|
Securities Information Processor
A securities information processor (SIP) is a part of the infrastructure of public market data providers in the United States that process, consolidate, and disseminate quotes and trade data from different US securities exchanges and market centers. An important purpose of the SIPs for US securities is to publish the prevailing National Best Bid Offer (NBBO). There are three exclusive SIPs in operation as of 2023. The UTP Plan oversees the SIP for securities listed on Nasdaq and over-the-counter securities, also called unlisted trading privileges securities. The Consolidated Tape Association (CTA) Plan oversees the SIP for securities listed on all other exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange, NYSE Arca, NYSE American, NYSE Chicago, and Cboe stock exchanges. The Options Price Reporting Authority (OPRA) oversees the SIP for all exchange-traded securities options in the US. History Securities Acts Amendments of 1975 The SIPs were introduced in 1975 through the passa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unlisted Trading Privileges
Unlisted Trading Privileges (UTP) oversees the Securities Information Processor for securities listed on Nasdaq and other securities that do not meet the requirements for listing on an exchange. Acquisition and distribution of market data Nasdaq established the UTP Plan to outline the consolidation and distribution of data through one centralized resource called the Securities Information Processor (SIP). The securities listed on Nasdaq can be quoted and traded from any US exchange. Trades and quotes on these securities are distributed on two separate feeds, the UTP Quotation Data Feed (UQDF) and the UTP Trade Data Feed (UTDF). UQDF provides traders a direct view of an NBBO. These feeds are considered level 1 or the top-of-book. National Market System (NMS) plan The NMS Plan regulates the UTP and Consolidated Tape Association (CTA) networks. The particulars for executing the regulation requires real-time reporting of transactions and their volumes, prices, and auditing detai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Exchange
The Members Exchange (MEMX) is an American technology-driven stock exchange founded by its members to serve the interest of its founders and their collective client base. The founding members, which include nine major financial organizations, claim they seek to transform markets around the goals of transparency, innovation, and competition in order to align exchange services with the interests of market participants. It is a member-formed equities trading platform, and competes with the major equity exchanges: NYSE, Nasdaq, and CBOE. The mission of the exchange is "to increase competition, improve operational transparency, reduce fixed costs and simplify the execution of equity trading in the U.S." Initially, after launch, MEMX is not charging for market data or connectivity. History MEMX was founded in early 2019 by a group of nine banks, financial services firms, market makers, and retail broker-dealers: BofA Securities, Charles Schwab Corporation, Citadel LLC, E-Trade, Fideli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Data Vendor
A financial data vendor provides market data to financial firms, traders, and investors. The data distributed is collected from sources such as stock exchange feeds, brokers and dealer desks or regulatory filings (e.g. an SEC filing). History Financial data vendors have been in existence as long as financial data has been available. The first technology that allowed data vendors to disseminate was the ticker tape starting in the 1870s. Financial data includes "pre-trade" such as bid-ask data necessary to price a financial instrument and post-trade data such as the last trade price and other transaction data. From ticker tape to television cameras, from databases to websites this multibillion-dollar industry provides data utilized in the financial sector. Paper ticker tape became obsolete in the 1960s, as television and computers were increasingly used to transmit financial information. The concept of the stock ticker lives on, however, in the news ticker, scrolling electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation NMS
Regulation National Market System (or Reg NMS) is a 2005 US financial regulation promulgated and described by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as "a series of initiatives designed to modernize and strengthen the National Market System for equity securities". The Reg NMS is intended to assure that investors receive the best (National best bid and offer, NBBO) price executions for their orders by encouraging competition in the marketplace. Some contend that the rule has contributed to the rise of high-frequency trading, which is sometimes regarded as High-frequency trading#Risks and controversy, controversial. History Established in 2005, its aim was to foster both "competition among individual markets and competition among individual orders" in order to promote efficient and fair price formation across securities markets. In 1972, before the SEC began its pursuit of a national market system, the market for securities was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Lot
A round lot (or board lot) is a normal unit of trading of a security, which is usually 100 shares of stock in US. Each stock exchange has its own regulations regarding round lot sizes: they can range anywhere from 1-100 shares, depending on the exchange. Any quantity less than this normal unit is referred to as an odd lot. See also *Odd lot *Odd lotter An odd lotter is an investor who purchases shares or other securities in small or unusual quantities. Stocks are typically traded in increments of 100 shares, a quantity known as a '' round lot'' or ''board lot''. The cost of 100 shares of a secur ... References {{Reflist Financial markets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BATS Global Markets
BATS Global Markets is a global stock exchange operator founded in Lenexa, Kansas, with additional offices in London, New York, Chicago, and Singapore. BATS was founded in June 2005, became a licensed U.S. stock exchange operator in 2008, and launched a pan-European market that October. As of February 2016, it operated four U.S. stock exchanges, two U.S. equity options exchanges, the pan-European stock market, and a global market for the trading of foreign exchange products. BATS was acquired by Cboe Global Markets in 2017. History The company was founded in June 2005 by Dave Cummings, a computer programmer. The name 'BATS' was originally an acronym for "Better Alternative Trading System". Cummings was inspired to start the company after observing Archipelago Holdings be acquired by the New York Stock Exchange and Instinet be acquired by NASDAQ within a week of each other in 2005. Cummings promoted BATS by emailing companies about the potential to trade outside the dominant e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securities Industry Automation Corporation
The Securities Industry Automation Corporation (SIAC) is a subsidiary of the NYSE Euronext. Its purpose is to provide technical services for the exchanges themselves, members and other financial institutions. In this role, SIAC provides the computers and other systems required to run the exchanges. It also owns communication lines and hardware to provide real-time quotes and transaction information to all market participants from the Consolidated Tape/Ticker System (CTS), Consolidated Quotation System (CQS), and Options Price Reporting Authority (OPRA). History SIAC was created on July 17, 1972, as a wholly owned subsidiary of the NYSE and American Stock Exchange. The NYSE owned two thirds of SIAC, while the AMEX owned one third. SIAC initially provided processing services for both NYSE and AMEX's clearing corporations, and continued to do so when these merged into the National Securities Clearing Corporation. As of 2002, the three remained SIAC's main sources of revenue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allison Lee
Allison Herren Lee is an American attorney and former government official who served as a member of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) from 2019 to 2022. A member of the Democratic Party, Lee briefly served as acting chair of the SEC from January to April 2021. After leaving the SEC, Lee became an adjunct professor at the New York University (NYU) School of Law In 2023, she joined the whistleblower law firm Kohn, Kohn & Colapinto. Education Lee received a degree in business from the University of Colorado, Boulder and a Juris Doctor from the University of Denver College of Law. During her time at law school, Lee was salutatorian, a chancellor’s Scholar, and served on the school's Law Review. Career Prior to joining the SEC, Lee worked in private practice as a partner at Sherman & Howard LLC. She also served as a Special Assistant U.S. Attorney and was a member of the American Bar Association’s former Committee on Public Company Disclosure. U.S. Securitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securities Exchange Commission
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street crash of 1929. Its primary purpose is to enforce laws against market manipulation. Created by Section 4 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (now codified as and commonly referred to as the Exchange Act or the 1934 Act), the SEC enforces the Securities Act of 1933, the Trust Indenture Act of 1939, the Investment Company Act of 1940, the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, and the Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002, among other statutes. Overview The SEC has a three-part mission: to protect investors; maintain fair, orderly, and efficient markets; and facilitate capital formation. To achieve its mandate, the SEC enforces the statutory requirement that public companies and other regulated entities submit quarterly and annual reports, as well as other periodic disclosures. In addition to annual financial reports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miami International Holdings
MIAX’s parent holding company, Miami International Holdings, Inc., owns Miami International Securities Exchange, LLC (MIAX®), MIAX PEARL, LLC (MIAX Pearl®), MIAX Emerald, LLC (MIAX Emerald®), MIAX Sapphire LLC (MIAX Sapphire™), MIAX Futures Exchange, LLC (MIAX Futures™), MIAX Derivatives Exchange (MIAXdx™), Dorman Trading, LLC (Dorman Trading), The Bermuda Stock Exchange (BSX) and The International Stock Exchange (TISE). MIAX, MIAX Pearl, MIAX Emerald and MIAX Sapphire are national securities exchanges registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission that are enabled by MIAX’s in-house built, proprietary technology. MIAX offers trading of options on all four exchanges as well as cash equities through MIAX Pearl Equities™. The MIAX trading platform was built to meet the high-performance quoting demands of the U.S. options trading industry and is differentiated by throughput, latency, reliability and wire-order determinism. MIAX Futures is a registered exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
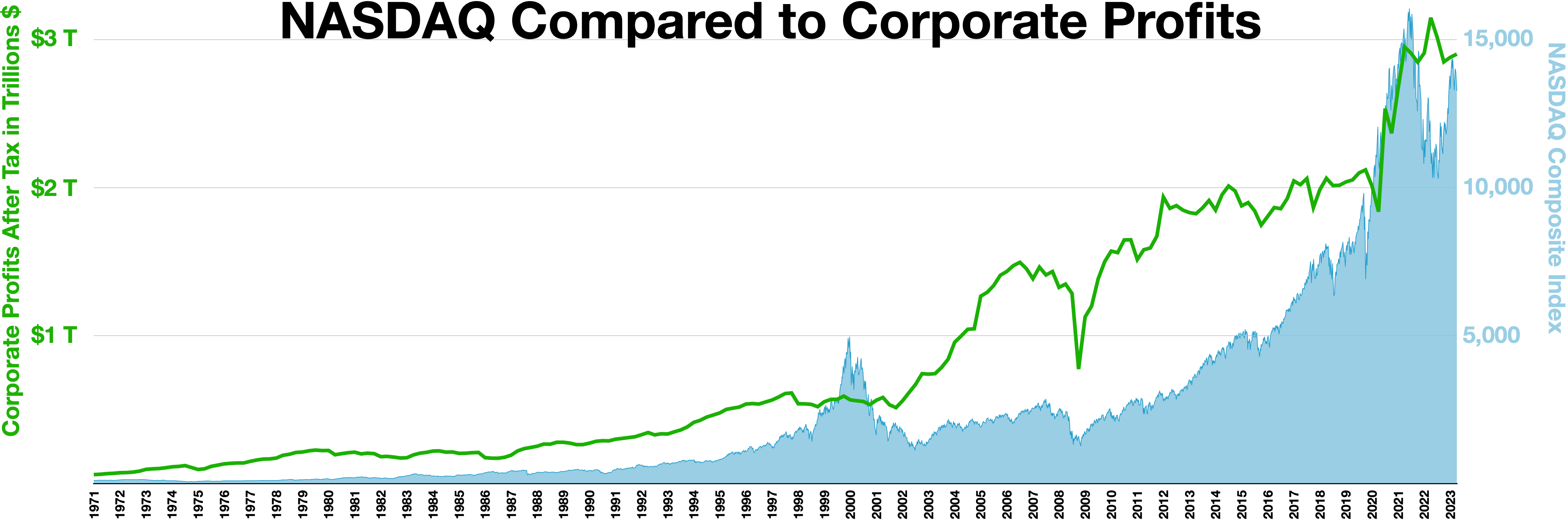
Nasdaq
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc. (which the exchange also lists; ticker symbol NDAQ), which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges. Although it trades stock of healthcare, financial, media, entertainment, retail, hospitality, and food businesses, it focuses more on technology stocks. The exchange is made up of both American and foreign firms, with China and Israel being the largest foreign sources. History 1972–2000 Nasdaq, Inc. was founded in 1971 by the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD), which is now known as the Financial Industry Regulatory A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securities Exchange Act Of 1934
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (also called the Exchange Act, '34 Act, or 1934 Act) (, codified at et seq.) is a law governing the secondary trading of securities (stocks, bonds, and debentures) in the United States of America. A landmark piece of wide-ranging legislation, the Act of '34 and related statutes form the basis of regulation of the financial markets and their participants in the United States. The 1934 Act also established the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the agency primarily responsible for enforcement of United States federal securities law. Companies raise billions of dollars by issuing securities in what is known as the primary market. Contrasted with the Securities Act of 1933, which regulates these original issues, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 regulates the secondary trading of those securities between persons often unrelated to the issuer, frequently through brokers or dealers. Trillions of dollars are made and lost each year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |