|
Second Battle Of Târgu Frumos
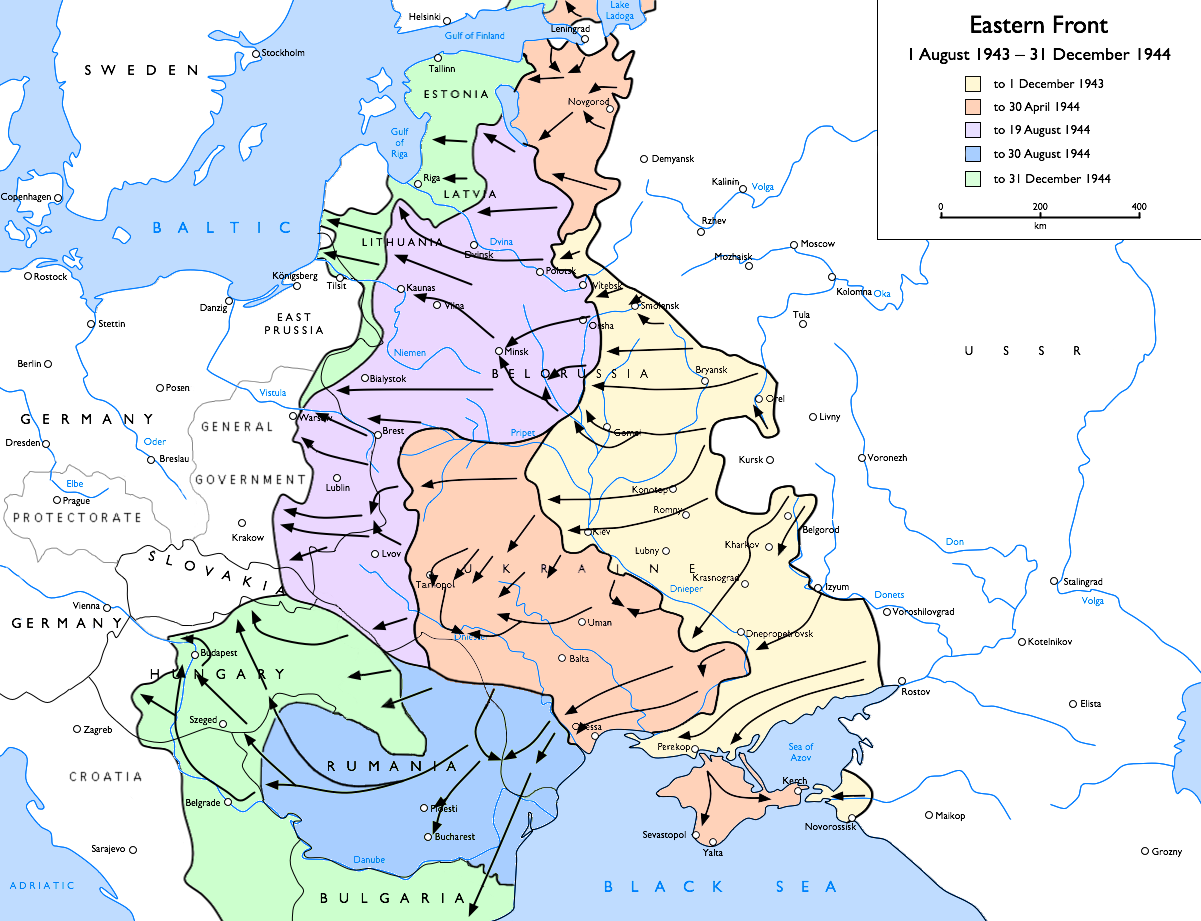
The Second Battle of Târgu Frumos was a military engagement primarily between the Wehrmacht and Red Army forces in May 1944, near Iași, Romania. The battle was the main engagement of the Battle of Târgu Frumos, Târgu Frumos Operation, and is often referred simply as the Battle of Târgu Frumos. Military historian David Glantz claims the battle was part of the First Jassy-Kishinev Offensive, which resulted from a Stavka order to the forces of the 2nd Ukrainian Front, 2nd & 3rd Ukrainian Fronts to commence a coordinated invasion of Romania. The offensive was directed towards Iași, with a secondary objective of establishing bridgeheads across the Prut, Prut River. The battle of Târgu-Frumos was only briefly described by Soviet historians. Recently, Russian historians have begun describing this as a distinct battle. For example, the four volume ''Great Patriotic War'' (1998) prepared for the Russian Federation states: Thus, during the Târgu-Frumos operation, the 2nd Ukrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
52nd Army (Soviet Union)
The 52nd Army was a field army of the Red Army of the Soviet Union in World War II, formed twice. History It was created on 25 August 1941 from the headquarters of the 25th Rifle Corps and defended north of Novgorod. On 26 September 1941, the 52nd Army headquarters was used to form the 4th Army (II Formation). The 52nd Army headquarters was reestablished on 28 September 1941. In May 1943, the army was moved to control of the Reserve of the Supreme High Command (''Stavka'' Reserve). ''Stavka'' released the 52nd Army to subordination of the Steppe Front in July 1943, and the 52nd Army thereafter fought in Ukraine, southern Poland, southeastern Germany, and finally in northern Czechoslovakia. The army took part in the following operations: :1941 ::Tikhvin Defensive Operation :1942 ::Tikhvin Offensive ::Lyuban Offensive Operation :1943 ::Chernigov-Poltava Offensive ::Cherkassy Offensive :1944 ::Kirovograd Offensive :: Korsun–Shevchenkovsky Offensive ::Uman–Botoșani Offensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Târgu Frumos
Târgu Frumos (also spelled ''Tîrgu Frumos'', sometimes ''Târgul / Tîrgul Frumos''), ) is a town in Iași County, Western Moldavia, Romania. Eleven villages were administered by the town until 2004, when they were split off to form Balș, Costești, and Ion Neculce communes. History During World War II, in March and May 1944, this area was the scene of the two Battles of Târgu Frumos, part of the First Jassy-Kishinev Offensive. According to the 1930 census, 1,608 Jews lived in Târgu Frumos. In the fall of 1940, all Jewish men, from 18 to 50 years old, were subjected to forced labor. Many were sent to the work camp Tudoreni-Rechita, situated in Botoșani County, while others were deported to Transnistria. Târgu Frumos was also a 24-hour stop of the "Death train" going to the Călărași camp. On July 1, 1941, when the train arrived in Târgu Frumos, 654 bodies were removed from the train and transported to the local Jewish cemetery where they were buried. Demographics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into Regions of Belarus, six regions. Minsk is the capital and List of cities and largest towns in Belarus, largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the Partitions of Poland, 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Belarusian history in the Russian Empire, Russian Empire for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberkommando Des Heeres
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat at Moscow in December 1941. During World War II, OKH had the responsibility of strategic planning of Armies and Army Groups. The General Staff of the OKH managed operational matters. Each German Army also had an Army High Command ( or AOK). The Armed Forces High Command () then took over this function for theatres other than the Eastern front. The OKH commander held the title of Commander-in-chief of the Army (). After the Battle of Moscow, the OKH commander Field marshal Walther von Brauchitsch was removed from office, and Hitler appointed himself as Commander-in-Chief of the Army. From 1938, OKH was, together with () and () formally subordinated to the . OKH vs OKW OKH had been independent until February 1938, when Hitler creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789).See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 It operates under the authority, direction, and control of the United States Secretary of Defense, United States secretary of defense. It is one of the six armed forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Army is the most senior branch in order of precedence amongst the armed services. It has its roots in the Continental Army, formed on 14 June 1775 to fight against the British for independence during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Maria Von Senger Und Etterlin
Ferdinand Maria Johann Fridolin von Senger und Etterlin (8 June 1923 – 10 January 1987) was a soldier in the German Army in both the Wehrmacht of World War II and the postwar Bundeswehr, as well as a civilian jurist in the German Federal service. As an officer in the Bundeswehr, he rose to the rank of general, and completed his military service as commander-in-chief of NATO's Allied Forces Central Europe ( AFCENT). He also authored numerous books on military-related subjects. Early years Senger und Etterlin was born on June 8, 1923, in Tübingen, Germany, into a family rich in military tradition, with over 250 years of service to various German polities. His father, Fridolin von Senger und Etterlin, who served as a Wehrmacht officer throughout the Second World War, reached the rank of General der Panzertruppe ("General of Armoured Troops"), and began his own highly decorated military service before the First World War in service with the Reichswehr. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasso Von Manteuffel
Hasso Eccard Freiherr von Manteuffel (14 January 1897 – 24 September 1978) was a German baron born to the Prussian noble Manteuffel, von Manteuffel family and was a general during World War II who commanded the 5th Panzer Army. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves, Swords and Diamonds of Nazi Germany. After the war, he was elected to the ''Bundestag'' (West German legislature) and was the defense-policy spokesman of the Free Democratic Party of Germany, Free Democratic Party. A proponent of West German rearmament, he was responsible for coining the new name for the post-World War II West Germany, West German armed forces, the ''Bundeswehr''. Early career Hasso von Manteuffel began his military career during the World War I, First World War. In 1919, he joined the ''Freikorps'' and then the newly created ''Reichswehr''. In February 1937 he joined the Panzer Troop Command of the OKH, and in February 1939 became a senior professor at Panzer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prut
The Prut (also spelled in English as Pruth; , ) is a river in Eastern Europe. It is a left tributary of the Danube, and is long. Part of its course forms Romania's border with Moldova and Ukraine. Characteristics The Prut originates on the eastern slope of Mount Hoverla, in the Carpathian Mountains in Ukraine ( Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast). At first, the river flows to the north. Near Yaremche it turns to the northeast, and near Kolomyia to the south-east. Having reached the border between Moldova and Romania, it turns even more to the south-east, and then to the south. It eventually joins the Danube near Giurgiulești, east of Galați and west of Reni. Between 1918 and 1939, the river was partly in Poland and partly in Greater Romania (Romanian: ''România Mare''). Prior to World War I, it served as a border between Romania and the Russian Empire. After World War II, the river once again denoted a border, this time between Romania and the Soviet Union. Nowadays, for a length of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Ukrainian Front
The 3rd Ukrainian Front () was a Front of the Soviet Red Army during World War II. It was founded on 20 October 1943, on the basis of a Stavka order of October 16, 1943, by renaming the Southwestern Front. It included 1st Guards Army, 8th Guards Army, 6th, 12th, and 46th Armies and 17th Air Army. Later it included 5th Shock, 4th and 9th Guards Army, 26th, 27th, 28th, 37th, 57th Army, 6th Guards Tank Army, and the Bulgarian First, Second and Fourth Armies. The Danube Flotilla was assigned to the Front's operational control. This included the 83rd Naval Infantry Brigade. Zaporizhzhia and Dnipropetrovsk offensive operations In the first half of October 1943, Southwestern Front (3rd Ukrainian Front from 20 October) commanded by Army General Rodion Malinovsky was tasked with attacking the German Panther-Wotan line, and later securing the bridgeheads on the eastern bank of the Dnieper on the Izyum - Dnipropetrovsk axis during the Battle of the Lower Dnieper. But the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Ukrainian Front
The 2nd Ukrainian Front () was a front of the Red Army during the Second World War. History On October 20, 1943, the Steppe Front was renamed the 2nd Ukrainian Front. In mid-May 1944 Malinovsky took over the 2nd Ukrainian Front. During the Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, 2nd Ukrainian Front, led by Army General Rodion Malinovsky, comprised: * 6th Guards Tank Army – Major General A.G. Kravchenko * 4th Guards Army – Ivan Galanin * 7th Guards Army – Lieutenant General M.S. Shumilov * 27th Army – Lieutenant General S.G. Trofimenko * 40th Army – Lieutenant General Filipp Zhmachenko * 52nd Army – Lieutenant General K.A. Koroteev * 53rd Army – Lieutenant General Ivan Managarov * 18th Tank Corps – Major General V.I. Polozkov * Cavalry-Mechanized Group Gorshkov – Major General Sergey Gorshkov ** 5th Guards Cavalry Corps ** 23rd Tank Corps – Lieutenant General Alexey Akhmanov On 1 January 1945, during the Siege of Budapest, the Front cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine. In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrative staff, and to the General Headquarters in the late 19th-century Imperial Russian armed forces and subsequently in the Soviet Union. In Western literature it is sometimes written in uppercase (''STAVKA''), although it is not an acronym. ''Stavka'' may refer to its members, as well as to the headquarters location (its original meaning from the old Russian word '' ставка'', 'tent'). Stavka of the Supreme Commander during World War I The commander-in-chief of the Russian army at the beginning of World War I was Grand Duke Nicholas Nicholaievitch, a grandson of Tsar Nicholas I. Appointed at the last minute in August 1914, he played no part in formulating the military plans in use at the beginning of the war. Nikolai Yanushke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |