|
Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant branch of the House of Wettin. History Division of Leipzig In the late 15th century much of what is now Thuringia, including the area around Weimar, was held by the Wettin Electors of Saxony. According to the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin lands had been divided between Elector Ernest of Saxony and his younger brother Albert III, with the western lands in Thuringia together with the electoral dignity going to the Ernestine branch of the family. Ernest's grandson Elector John Frederick I of Saxony forfeited the electoral dignity in the 1547 Capitulation of Wittenberg, after he had joined the revolt of the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League against the Habsburg emperor Charles V, was defeated, captured and banned. Nevertheless, according to the 1552 Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach () was a German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was raised to a grand duchy in 1815 by resolution of the Congress of Vienna. In 1903, it officially changed its name to the Grand Duchy of Saxony (), but this name was rarely used. The grand duchy came to an end in the German Revolution of 1918–19 with the other monarchies of the German Empire. It was succeeded by the Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, which was merged into the new Free State of Thuringia two years later. The full grand ducal style was Grand Duke of Saxe- Weimar- Eisenach, Landgrave in Thuringia, Margrave of Meissen, Princely Count of Henneberg, Lord of Blankenhayn, Neustadt and Tautenburg. The Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach branch has been the most genealogically senior extant branch of the House of Wettin since 1672. Geography The Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach () was an Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all three duchies was Eisenach. History In the 15th century, much of what is now the German state of Thuringia, including the area around Eisenach, was in the hands of the Wettin dynasty, since 1423 Prince-electors of Saxony. In 1485, the Wettin lands were divided according to the Treaty of Leipzig, with most of the Thuringian lands going to Elector Ernest of Saxony and his descendants. The Ernestine Wettins also retained the title of Elector. However, when Ernest's grandson John Frederick the Magnanimous revolted against Emperor Charles V during the Schmalkaldic War, he was defeated at the 1547 Battle of Mühlberg and deprived of the electorate in favour of his Wettin cousin Maurice. According to the Capitulation of Wittenberg he was only allowed to retain the lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
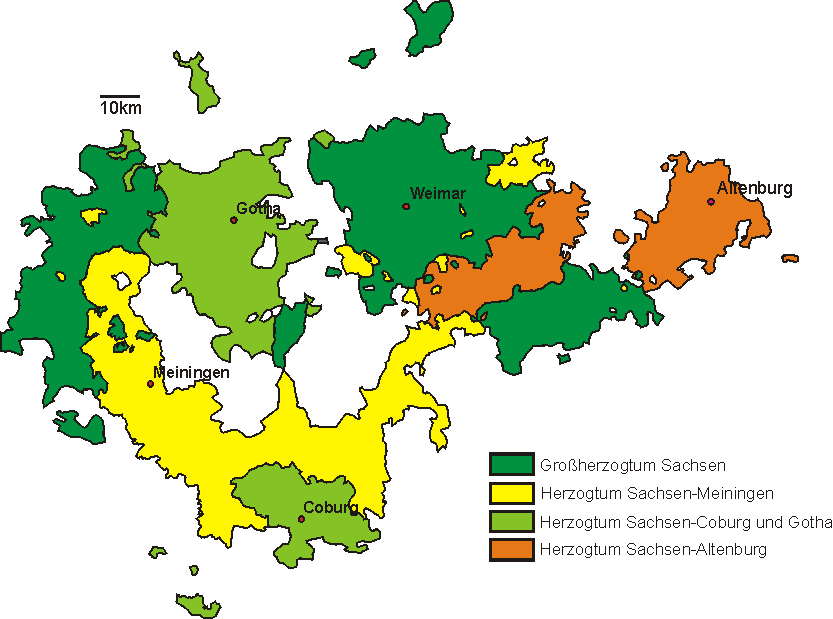
Ernestine Duchies
The Ernestine duchies (), also known as the Saxon duchies (, although the Albertine appanage duchies of Weissenfels, Merseburg and Zeitz were also "Saxon duchies" and adjacent to several Ernestine ones), were a group of small states whose number varied, which were largely located in the present-day German state of Thuringia and governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin. In 1800, there were seven such duchies (two held in personal unions with others) that collectively totaled 7,693 square kilometers of territory and were populated by 445,000 inhabitants.Wilson, Peter (1998). ''German Armies: War and German Society, 1648–1806.'' London: UCL Press. Page 158. Combined total populations and areas of Gotha and Altenburg. Overview The Saxon duchy began fragmenting in the 15th century as a result of the old German succession law that divided inheritances among all sons. In addition, every son of a Saxon duke inherited the title of duke. Brothers sometimes rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several Middle Ages, medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state (Germany), German state of Thuringia, in Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany between Erfurt to the west and Jena to the east, southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouring cities of Erfurt and Jena, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia, with approximately 500,000 inhabitants. The city itself has a population of 65,000. Weimar is well known because of its cultural heritage and importance in German history. The city was a focal point of the German Enlightenment and home of the leading literary figures of Weimar Classicism, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller. In the 19th century, composers such as Franz Liszt made Weimar a music centre. Later, artists and architects including Henry van de Velde, Wassily Kandinsky, Paul Klee, Lyonel Feininger, and Walter Gropius came to the city and founded the Bauhaus movement, the most important German design school of the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss-Gera. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. Territory Saxe-Altenburg had an area of 1,323 km2 (510 sq. mi.) and a population of 207,000 in 1905. Its capital was Altenburg. The duchy consisted of two separate areas: the Ostkreis, containing the cities of Altenburg, Schmölln, Gößnitz, Lucka und Meuselwitz (including the exclave of Mumsdorf), Roschütz, Hilbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Jena
The Duchy of Saxe-Jena was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1672 for Bernhard, fourth son of Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Jena was reincorporated into Saxe-Weimar on the extinction of Bernhard's line in 1690. Dukes of Saxe-Jena * Bernhard II (1672–1678) * Johann Wilhelm (1678–1690) ''Reincorporated into Saxe-Weimar''. References {{Coord missing, Thuringia 1672 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1690 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1672 Jena Jena (; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 in ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Gotha
Saxe-Gotha () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine duchies, Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin, Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha (town), Gotha. History The duchy was established in 1640, when Duke Wilhelm, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Wilhelm von Saxe-Weimar created a subdivision for his younger brother Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest I the Pious. Duke Ernest took his residence at Gotha (town), Gotha, where he had ''Schloss Friedenstein'' built between 1643 and 1654. At the same time, the Duchy of Saxe-Eisenach was created for the third brother Albert IV, Duke of Saxe-Eisenach, Albert IV. Nevertheless, Albert died in 1644, and Ernest inherited large parts of his duchy, though not the core territory around the residence at Eisenach and the Wartburg, which fell to his elder brother Wilhelm of Saxe-Weimar. Ernest could also incorporate several remaining estates of the extinct House of Henneberg in 166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederation Of The Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria and Russian Empire, Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted for only seven years, from 1806 to 1813, dissolving after Napoleon's defeat in the War of the Sixth Coalition.Hans A. Schmitt. "Germany Without Prussia: A Closer Look at the Confederation of the Rhine". ''German Studies Review'' 6, No. 4 (1983), pp 9–39. The founding members of the confederation were German princes of the Holy Roman Empire. They were later joined by 19 others, altogether ruling a total of over 15 million people. This granted a significant strategic advantage to the French Empire on its eastern frontier by providing a buffer between France and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent interlinked, such as by sharing some limited governmental institutions. Unlike a personal union, in a federation or a unitary state, a central (federal) government spanning all member states exists, with the degree of self-governance distinguishing the two. The ruler in a personal union does not need to be a hereditary monarch. The term was coined by German jurist Johann Stephan Pütter, introducing it into ''Elementa iuris publici germanici'' (Elements of German Public Law) of 1760. Personal unions can arise for several reasons, such as: * inheritance through a dynastic union, e.g. Louis X of France inherited France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Frederick I, Elector Of Saxony
John Frederick I (, 30 June 1503 – 3 March 1554), called the Magnanimous (), was the Elector of Saxony (1532–1547) until he was deprived of this title in the Capitulation of Wittenberg by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. He was leading the Schmalkaldic League, a military alliance of Lutheran principalities. Early years John Frederick was the eldest son of John, Elector of Saxony by his first wife, Sophie of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. His mother died fourteen days after his birth, on 12 July 1503. John Frederick received his education from George Spalatin, whom he highly esteemed during his whole life. Spalatin was Martin Luther's friend and advisor and thus, through Spalatin's schooling, John Frederick developed a devotion to the teachings of Luther. His knowledge of history was comprehensive, and his library, which extended over all sciences, was one of the largest in Germany. He cultivated a personal relationship with Luther, beginning to correspond with him in the days when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a bank (geography), left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking, hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof, Germany, Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |