|
Scalovia
Scalovia or Skalvia (, , , ) was the area of Prussia originally inhabited by the now extinct Baltic tribe of Skalvians or Scalovians which according to the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of Peter of Dusburg lived to the south of the Curonians, by the lower Nemunas river, in the times around 1240. Jodocus Hondius mentions in 1641 that in "Sclavonia liegen Ragneta, Tilsa, Renum, Liccovia, Salavia, Labia, Tapia, Vintburg, Christader, Bayria, Cestia, Norbeitia, Bensdorff / Angenburg und Dringofordt" Jodocus Hondius, ''Atlas Minor'', :114 The centre of Scalovia was supposed to be Ragnit (Ragneta)(Raganita)(Rogneta) and in the west it bordered the Curonian Lagoon as far as the town of Russ and with Samogitia up north and with Nadrovia in the south. The origin of the name according to Prussian chronicles is derived from one of the Prussian brothers name Schalauo and resembles the name of the town Salavia. The inhabitants can be traced back to burial grounds with cremated remains and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
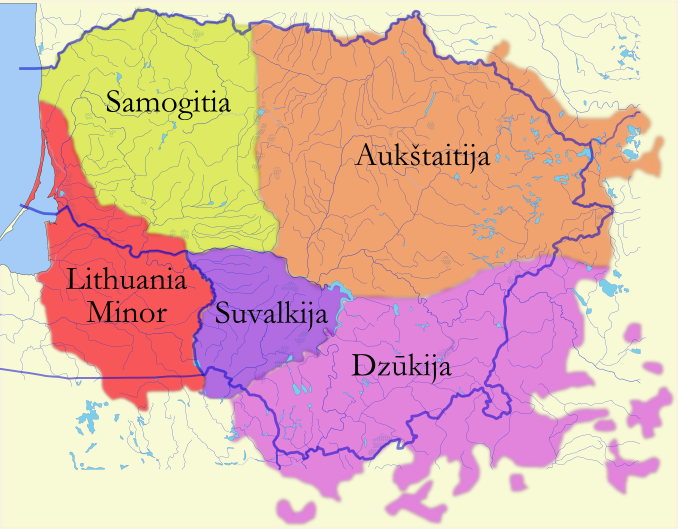
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor (; ; ) or Prussian Lithuania (; ; ) is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is a historical region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Lithuania and the Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the land was repopulated by Lithuanian newcomers, returning refugees, and the remaining indigenous Baltic peoples; the term Lithuania Minor appeared for the first time between 1517 and 1526. With the exception of the Klaipėda Region, which became a mandated territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skalvians
The Scalovians (; ), also known as the Skalvians, ''Schalwen'' and ''Schalmen'', were a Baltic tribe related to the Prussians. According to the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of Peter of Dusburg, the now extinct Scalovians inhabited the land of Scalovia south of the Curonians and Samogitians, by the lower Neman River ca. 1240. Geography This region is located at both sides of the river Memel north of Nadruvians and south of Samogitia. In the North-East it stretched to rivers Šešupė, Ežeruona and Jūra. In the East it bordered on Sudovia, in the North-West on river Minija, in the West on the Curonian Lagoon and in the South-West on river Gilija. The center were the towns of Rusnė, Ragainė and Tilžė. Name The meaning is uncertain: ''skalwa'' "splinter (living split off)" or ''skalauti'' "between waters". According to Prussian legends, the tribe's name is derived from one of the sons of King Widewuto named Schalauo. History The inhabitants can be traced back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia (region)
Prussia (; ; ; ; ; //) is a Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region in Central Europe on the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, that ranges from the Vistula delta in the west to the end of the Curonian Spit in the east and extends inland as far as Masuria, divided between Poland (Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship), Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast) and Lithuania (Lithuania Minor). This region is often also referred to as Old Prussia. Tacitus's ''Germania (book), Germania'' (98 AD) is the oldest known record of an eyewitness account on the territory and its inhabitants. Pliny the Elder had already confirmed that the Romans had navigated into the waters beyond the ''Cimbric peninsula'' (Jutland). Swedes (Germanic tribe), Suiones, Sitones, Goths and other Germanic people had temporarily settled to the east and west of the Vistula River during the Migration Period, adjacent to the Aesti, who lived further to the east. Overview The region's inhabitants of the Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Tribe
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct, but made a large influence on the living branches, especially on literary Lithuanian language. The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, Ukraine and Russia. In the first millenniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Terrae Prussiae
''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' () is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, completed some 100 years after the conquest of the crusaders into the Baltic region. It is a major source for information on the Order's battles with Old Prussians and Lithuanians. Contents and reliability The chronicle is written in Latin and consists of four volumes. The first volume gives the background of the Order and its crusades in Outremer. The second volume narrates how the Order arrived to the Prussian land, while the third volume details wars with Old Prussians and other Baltic tribes. The fourth volume provides a historical context of other contemporary events in the world. The chronicle has an addendum of another 20 chapters dealing with events of 1326-1330, which may also have been written by Peter of Dusburg. The chronicle is based on local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Of Dusburg
Peter of Dusburg (; ; died after 1326), also known as Peter of Duisburg, was a Priest-Brother and chronicler of the Teutonic Knights. He is known for writing the ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'', which described the 13th and early 14th century Teutonic Knights and Old Prussians in Prussia (region), Prussia. Life Peter's dates of birth and death are unknown, although he lived from the second half of the 13th century until the first half of the 14th century. Initially it was thought he was from Duisburg, Germany, and in some texts he is referred to as "Peter of Duisburg". Other research indicates he may have instead come from Doesburg, the Netherlands.Pollakówna, Marzena. ''Kronika Piotra z Dusburga'' ("The Chronicle of Peter of Dusburg"), Acta Poloniae Historica, Wrocław, Warsaw, Kraków, vol. 19, pp. 69-88. 1968; In 1324, probably while in Königsberg,Christiansen, pg. 224 Peter began working on his ''Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' on behalf of Grand Master Werner von Orseln. By 1326 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.'' The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. They eventually merged with other Baltic tribes contributing to the ethnogenesis of present-day Latvians and Lithuanians. Curonians gave their name to the region of Courland (''Kurzeme''), Kuršėnai town, Curonian spit and many other localities. They spoke the Curonian language. Origin The ethnic origin of the Curonians has been disputed in the past. Some researchers place the Curonians in the eastern Baltic group.Östen Dahl (ed.) 2001, ''The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact,'' vol. 1 Others hold that the Curonians were related to Old Prussians who belonged in the western Baltic group. History The historical Curonians were described in contemporary sources as warriors, sailors and pirates. They are on the record havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemunas
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its southern channel. It drains into the Curonian Lagoon, narrowly connected to the Baltic Sea. The long Neman is a major Eastern European river. It flows generally west to Grodno within of the Polish border, north to Kaunas, then westward again to the sea. The largest river in Lithuania, and the third-largest in Belarus, it is navigable for most of its length. It starts from two small headwaters merging about southwest of the town of Uzda – about southwest of capital city Minsk. Only , an eastward meander, contributes to the Belarus–Lithuania border. Thereafter the river includes notable loops along a minor tectonic fault. Its drainage basin settled in the late Quaternary to be roughly along the edge of the last glacial sheet so dates to about 25,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jodocus Hondius
Jodocus Hondius (Latinized version of his Dutch name: ''Joost de Hondt'') (17 October 1563 – 12 February 1612) was a Flemish and Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is sometimes called Jodocus Hondius the Elder to distinguish him from his son Jodocus Hondius II. Hondius is best known for his early maps of the New World and Europe, for re-establishing the reputation of the work of Gerard Mercator, and for his portraits of Francis Drake. He inherited and republished the plates of Mercator, thus reviving his legacy, also making sure to include independent revisions to his work. One of the notable figures in the Golden Age of Dutch cartography (c. 1570s–1670s), he helped establish Amsterdam as the center of cartography in Europe in the 17th century. Biography Hondius was born in Wakken and grew up in Ghent. In his early years he established himself as an engraver, instrument maker and globe maker. In 1584 he moved to London with his sister Jacomina to escape religiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragnit
Neman (; ; ), is a town and the administrative center of Nemansky District in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located in the historic region of Lithuania Minor, on the steep southern bank of the Neman River, where it forms the Russian border with the Klaipėda Region in Lithuania, and northeast of Kaliningrad, the administrative center of the oblast. Population figures: History ''Ragnita'' (from Old Prussian: ''ragas'', "spur"), founded in 1288, was a settlement of the Baltic (Old Prussian) tribe of Skalvians. It was contested by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since its creation in the 13th century, and on April 23, 1289 it was conquered by the Teutonic Knights, who built a castle there between 1397 and 1409, which later became the seat of a ''Komtur''. Construction works were supervised by the Master of the Teutonic Order Konrad Fellenstein of Marienburg. A few decades later, a now-destroyed 25 meter guard tower was built onto the castle. The stronghold was called ''Landesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of about 100,450 square kilometres in Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast. Human history In the 13th century, the area around the lagoon was part of the ancestral lands of the Curonians and Old Prussians. Later it bordered the historical region of Lithuania Minor. At the northern end of the Spit, the Klaipėda Strait connects the lagoon to the Baltic Sea, and the place was chosen by the Teutonic Knights in 1252 to found Memelburg Castle and the city of Klaipėda. In 1454, King Casimir IV Jagiellon incorporated the region to the Kingdom of Poland upon the request of the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation. Following the peace treaty of 1466, the lagoon became a part of Poland as a fief held by the Teutonic Knights,Górski, pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania alongside Lithuania proper. Žemaitija is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its capital city is Telšiai and the largest city is Šiauliai (located on the border between Samogitia and Aukštaitija). Throughout centuries, Samogitia developed a separate culture featuring diverse architecture, folk costumes, dances, songs, traditions, and a distinct Samogitian language. Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle, Plungė Manor and Hill of Crosses. Etymology and alternative names The region is primarily referred to by its Lithuanian name, ''Žemaitija'', in both local and national contexts. The Latin language, Latin-derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |