|
Seeboden Am Millstätter See
Seeboden am Millstätter See () is a market town in Spittal an der Drau District in Carinthia (state), Carinthia, Austria. Geography The municipal area stretches from the western shore of Millstätter See to the town boundary of the district capital Spittal an der Drau. In the north it reaches up to Mt. Tschiernock at , part of the Millstätter Alpe crest in the Nock Mountains. Divisions The municipal area consists of the four cadastral community, cadastral communities Lieseregg, Lieserhofen, Seeboden and Treffling. It comprises 22 villages and hamlets (population in 2001 in parentheses): Seeboden proper is a dispersed settlement area that grew together from the former villages of Gritschach, Kraut, Reich, and Wirlsdorf. History Several prehistoric excavation finds denote a continuous settlement on the western bight of Millstätter See at least since the Neolithic. In the Hallstatt culture, Celtic tribes settled along the nearby Drava Valley, their kingdom Noricum became a R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality (Austria)
In the Republic of Austria, the municipality (, sometimes also ) is the administrative division encompassing a single village, town, or city. The municipality has municipal corporation, corporate status and local self-government on the basis of parliamentary democracy, parliamentary-style representative democracy: a municipal council () elected through a form of party-list proportional representation, party-list system enacts municipal laws, a municipal executive board () and a mayor (, grammatical gender, fem. ) appointed by the council are in charge of municipal administration. Austria is currently (January 1, 2020) partitioned into 2,095 municipalities, ranging in population from about fifty (the village of Gramais in Tyrol (state), Tyrol) to almost two million (the city of Vienna). There is no unincorporated area, unincorporated territory in Austria. Basics The existence of municipalities and their role as carriers of the right to self-administration are guaranteed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spittal An Der Drau
Spittal an der Drau is a town in the western part of the Austrian federal state of Carinthia (state), Carinthia. It is the administrative centre of Spittal an der Drau District, Austria's second largest district (''Districts of Austria, Bezirk'') by area. Geography The town is located on the southern slopes of the Gurktal Alps (Nock Mountains), between the Lurnfeld Basin and the Lower Drau Valley. Despite its name, the historic core of Spittal originated on the banks of the small Lieser (river in Carinthia), Lieser tributary, which flows into the Drau at the foot of Mt. Goldeck, a peak of the Gailtal Alps south of the town. Its summit can be reached by Aerial lift, cable car. The municipal area consists of seven Katastralgemeinden: Amlach, Edling, Großegg, Molzbichl, Olsach, Spittal proper, and St. Peter-Edling. In Großegg (incorporated in 1973), the area of Spittal extends to the southern shore of Lake Millstatt. History The settlement was first mentioned in an 1191 deed issue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radstädter Tauern Pass
Radstädter Tauern Pass (el. ) is a high mountain pass in the Austrian state of Salzburg, connecting the town of Radstadt in the Pongau region with Mauterndorf in Lungau. Geography The pass separates the Radstadt Tauern in the west and the Schladming Tauern in the east, both part of the Niedere Tauern mountain range in the Central Eastern Alps. It is crossed by the ''Katschberg Straße'' (B 99) road, which runs from Bischofshofen on the Salzach River via Radtstadt in the Enns Valley to Sankt Michael im Lungau on the Mur River. From Sankt Michael it leads further southwards across the Katschberg Pass to Spittal an der Drau in Carinthia. A little to the west and about lower, the parallel Tauern Autobahn (A 10) crosses the Radstadt Tauern in the Tauern Road Tunnel. The road probably was already used by the Celtic Taurisci tribe. It was rebuilt as a Roman road during the rule of Emperor Septimius Severus from 193 onwards, leading from Iuvavum (Salzburg) in the Noricum provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teurnia
Teurnia (later Tiburnia) was a Roman Empire, Roman city (''municipium''). Today its ruins lie in western Carinthia (state), Carinthia. In Late Antiquity, late antiquity it was also a bishop's see, and towards the end of Roman times it was mentioned as the capital of the province of Noricum#Roman rule, Noricum mediterraneum. History Ancient Teurnia was situated on a wooded hill at the village of ''St. Peter in Holz (Slovenian: Sveti Peter v Lesu)'' in the municipality of Lendorf in the Lurnfeld valley, four kilometres to the west of Spittal an der Drau in Upper (i.e. western) Carinthia, Austria. As early as 1100 BC, people had lived there on Holzerberg hill, which may well have also been the centre of the Celtic Taurisci nation before c. 50 AD the Roman town was built with a Forum (Roman), forum, a market basilica, a temple on the city's Capitol, Thermae or public baths, terraced housing on two terraces, and a temple dedicated to Grannus, the Celtic counterpart deity of Asclepius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the second century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. It is currently a (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
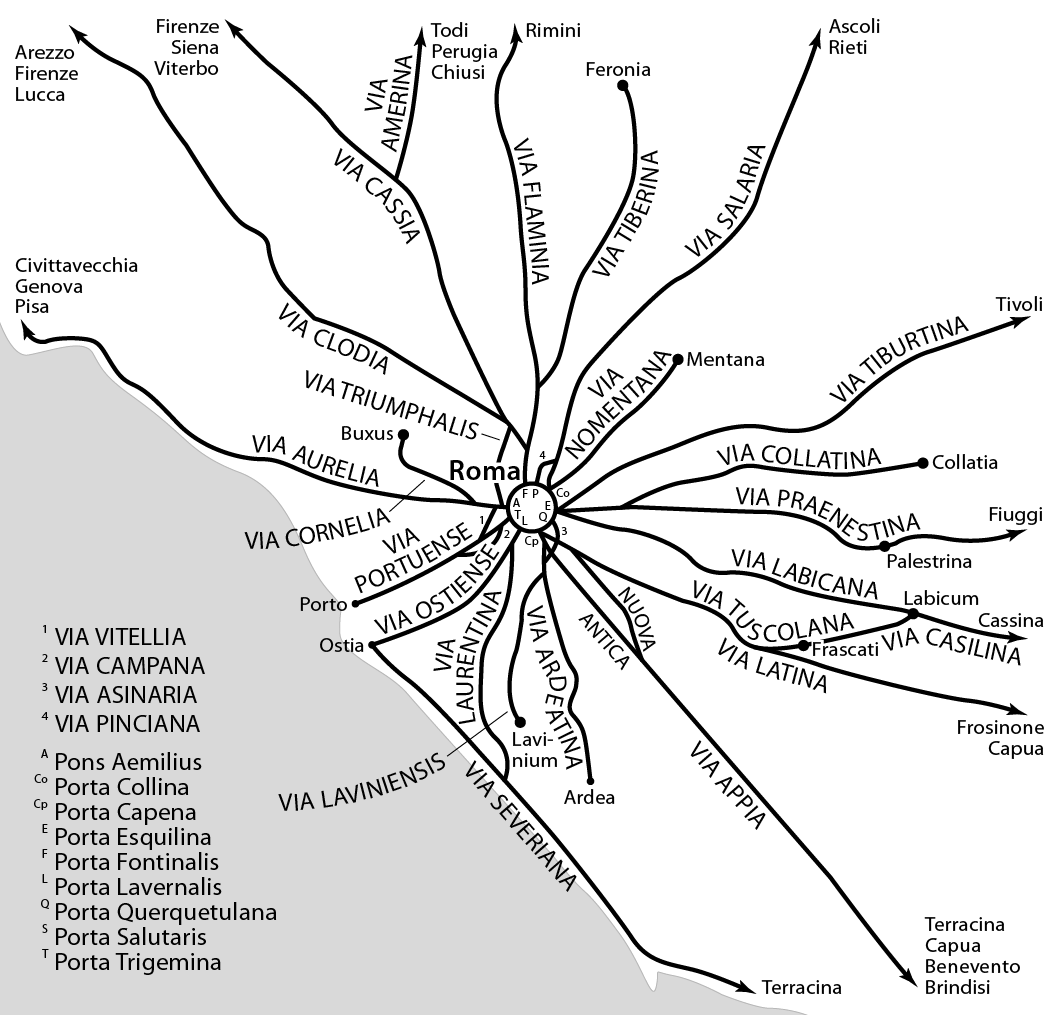
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, Raetia and Vindelici to the west, Pannonia to the east and south-east, and Italia ( Venetia et Histria) to the south. The kingdom was founded around 400 BC, and had its capital at the royal residence at Virunum on the Magdalensberg. Area and population Around 800 BC, the region was inhabited mostly by the people of the Hallstatt culture. Around 450 BC, they merged with the people of other areas in the south-western regions of Germany and eastern France. The country is mountainous and rich in iron and salt. It supplied material for the manufacturing of arms in Pannonia, Moesia, and northern Italy. The famous Noric steel was largely used in the making of Roman weapons (e.g. Horace, ''Odes'', i.16.9-10: ''Noricus ensis'', "a Noric s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drava
The Drava or Drave (, ; ; ; ; ), historically known as the Dravis or Dravus, is a river in southern Central Europe.''Utrata Fachwörterbuch: Geographie - Englisch-Deutsch/Deutsch-Englisch'' by Jürgen Utrata (2014). Retrieved 10 Apr 2014. With a length of ,Joint Drava River Corridor Analysis Report , 27 November 2014 or , if the length of its Sextner Bach source is added, it is the fifth or sixth longest tributary of the |
Hallstatt Culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC (Bronze Age Europe, Late Bronze Age) and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations. It is named for its type site, Hallstatt, a lakeside village in the Austrian Salzkammergut southeast of Salzburg, Austria, Salzburg, where there was a rich salt mine, and some 1,300 burials are known, many with fine artifacts. Material from Hallstatt has been classified into four periods, designated "Hallstatt A" to "D". Hallstatt A and B are regarded as Late Bronze Age and the terms used for wider areas, such as "Hallstatt culture", or "period", "style" and so on, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |