|
SciDB
SciDB is a column-oriented database management system (DBMS) designed for multidimensional data management and analytics common to scientific, geospatial, financial, and industrial applications. It is developed by Paradigm4 and co-created by Michael Stonebraker. History Stonebraker claims that arrays are 100 times faster in SciDB than in a relational DBMS on a class of problems. It is swapping rows and columns for mathematical arrays that put fewer restrictions on the data and can work in any number of dimensions unlike the conventionally widely used relational database management system model, in which each relation supports only one dimension of records. A 2011 conference presentation on SciDB promoted it as "not Hadoop Apache Hadoop () is a collection of Open-source software, open-source software utilities for reliable, scalable, distributed computing. It provides a software framework for Clustered file system, distributed storage and processing of big data usin ...". Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Stonebraker
Michael Ralph Stonebraker (born October 11, 1943) is an American computer scientist specializing in database, database systems. Through a series of academic prototypes and commercial startups, Stonebraker's research and products are central to many relational databases. He is also the founder of many database companies, including Actian, Ingres Corporation, Illustra, Paradigm4, StreamBase Systems, Tamr, Vertica, VoltDB and Hopara, and served as chief technical officer of Informix Corporation, Informix. For his contributions to database research, Stonebraker received the 2014 Turing Award, often described as "the Nobel Prize for computing." Stonebraker's career can be broadly divided into two phases: his time at University of California, Berkeley when he focused on relational database management systems such as Ingres (database), Ingres and Postgres, and, starting in 2001, at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) where he developed more novel data management techniques such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affero General Public License
The GNU Affero General Public License (GNU AGPL) is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU GPL version 3 and the ''Affero General Public License'' (non-GNU). It is intended for software designed to be run over a network, adding a provision requiring that the corresponding source code of modified versions of the software be prominently offered to all users who interact with the software over a network. The Open Source Initiative approved the GNU AGPLv3 as an open source license in March 2008 after the company Funambol submitted it for consideration through its CEO Fabrizio Capobianco. History In 2000, while developing an e-learning and e-service business model at Mandriva, Henry Poole met with Richard Stallman in Amsterdam and discussed the issue of the GPLv2 license not requiring Web application providers to share source code with the users interacting with their software over a network. Over the followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
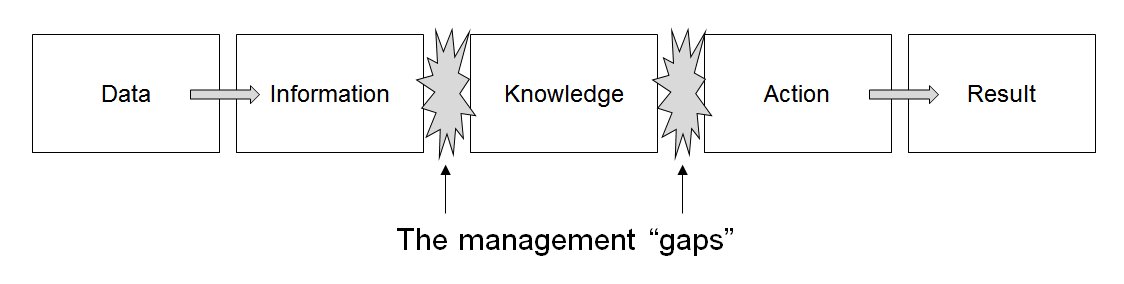
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making. Concept The concept of data management emerged alongside the evolution of computing technology. In the 1950s, as computers became more prevalent, organizations began to grapple with the challenge of organizing and storing data efficiently. Early methods relied on punch cards and manual sorting, which were labor-intensive and prone to errors. The introduction of database management systems in the 1970s marked a significant milestone, enabling structured storage and retrieval of data. By the 1980s, relational database models revolutionized data management, emphasizing the importance of data as an asset and fostering a data-centric mindset in business. This era also saw the rise of data governance practices, which prioritized the organization and regulation of data to ensure quality and complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Storage
Structuring, also known as smurfing in banking jargon, is the practice of executing financial transactions such as making bank deposits in a specific pattern, calculated to avoid triggering financial institutions to file reports required by law, such as the United States' Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Internal Revenue Code section 6050I (relating to the requirement to file Form 8300). Structuring may be done in the context of money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes. Legal restrictions on structuring are concerned with limiting the size of domestic transactions for individuals. Definition Structuring is the act of parceling what would otherwise be a large financial transaction into a series of smaller transactions to avoid scrutiny by regulators and law enforcement. Typically each of the smaller transactions is executed in an amount below some statutory limit that normally does not require a financial institution to file a report with a government agency. Criminal enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Database Management Systems
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * ''Free'' (film), a 2001 American dramedy * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing Architecture
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers. The components of a distributed system communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to microservices to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. Distributed systems cost significantly more than monolithic architectures, primarily due to increased needs for additional hardware, servers, gateways, firewalls, new subnets, proxies, and so on. Also, distributed systems are prone to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Document-oriented Databases
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as Semi-structured model, semi-structured data. Document-oriented databases are one of the main categories of NoSQL databases, and the popularity of the term "document-oriented database" has grown with the use of the term NoSQL itself. XML databases are a subclass of document-oriented databases that are optimized to work with XML documents. Graph databases are similar, but add another layer, the ''relationship'', which allows them to link documents for rapid traversal. Document-oriented databases are inherently a subclass of the Key-value database, key-value store, another NoSQL database concept. The difference lies in the way the data is processed; in a key-value store, the data is considered to be inherently opaque to the database, whereas a document-oriented system relies on internal structure in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Data Stores
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample * Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold * Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Object Database Management Systems
This is a comparison of notable object database management systems, showing what fundamental object database features are implemented natively. See also * Comparison of object–relational database management systems *Comparison of relational database management systems *Object–relational database An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inherit ... References External links ObjectFile at GitHub {{DEFAULTSORT:Comparison of object database management systems Database management systems Object-oriented database management systems object database management systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Structured Storage Software
Structured storage is computer storage for structured data, often in the form of a distributed database. Computer software formally known as structured storage systems include Apache Cassandra, Google's Bigtable and Apache HBase. Comparison The following is a comparison of notable structured storage systems. See also * NoSQL NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ... References {{Cloud computing Structured storage structured storage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column-oriented DBMS
Data orientation is the representation of tabular data in a linear memory model such as in-disk or in-memory. The two most common representations are column-oriented (columnar format) and row-oriented (row format). The choice of data orientation is a trade-off and an architectural decision in databases, query engines, and numerical simulations. As a result of these tradeoffs, row-oriented formats are more commonly used in Online transaction processing (OLTP) and column-oriented formats are more commonly used in Online analytical processing (OLAP). Examples of column-oriented formats include Apache ORC, Apache Parquet, Apache Arrow, formats used by BigQuery, Amazon Redshift and Snowflake. Predominant examples of row-oriented formats include CSV, formats used in most relational databases, the in-memory format of Apache Spark, and Apache Avro. Description Tabular data is two dimensional — data is modeled as rows and columns. However, computer systems represent d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadoop
Apache Hadoop () is a collection of Open-source software, open-source software utilities for reliable, scalable, distributed computing. It provides a software framework for Clustered file system, distributed storage and processing of big data using the MapReduce programming model. Hadoop was originally designed for computer clusters built from commodity hardware, which is still the common use. It has since also found use on clusters of higher-end hardware. All the modules in Hadoop are designed with a fundamental assumption that hardware failures are common occurrences and should be automatically handled by the framework. Overview The core of Apache Hadoop consists of a storage part, known as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), and a processing part which is a MapReduce programming model. Hadoop splits files into large blocks and distributes them across nodes in a cluster. It then transfers JAR (file format), packaged code into nodes to process the data in parallel. This appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |