|
Self-sustaining
Self-sustainability and self-sufficiency are overlapping states of being in which a person, being, or system needs little or no help from, or interaction with others. Self-sufficiency entails the self being enough (to fulfill needs), and a self-sustaining entity can maintain self-sufficiency indefinitely. These states represent types of personal or collective autonomy. A self-sufficient economy is one that requires little or no trade with the outside world and is called an autarky. Description Self-sustainability is a type of sustainable living in which nothing is consumed other than what is produced by the self-sufficient individuals. Self-sustainability is a comprehensive approach to sustainable living that extends beyond mere environmental responsibility to encompass economic independence, reduced reliance on major corporations, and minimizing environmental impact through personal actions. Examples of attempts at self-sufficiency in North America include simple living, food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Person
A person (: people or persons, depending on context) is a being who has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of '' personhood'' and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about '' personal identity'' and '' self'': both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using Systems theory, whole-systems thinking. It applies these principles in fields such as regenerative agriculture, town planning, rewilding (conservation biology), rewilding, and community resilience. The term was coined in 1978 by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren, who formulated the concept in opposition to modern industrialized methods, instead adopting a more traditional or "natural" approach to agriculture. Multiple thinkers in the early and mid-20th century explored no-dig gardening, no-till farming, and the concept of "permanent agriculture", which were early inspirations for the field of permaculture. Mollison and Holmgren's work from the 1970s and 1980s led to several books, starting with ''Permaculture One'' in 1978, and to the development of the "Permaculture Design Course" which has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
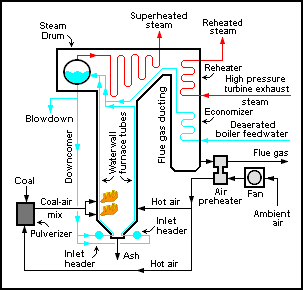
Boiler (power Generation)
file:Dampfkessel für eine Stationärdampfmaschine im Textilmuseum Bocholt.jpg, An industrial boiler, originally used for supplying steam to a stationary steam engine A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed ''boilers'' and worked at low to medium pressure () but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a ''steam generator''. A boiler or steam generator is used wherever a source of steam is required. The form and size depends on the application: mobile steam engines such as steam locomotives, portable engines and Traction engine, steam-powered road vehicles typically use a smaller boiler that forms an integral part of the vehicle; stationary steam engines, industrial installations and power stations will usually have a larger separate steam generating facility connected to the point-of-use by piping. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
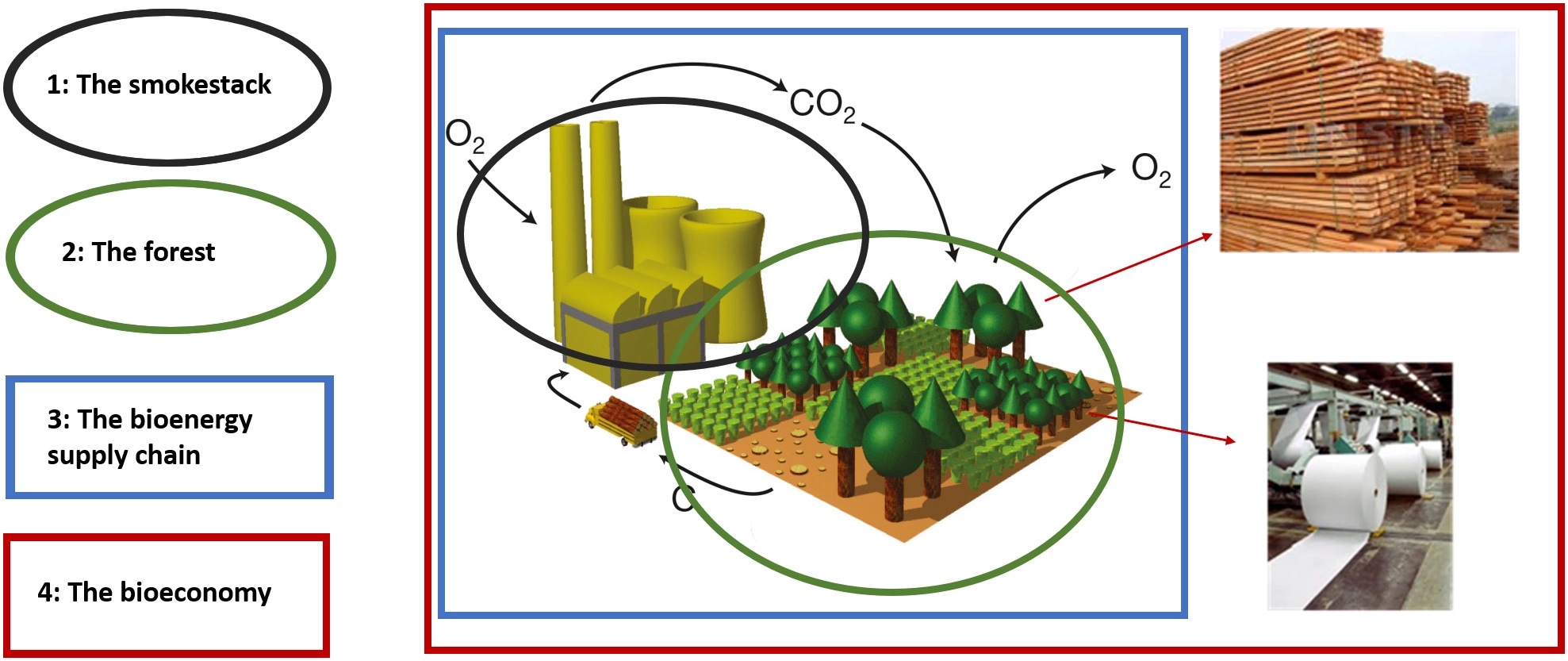
Biomass (energy)
In the context of energy production, biomass is matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms which is used for bioenergy production. Examples include wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues including straw, and Biodegradable waste, organic waste from industry and households. Wood and wood residues is the largest biomass energy source today. Wood can be used as a fuel directly or processed into pellet fuel or other forms of fuels. Other plants can also be used as fuel, for instance maize, switchgrass, miscanthus and bamboo. The main Waste energy, waste feedstocks are wood waste, agricultural waste, municipal solid waste, and manufacturing waste. Upgrading raw biomass to higher grade fuels can be achieved by different methods, broadly classified as thermal, chemical, or biochemical. The Greenhouse gas emissions, climate impact of bioenergy varies considerably depending on where biomass feedstocks come from and how they are grown. For example, wood fuel, bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm Oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from oil crops in 2014. Palm oils are easier to stabilize and maintain quality of flavor and consistency in ultra-processed foods, so they are frequently favored by food manufacturers. Globally, humans consumed an average of of palm oil per person in 2015. Demand has also increased for other uses, such as cosmetics and biofuels, encouraging the growth of palm oil plantations in tropical countries. The mass production of palm oil in the tropics has attracted the concern of environmental and human rights groups. The palm oil industry is a significant contributor to deforestation in the tropics where palms are grown and has been cited as a factor in social problems due to allegations of human rights violations among growers. In 2018, a repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Management And Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The office's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, while it also examines agency programs, policies, and procedures to see whether they comply with the president's policies and coordinates inter-agency policy initiatives. Russell Vought is the current director of the OMB since February 2025. History The Bureau of the Budget, OMB's predecessor, was established in 1921 as a part of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury by the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, which President Warren G. Harding signed into law. The Bureau of the Budget was moved to the Executive Office of the President of the United States, Executive Office of the President in 1939 and was run by Harold D. Smith during the government's rapid expansion of spending during World War II. James L. Sundquist, a staffer at the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idaho Department Of Labor
The Idaho Department of Labor is a state agency in Idaho. The agency is responsible for economic development, labor relations, workforce, technology, volunteerism, and workforce development. It also processes requests for unemployment benefits Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work d ... and unemployment insurance. The agency is managed by the Idaho Director of Labor who is selected by the governor of Idaho. References State departments of labor of the United States State agencies of Idaho {{Idaho-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings: * The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, ''i.e.'' a random, time. * The probability that an item will operate satisfactorily at a given point in time when used under stated conditions in an ideal support environment. Normally high availability systems might be specified as 99.98%, 99.999% or 99.9996%. The converse, unavailability, is 1 minus the availability. Representation The simplest representation of availability (''A'') is a ratio of the expected value of the uptime of a system to the aggregate of the expected values of up and down time (that results in the "total amount of time" ''C'' of the observation window) : A = \frac = \frac Another equation for availability (''A'') is a ratio of the Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
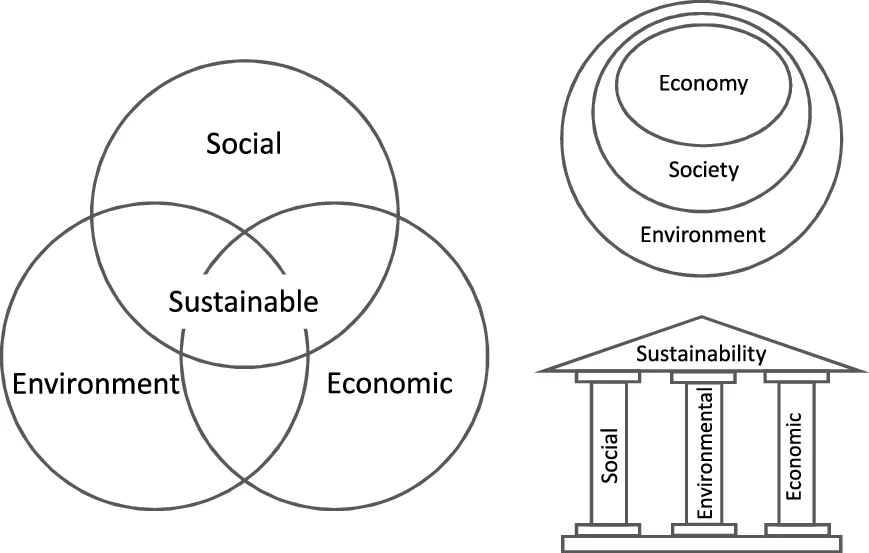
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of System Quality Attributes
Within systems engineering, quality attributes are realized non-functional requirements used to evaluate the performance of a system. These are sometimes named architecture characteristics, or "ilities" after the suffix many of the words share. They are usually architecturally significant requirements that require architects' attention. In software architecture, these attributed are known as "architectural characteristic" or non-functional requirements. Note that it's software architects' responsibility to match these attributes with business requirements and user requirements. Note that synchronous communication between software architectural components, entangles them and they must share the same architectural characteristics. Quality attributes Notable quality attributes include: * accessibility * accountability * accuracy * adaptability * administrability * affordability * agility * auditability * autonomy * availability * compatibility * composability * con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidies
A subsidy, subvention or government incentive is a type of government expenditure for individuals and households, as well as businesses with the aim of stabilizing the economy. It ensures that individuals and households are viable by having access to essential goods and services while giving businesses the opportunity to stay afloat and/or competitive. Subsidies not only promote long term economic stability but also help governments to respond to economic shocks during a recession or in response to unforeseen shocks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Subsidies take various forms— such as direct government expenditures, tax incentives, soft loans, price support, and government provision of goods and services. For instance, the government may distribute direct payment subsidies to individuals and households during an economic downturn in order to help its citizens pay their bills and to stimulate economic activity. Here, subsidies act as an effective financial aid issued when the ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |