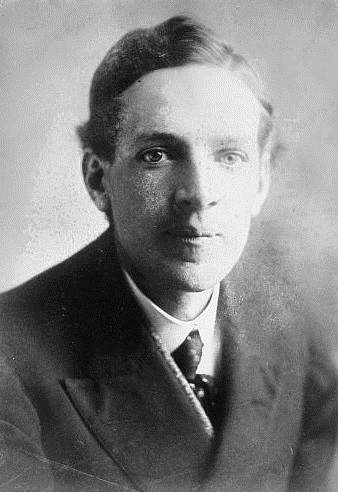|
Scudder Klyce
Scudder Klyce (November 7, 1879 in Friendship, Tennessee – January 28, 1933 in Winchester, Massachusetts) was an American philosopher, scientist and naval officer. He is known for his work, ''Universe'', which attempted to accumulate the knowledge of mankind into a single book to collect and deliver a solution for all the problems of humanity. Life Klyce studied at the University of Arkansas. In his youth, served in the Spanish–American War, and participated in the Philippine campaign. In 1902 he graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland, where he later filed a post-graduate study for engineering. In 1908 he married Etheldreda Hovey († 1917). They had one son, Stephen Klyce. His second, (1917) closed marriage was with Laura Tilden Kent. They had two children, William and Dorothy Klyce Klyce. His duty in the Navy involved protecting shipping interests during the Honduras Nicaragua War of 1907. On 2 May 1907 Klyce was promoted to Commander in the U.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friendship, Tennessee
Friendship is a city in Crockett County, Tennessee. The population was 668 at the 2010 census. Also used to be the location of Friendship High School before it was closed for consolidation Geography Friendship is located at (35.910370, -89.241827). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 608 people, 246 households, and 171 families residing in the city. The population density was 466.4 people per square mile (180.6/km2). There were 264 housing units at an average density of 202.5 per square mile (78.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 85.36% White, 11.68% African American, 0.33% Native American, 2.14% from other races, and 0.49% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.45% of the population. There were 246 households, out of which 32.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.6% were married couples living together, 15.9% had a female hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Emerson Ritter
William Emerson Ritter (November 21, 1856 – January 10, 1944) was an American biologist. Ritter initiated and shaped the Marine Biological Association of San Diego (now Scripps Institution of Oceanography of UC San Diego) and the American Society for the Dissemination of Science (now the Society for Science and the Public and Science News). Innovative and entrepreneurial, with a deep desire for human service, he worked tirelessly to educate people in science thinking. He was the first biologist to propose a theory of systems, and seems to be the originator of the term organicism for biological purposes. Early life William Emerson Ritter was born on a farm on November 21, 1856 in Hampden Township, Columbia County, Wisconsin. His parents, Horatio and Leonora Ritter, moved from New York a few years earlier. The Ritter household included William, his brother Frank, his sisters Mary, Ella, and Flora, and his maternal grandparents, Nathan and Ruby Eason. For the first few years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Philosophers
American philosophy is the activity, corpus, and tradition of philosophers affiliated with the United States. The ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' notes that while it lacks a "core of defining features, American Philosophy can nevertheless be seen as both reflecting and shaping collective American identity over the history of the nation"."American philosophy" at the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy Retrieved on May 24, 2009 The philosophy of the is largely seen as an extension of the |
Morris Llewellyn Cooke
Morris Llewellyn Cooke (May 11, 1872 – March 5, 1960) was an American engineer, best known for his work on Scientific Management and Rural Electrification. Biography Born in Carlisle, Pennsylvania as one of eight children of William Harvey Cooke and Elizabeth Richmond Marsden, Cooke attended Lehigh University and obtained his degree in mechanical engineering in 1895. He then joined the work force as a machinist. In 1900 he married Eleanor Bushnell Davis, a granddaughter of the industrialist Daniel Bushnell. Cooke directed the Rural Electrification Administration from May 1935 through March 1937. In March 1937, Cooke resigned and was succeeded by John Carmody. In 1940 Cooke became a technical consultant for the Office of Production Management, where he led an American technical mission to Brazil. In 1943 he headed the War Labor Board panel to mediate a coal miners' strike. In 1946-1947 he was a member of a committee to survey the patent system. In 1950 President Harry S. Truma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarky
Anarky is a supervillain appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. Co-created by Alan Grant (writer), Alan Grant and Norm Breyfogle, he first appeared in ''Detective Comics'' #608 (November 1989), as an adversary of Batman. Anarky is introduced as Lonnie Machin, a child prodigy with knowledge of radical philosophy and driven to overthrow governments to improve social conditions. Stories revolving around Anarky often focus on political and philosophical themes. The character, who is named after the philosophy of anarchism, primarily espouses anti-statism and attacks capitalism; however, multiple social issues have been addressed through the character, including environmentalism, antimilitarism, economic inequality, and political corruption. Inspired by multiple sources, early stories featuring the character often included homages to political and philosophical texts, and referenced anarchist philosophers and theorists. The inspiration for the creation of the chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. (doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with their first comic under the DC banner being published in 1937. The majority of its publications take place within the fictional DC Universe and feature numerous List of DC Comics characters, culturally iconic heroic characters, such as Superman, Batman, Wonder Woman, Flash (DC Comics character), Flash, Aquaman, Green Lantern, and Cyborg (comics), Cyborg. It is widely known for some of the most famous and recognizable teams including the Justice League, the Justice Society of America, the Suicide Squad, and the Teen Titans. The universe also features a large number of well-known supervillains such as the Joker (character), Joker, Lex Luthor, the Cheetah (character), Cheetah, the Eobard Thawne, Reverse-Flash, Black Manta, Sinestro, and Darkseid. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detective Comics
''Detective Comics'' is an American comic book series published by Detective Comics, later shortened to DC Comics. The first volume, published from 1937 to 2011 (and later continued in 2016), is best known for introducing the superhero Batman in ''Detective Comics'' #27 (cover-dated May 1939). A second series of the same title was launched in September 2011, but in 2016, reverted to the original volume numbering. The series is the source of its publishing company's name, and—along with ''Action Comics'', the series that launched with the debut of Superman—one of the medium's signature series. The series published 881 issues between 1937 and 2011 and is the longest continuously published comic book in the United States. Publication history ''Detective Comics'' was the final publication of the entrepreneur Major Malcolm Wheeler-Nicholson, whose comics company, National Allied Publications, would evolve into DC Comics, one of the world's two largest comic book publisher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Grant (writer)
Alan Grant (9 February 194920 July 2022) was a British comic book writer known for writing Judge Dredd in '' 2000 AD'' as well as various Batman titles from the late 1980s to the early 2000s. He was the co-creator of the characters Anarky, Victor Zsasz, and the Ventriloquist. Career Early career and ''2000 AD'' Grant first entered the comics industry in 1967 when he became an editor for D.C. Thomson before moving to London from Dundee in 1970 to work for IPC on various romance magazines. After going back to college and having a series of jobs, Grant found himself back in Dundee and living on Social Security. He then met John Wagner, another former D.C. Thomson editor, who was helping put together a new science fiction comic magazine for IPC, ''2000 AD'', and was unable to complete his other work. Wagner asked Grant if he could help him write the ''Tarzan'' comic he was working on; so began the Wagner/Grant writing partnership. Wagner asked Grant to write a strip for '' Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Winslow Taylor
Frederick Winslow Taylor (March 20, 1856 – March 21, 1915) was an American mechanical engineer. He was widely known for his methods to improve industrial efficiency. He was one of the first management consultants. In 1909, Taylor summed up his efficiency techniques in his book '' The Principles of Scientific Management'' which, in 2001, Fellows of the Academy of Management voted the most influential management book of the twentieth century. His pioneering work in applying engineering principles to the work done on the factory floor was instrumental in the creation and development of the branch of engineering that is now known as industrial engineering. Taylor made his name, and was most proud of his work, in scientific management; however, he made his fortune patenting steel-process improvements. As a result, scientific management is sometimes referred to as ''Taylorism''. Biography Taylor was born in 1856 to a Quaker family in Germantown, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Taylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upton Sinclair
Upton Beall Sinclair Jr. (September 20, 1878 – November 25, 1968) was an American writer, muckraker, political activist and the 1934 Democratic Party nominee for governor of California who wrote nearly 100 books and other works in several genres. Sinclair's work was well known and popular in the first half of the 20th century, and he won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 1943. In 1906, Sinclair acquired particular fame for his classic muck-raking novel, '' The Jungle'', which exposed labor and sanitary conditions in the U.S. meatpacking industry, causing a public uproar that contributed in part to the passage a few months later of the 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act and the Meat Inspection Act. In 1919, he published '' The Brass Check'', a muck-raking exposé of American journalism that publicized the issue of yellow journalism and the limitations of the "free press" in the United States. Four years after publication of ''The Brass Check'', the first code of ethics fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore William Richards
Theodore William Richards (January 31, 1868 – April 2, 1928) was the first American scientist to receive the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, earning the award "in recognition of his exact determinations of the atomic weights of a large number of the chemical elements." Biography Theodore Richards was born in Germantown, Pennsylvania, to William Trost Richards, a land- and seascape painter, and Anna Matlack Richards, a poet. Richards received most of his pre-college education from his mother. During one summer's stay at Newport, Rhode Island, Richards met Professor Josiah Parsons Cooke of Harvard, who showed the young boy Saturn's rings through a small telescope. Years later Cooke and Richards would work together in Cooke's laboratory. Beginning in 1878, the Richards family spent two years in Europe, largely in England, where Theodore Richards' scientific interests grew stronger. After the family's return to the United States, he entered Haverford College, Pennsylvania in 1883 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winchester, Massachusetts
Winchester is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, located 8.2 miles (13.2 km) north of downtown Boston as part of the Greater Boston metropolitan area. It is also one of the List of Massachusetts locations by per capita income, wealthiest municipalities in Massachusetts. The population was 22,970 at the 2020 United States Census. History Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans inhabited the area that would become Winchester for thousands of years prior to European colonization of the Americas. At the time of contact, the area was inhabited by the Naumkeag people, from whom the land that would become Winchester was purchased for the settlement of Charlestown in 1639. From the 17th century until the middle of the 19th century, parts of Arlington, Massachusetts, Arlington, Medford, Massachusetts, Medford, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, and Woburn, Massachusetts, Woburn comprised what is now Winchester. In the early years of the settlement, the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |