|
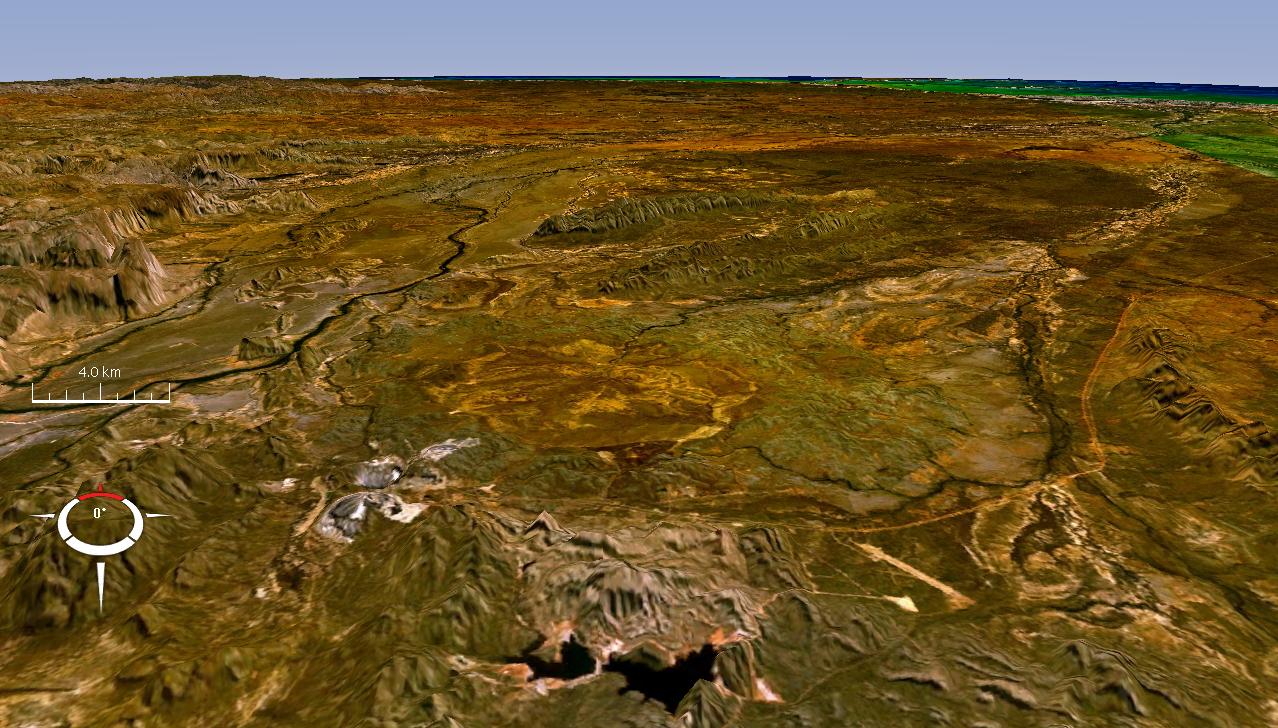
Selwyn Range (Australia)
: ''For the Selwyn Range in the Canadian Rockies, see: Selwyn Range (Canada). Note also the Selwyn Mountains on the border between the Yukon and Northwest Territories in Canada.'' The Selwyn Range (also known as the Isa Highlands) is a rugged mountain range near Mount Isa and Cloncurry in north-west Queensland, Australia, composed largely of Proterozoic metamorphic rocks. It is drained in the north by the Williams and Fullarton rivers, which run into the Gulf of Carpentaria, and in the south by the McKinlay River and its tributary, Boorama Creek which drain also into the Gulf of Carpentaria. The area is heavily mineralised, containing copper, gold, lead, and zinc, and is important for mining. The Kalkadoon people are the traditional owners of the land. Kalkatunga (also known as Kalkadoon, Kalkadunga, Kalkatungu) is an Australian Aboriginal language The Indigenous languages of Australia number in the hundreds, the precise number being quite uncertain, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selwyn Range (Canada)
The Selwyn Range is a mountain range in the Canadian Rockies in British Columbia. A subrange of the Park Ranges of the Continental Ranges, it is located west of Jasper National Park, east of Valemount and south of Mount Robson Provincial Park.BivuacSelwyn Range Retrieved August 7, 2007 It was named after Alfred Selwyn, the first director of the Geological Survey of Canada. The Fraser River originates in this mountain range, near Fraser Pass. See also *Overlander Mountain Overlander Mountain is a summit in British Columbia, Canada. Description Overlander Mountain, elevation 2,687-meters (8,816-feet), is located in Mount Robson Provincial Park, just south and within view of the park's visitor centre. It is the ... * Klapperhorn Mountain * Mount McKirdy References * Mountain ranges of British Columbia Ranges of the Canadian Rockies {{BritishColumbiaInterior-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see differences between British, American, and Australian English explained below). Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests. Extensive efforts by conservationist groups have been made to preserve woodlands from urbanization and agriculture. For example, the woodlands of Northwest Indiana have been preserved as part of the Indiana Dunes. Definitions United Kingdom ''Woodland'' is used in British woodland management t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalypt
Eucalypt is a descriptive name for woody plants with capsule fruiting bodies belonging to seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australasia: ''Eucalyptus'', '' Corymbia'', '' Angophora'', '' Stockwellia'', '' Allosyncarpia'', '' Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum''. Taxonomy For an example of changing historical perspectives, in 1991, largely genetic evidence indicated that some prominent ''Eucalyptus'' species were actually more closely related to ''Angophora'' than to other eucalypts; they were accordingly split off into the new genus ''Corymbia''. Although separate, all of these genera and their species are allied and it remains the standard to refer to the members of all seven genera ''Angophora'', ''Corymbia'', ''Eucalyptus'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' as "eucalypts" or as the eucalypt group. The extant genera ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' comprise s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the Season, solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions of Earth, polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Mount Isa
The City of Mount Isa is a local government area in north west Queensland. The City covers the urban locality of Mount Isa, the administrative centre, and surrounding area, sharing a boundary with the Northern Territory to the west. Mount Isa is a reasonably affluent district. The largest industry in the city is the Mount Isa Mines, a source of lead, copper, silver and zinc. Cattle grazing and tourism are other industries of note. History The city was inhabited by the Kalkadoon and Indjilandji people, whose livelihood depended on hunting and gathering, fishing and trade for several thousands of years, before the European settlers arrived here. The Kalkadoon craftsmen were known for their stone implements and handmade tools which were traded with other Aboriginal groups spread all over the western Queensland. Kalkatunga (also known as Kalkadoon, Kalkadunga, Kalkatungu) is an Australian Aboriginal language. The Kalkatunga language region is North-West Queensland including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Queensland
The Gulf Country is the region of woodland and savanna grassland surrounding the Gulf of Carpentaria in north western Queensland and eastern Northern Territory on the north coast of Australia. The region is also called the Gulf Savannah. It contains large reserves of zinc, lead and silver. The Gulf Country is crossed by the Savannah Way highway. Location and description The Gulf Country is a block of dry savanna between the wetter areas of Arnhem Land and the Top End of the Northern territory to the west and the Cape York Peninsula of Far North Queensland to the east, while to the south and east lie upland plains of Mitchell grasses and the Einasleigh Uplands. The Northern Territory side of the area is the Gulf Fall area of sandstone slopes and gorges draining the interior uplands into the gulf. The main land uses in the Gulf Country are beef cattle and mining. The region covers an area of . The landscape is generally flat and low-lying tropical savannah cut through with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Aboriginal Languages
The Indigenous languages of Australia number in the hundreds, the precise number being quite uncertain, although there is a range of estimates from a minimum of around 250 (using the technical definition of 'language' as non-mutually intelligible varieties) up to possibly 363. The Indigenous languages of Australia comprise numerous language families and isolates, perhaps as many as 13, spoken by the Indigenous peoples of mainland Australia and a few nearby islands. The relationships between the language families are not clear at present although there are proposals to link some into larger groupings. Despite this uncertainty, the Indigenous Australian languages are collectively covered by the technical term "Australian languages", or the "Australian family". The term can include both Tasmanian languages and the Western Torres Strait language, but the genetic relationship to the mainland Australian languages of the former is unknown, while the latter is Pama–Nyungan, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalkatungu Language
Kalkatungu (also ''Kalkutungu'', ''Galgadungu'', ''Kalkutung'', ''Kalkadoon'', or ''Galgaduun'') is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language formerly spoken around the area of Mount Isa and Cloncurry, Queensland. Classification Apart from the closely related language, Wakabunga, Kalkatungu is sometimes grouped with Yalarnnga The Yalarnnga, also known as the Jalanga, are an Indigenous Australian people of the state of Queensland. Language Yalarnnga is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language, hypothesized to be one of the two Galgadungic languages of the Pama–Ny ... as the Kalkatungic (Galgadungic) branch of the Pama–Nyungan family. O'Grady et al., however, classify it as the sole member of the "Kalkatungic group" of the Pama-Nyungan family, and Dixon (2002) regards Kalkatungic as an areal group. Revival Emeritus Professor Barry Blake, Sheree Blackley and others have revived the language based on recordings, written grammars and personal memories. Robert Ah Wing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalkatungu
The Kalkadoon (properly Kalkatungu) are descendants of an Indigenous Australian tribe living in the Mount Isa region of Queensland. Their forefather tribe has been called "the elite of the Aboriginal warriors of Queensland". In 1884 they were massacred at "Battle Mountain" by settlers and police. Language Kalkatung belonged to the Kalkatungic branch of the Pama-Nyungan language family, the other being Yalarnnga which was spoken to its south in the area of Djarra, in Queensland. Kalkatungu was spoken around Mount Isa, Queensland. Nothing is known of a third language Wakabunga sometimes thought to have had a genetic relation to the other two. Remnants of the language collected from the last native speakers by Barry Blake allowed the rudiments of the grammar and the language to be reconstructed. According to Robert M. W. Dixon there is a 43% overlap in vocabulary existed with Yalarnnga but with a different grammar and only 10% percent of verbs cognate. Both have bounded prono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |