge. Function Spermatogenesis, the process for producing spermatozoa, takes place i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which Cellular differentiation, differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their Ploidy, chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The sper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatozoon
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is the male gamete that Fertilization, joins with an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, that normally develops into an embryo.) Sperm cells contribute approximately half of the nuclear gene, genetic information to the diploid offspring (excluding, in most cases, mitochondrial DNA). In mammals, the sex of the offspring is determined by the sperm cell: a spermatozoon bearing an X chromosome will lead to a female (XX) offspring, while one bearing a Y chromosome will lead to a male (XY) offspring. Sperm cells were first observed in Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's laboratory in 1677. Mammalian spermatozoa Humans The sperm cell of ''Homo sapiens'' is the small Gamete, reproductive cell produced by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leydig Cell
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle and produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH). They are polyhedral in shape and have a large, prominent nucleus, an eosinophilic cytoplasm, and numerous lipid-filled vesicles. Males have two types of leydig cells that appear in two distinct stages of development: the fetal type and the adult type. Structure The mammalian Leydig cell is a polyhedral epithelioid cell with a single eccentrically located ovoid nucleus. The nucleus contains one to three prominent nucleoli and large amounts of dark-staining peripheral heterochromatin. The acidophilic cytoplasm usually contains numerous membrane-bound lipid droplets and large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Besides the abundance of SER with scattered patches of rough endoplasmic reticulum, several mitochondria are also prominent within the cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to Sexual reproduction, reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of fertility, reproductive capacity, are excluded. It is also a normal state in women after menopause. In humans, ''infertility'' is defined as the inability to become pregnant after at least one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner. There are many causes of infertility, including some that Assisted reproductive technology, medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year, with estimates ranging from 12% to 28%. Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymes
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes described as a ''type'' of enzyme rather than being ''like'' an enzyme, but even in the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl radical (OH.), and singlet oxygen(1O2). ROS are pervasive because they are readily produced from O2, which is abundant. ROS are important in many ways, both beneficial and otherwise. ROS function as signals, that turn on and off biological functions. They are intermediates in the redox behavior of O2, which is central to fuel cells. ROS are central to the photodegradation of organic pollutants in the atmosphere. Most often however, ROS are discussed in a biological context, ranging from their effects on aging and their role in causing dangerous genetic mutations. Inventory of ROS ROS are not uniformly defined. All sources include superoxide, singlet oxygen, and hydroxyl radical. Hydrogen peroxide is not nearly as reactive as these s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatozoon
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is the male gamete that Fertilization, joins with an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, that normally develops into an embryo.) Sperm cells contribute approximately half of the nuclear gene, genetic information to the diploid offspring (excluding, in most cases, mitochondrial DNA). In mammals, the sex of the offspring is determined by the sperm cell: a spermatozoon bearing an X chromosome will lead to a female (XX) offspring, while one bearing a Y chromosome will lead to a male (XY) offspring. Sperm cells were first observed in Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's laboratory in 1677. Mammalian spermatozoa Humans The sperm cell of ''Homo sapiens'' is the small Gamete, reproductive cell produced by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called Spermatogonial Stem Cells, spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm, sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatoz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonadal Ridge
In embryology, the genital ridge (genital fold or gonadal ridge) is the developmental precursor to the gonads. The genital ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic cells. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of cells (pre-granulosa cells). The genital ridge appears at approximately five weeks, and gives rise to the sex cords. Associated genes Genes associated with the developing gonad can be categorized into those that form the sexually indifferent gonad, those that determine whether the indifferent gonad will differentiate as male or female, and those that promote differentiation into male or female parts. Genes that form the sexually indifferent gonad are '' SF1'' and ''WT1''. Genes that determine sex are '' SRY'', ''SOX9'', and '' DAX1''. Genes driving the differentiation into male or female structures are ''SF1'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonadal Cord
Sex cords are embryonic structures which eventually will give rise (differentiate) to the adult gonads (reproductive organs). They are formed from the genital ridges - which will develop into the gonads - in the first 2 months of gestation (embryonic development) which depending on the sex of the embryo will give rise to male or female sex cords. These epithelial cells (from the genital ridges) penetrate and invade the underlying mesenchyme to form the primitive sex cords. This occurs shortly before and during the arrival of the primordial germ cells (PGCs) to the paired genital ridges. If there is a Y chromosome present, testicular cords will develop via the ''Sry gene'' (on the Y chromosome): repressing the female sex cord genes and activating the male. If there is no Y chromosome present the opposite will occur, developing ovarian cords. Prior to giving rise to sex cords, both XX and XY embryos have Müllerian ducts and Wolffian ducts. One of these structures will be repressed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |