|
Selkʼnam Language
Selkʼnam, also known by the exonym Ona, is a language formerly spoken by the Selkʼnam people in Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego in southernmost South America. One of the Chonan languages of Patagonia, Selkʼnam is now extinct, due to the late 19th-century Selkʼnam genocide by Spanish Argentines, European immigrants, high fatalities due to disease, and disruption of traditional society. One source states that the last fluent native speakers died in the 1980s. Radboud University Nijmegen, Radboud University linguist Luis Miguel Rojas-Berscia worked with two individuals to write a reference grammar of the language, namely, Herminia Vera-Ona (died 2014), a semi-speaker who spoke Ona until the age of 8, and , a young man who started learning the language after learning he was part-Selkʼnam at the age of 8. At the time the grammar was written, the latter was believed to be the only living individual fluent in Selkʼnam, albeit not natively. Classification Within the Southern Chon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, eighth-largest country in the world. Argentina shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a Federation, federal state subdivided into twenty-three Provinces of Argentina, provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and List of cities in Argentina by population, largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a Federalism, federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haush
The Haush or people were an Indigenous people who lived on the Mitre Peninsula of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. They were related culturally and linguistically to the Selkʼnam (also known as Ona) people who also lived on the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, and to the Tehuelche people of southern mainland Patagonia. Name ''Haush'' was the name given them by the Selkʼnam people, while the Yahgan (also known as Yámana) people called them ''Italum Ona'', meaning ''Eastern Ona''. Several authors state that their name for themselves was ''Manek'enk'' or ''Manek'enkn''. Martin Gusinde reported, however, that in the Haush language ''Manek'enkn'' simply meant ''people'' in general. Furlong notes that ''Haush'' has no meaning in the Selkʼnam language, while ''haush'' means ''kelp'' in the Yahgan language. Since the Selkʼnam probably met the Yahgan people primarily in Haush territory, Furlong speculates that the Selkʼnam borrowed ''haush'' as the name of the people f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uvular Consonant
Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be stops, fricatives, nasals, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and the symbol for the voiced fricative is used instead. Uvular affricates can certainly be made but are rare: they occur in most Turkic languages, most Persian languages, most Arabic languages, in some southern High-German dialects, as well as a few African and Native American languages. (Ejective uvular affricates occur as realizations of uvular stops in Kazakh, Bashkir, Arabic dialects, Lillooet, or as allophonic realizations of the ejective uvular fricative in Georgian.) Uvular consonants are typically incompatible with advanced tongue root, and they often cause retraction of neighboring vowels. Uvular consonants in IPA The uvular consonants identified by the International Phoneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velar Consonant
Velar consonants are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (also known as the "velum"). Since the velar region of the roof of the mouth is relatively extensive and the movements of the dorsum are not very precise, velars easily undergo assimilation, shifting their articulation back or to the front depending on the quality of adjacent vowels. They often become automatically ''fronted'', that is partly or completely palatal before a following front vowel, and ''retracted'', that is partly or completely uvular before back vowels. Palatalised velars (like English in ''keen'' or ''cube'') are sometimes referred to as palatovelars. Many languages also have labialized velars, such as , in which the articulation is accompanied by rounding of the lips. There are also labial–velar consonants, which are doubly articulated at the velum and at the lips, such as . This distinction disappea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-alveolar Consonant
Postalveolar (post-alveolar) consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the ''back'' of the alveolar ridge. Articulation is farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate, the place of articulation for palatal consonants. Examples of postalveolar consonants are the English palato-alveolar consonants , as in the words "ship", "'chill", "vision", and "jump", respectively. There are many types of postalveolar sounds—especially among the sibilants. The three primary types are ''palato-alveolar'' (such as , weakly palatalized; also ''alveopalatal''), ''alveolo-palatal'' (such as , strongly palatalized), and ''retroflex'' (such as , unpalatalized). The palato-alveolar and alveolo-palatal subtypes are commonly counted as "palatals" in phonology since they rarely contrast with true palatal consonants. Postalveolar sibilants For most sounds involving the tongue, the place of arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Consonant
Alveolar consonants (; UK also ) are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli (the sockets) of the upper teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (the apical consonants), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonants), as in French and Spanish. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all coronal places of articulation that are not palatalized like English palato-alveolar ''sh'', or retroflex. To disambiguate, the ''bridge'' (, ''etc.'') may be used for a dental consonant, or the under-bar (, ''etc.'') may be used for the postalveolars. differs from dental in that the former is a sibilant and the latter is not. differs from postalveolar in being unpalatalized. The bare letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilabial Consonant
In phonetics, a bilabial consonant is a labial consonant articulated with both lips. Frequency Bilabial consonants are very common across languages. Only around 0.7% of the world's languages lack bilabial consonants altogether, including Tlingit, Chipewyan, Oneida, and Wichita, though all of these have a labial–velar approximant /w/. Varieties The bilabial consonants identified by the International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ... (IPA) are: Owere Igbo has a six-way contrast among bilabial stops: . Other varieties The extensions to the IPA also define a () for smacking the lips together. A lip-smack in the non-percussive sense of the lips audibly parting would be . The IPA chart shades out ''bilabial lateral consonants'', wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Accent
A pitch-accent language is a type of language that, when spoken, has certain syllables in words or morphemes that are prominent, as indicated by a distinct contrasting pitch (music), pitch (tone (linguistics), linguistic tone) rather than by volume or length, as in some other languages like English language, English. Pitch-accent languages also contrast with fully tonal languages like Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, Thai language, Thai and Standard Chinese, in which practically every syllable can have an independent tone. Some scholars have claimed that the term "pitch accent" is not coherently defined and that pitch-accent languages are just a sub-category of tonal languages in general. Languages that have been described as pitch-accent languages include: most dialects of Serbo-Croatian, Slovene language, Slovene, Baltic languages, Ancient Greek, Vedic Sanskrit, Tlingit language, Tlingit, Turkish language, Turkish, Japanese language, Japanese, Limburgish, Norwegian language, No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
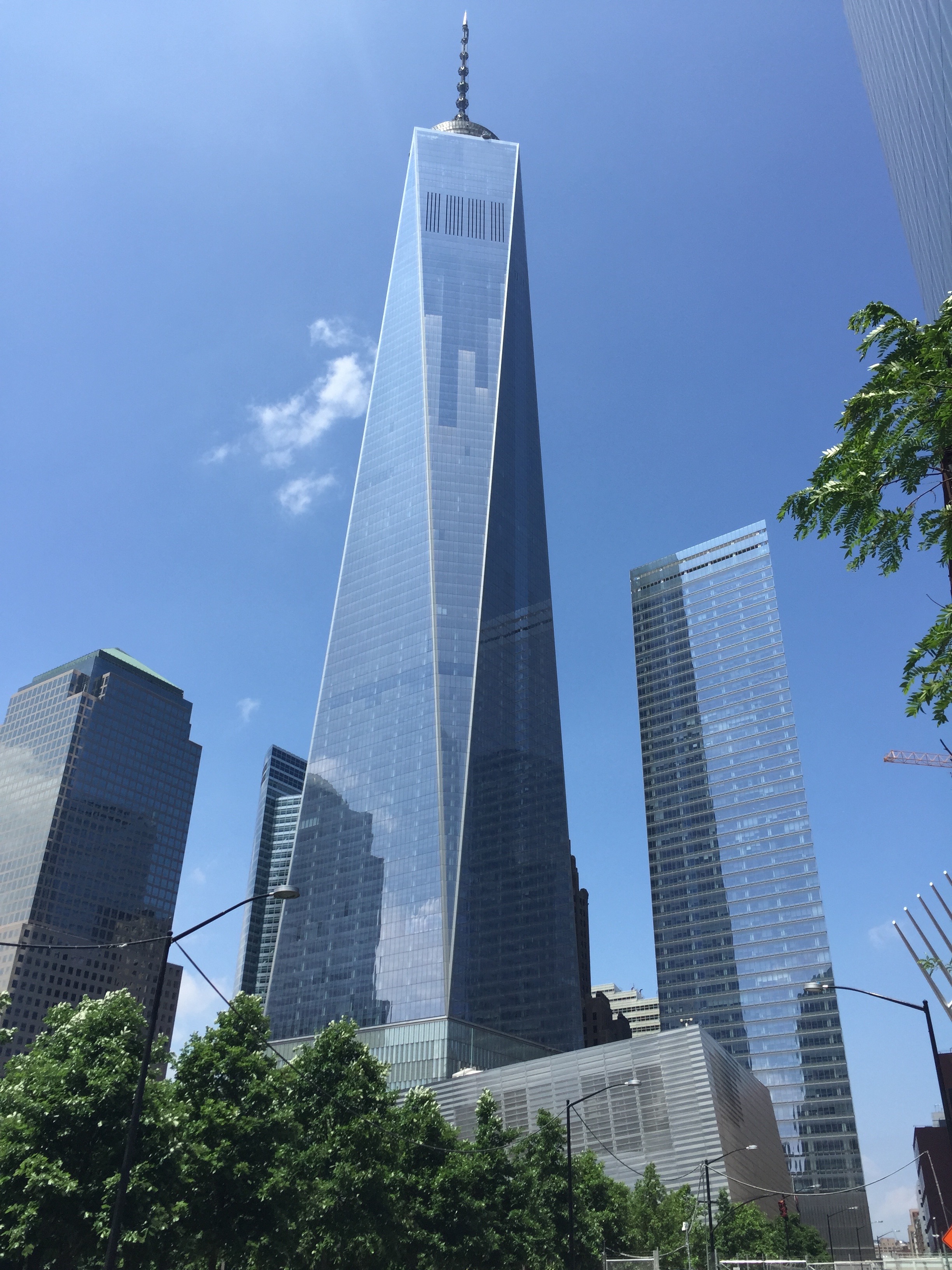
Condé Nast
Condé Nast () is a global mass media company founded in 1909 by Condé Nast (businessman), Condé Montrose Nast (1873–1942) and owned by Advance Publications. Its headquarters are located at One World Trade Center in the FiDi, Financial District of Lower Manhattan. The company's media brands attract more than 72 million consumers in print, 394 million in digital and 454 million across social media platforms. These include ''Vogue (magazine), Vogue'', ''The New Yorker'', ''Condé Nast Traveler'', ''Condé Nast Traveller'', ''GQ'', ''Glamour (magazine), Glamour'', ''Architectural Digest'', ''Vanity Fair (magazine), Vanity Fair, Pitchfork (website), Pitchfork'', ''Wired (magazine), Wired'', ''Bon Appétit'', and ''Ars Technica'', among many others. U.S. ''Vogue'' editor-in-chief Anna Wintour serves as Artistic Director and Global Chief Content Officer. In 2011, the company launched the Condé Nast Entertainment division, tasked with developing film, television, social and digit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. It was founded on February 21, 1925, by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a reporter for ''The New York Times''. Together with entrepreneur Raoul H. Fleischmann, they established the F-R Publishing Company and set up the magazine's first office in Manhattan. Ross remained the editor until his death in 1951, shaping the magazine's editorial tone and standards. ''The New Yorker''s fact-checking operation is widely recognized among journalists as one of its strengths. Although its reviews and events listings often focused on the Culture of New York City, cultural life of New York City, ''The New Yorker'' gained a reputation for publishing serious essays, long-form journalism, well-regarded fiction, and humor for a national and international audience, including work by writers such as Truman Capote, Vladimir Nabokov, and Alice Munro. In the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa River, Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Pampas, Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |