|
Savonian People
Savonians (; ), or Savo Finns, are a Finns#Subdivisions, subgroup (''heimo'') of Finns who live in the areas of the historical province of Savonia (historical province), Savonia. History Savonians are descendants of Tavastians, Tavastian and Karelian peasants who, during the Middle Ages, had settled in the areas that would later become known as ''Savonia'' in order to find new lands suitable for slash-and-burn agriculture. The Treaty of Nöteborg split the area between Sweden and Novgorod Republic, Savonia going to Sweden and Karelia to Novgorod. This tied Savonia to the Finnish language and Lutheran religion. While Savonia as a region was first mentioned in writing in 1323 in the treaty, Savonians as a separate group emerged around the year 1700 as a result of the mixing of Karelians and Tavastians. During 16th and 17th centuries, many Savonians emigrated to Eastern Norway and Central Sweden where they became known as the Forest Finns. In the 17th century, there was also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savo
Savo may refer to: Languages * Savo dialect, forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savo, Finland * Savo language, an endangered language spoken on Savo People * Savo (given name), a masculine given name from southern Europe (includes a list of people with the name) * ''Savo'', nickname of Steven Milne (born 1980), Scottish professional footballer * Savonians, Savo Finns, subgroup of Finnish people Places Finland * Savo (historical province), Finland * North Savo (Finnish: ''Pohjois-Savo''), Finland * South Savo (Finnish: ''Etelä-Savo''), Finland Solomon Islands * Savo Island, off Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands ** Battle of Savo Island (other), a number of World War II battles ** USS Savo Island, USS ''Savo Island'', a U.S. Navy escort carrier named in memory of the battle United States * Savo Township, South Dakota, a township in Brown County Other uses * 1494 Savo, an asteroid in the main-belt * Ki Savo, part of the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading * Savo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Nöteborg
The Treaty of Nöteborg, also known as the Treaty of Orehovsk (; ; ), is a conventional name for the peace treaty signed at Shlisselburg Fortress, Oreshek (; ) on 12 August 1323. It was the first agreement between Sweden and the Novgorod Republic regulating their border, mostly in the area which is now known as Finland. Three years later, Novgorod signed the Treaty of Novgorod (1326), Treaty of Novgorod with the Norwegians. Name At the time, the treaty had no distinguishing name. It was regarded as a "permanent peace" solution between Sweden and Novgorod. "The Treaty of Nöteborg" is a direct translation of the Swedish "''Nöteborgsfreden"''. The Russian term for the treaty, directly translated into English, is "The Peace of Orehovsk", latinized as "Orehovskii Mir", or "''Ореховский мир"'' in Cyrillic script. The Swedish "Nöteborg" and the Russian "Orehovsk" are names for an old Shlisselburg Fortress, fortress in Shlisselburg. The Finnish term for the treaty, "Pähk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harri Hakkarainen
Harri Tapio Hakkarainen (born 16 October 1969 in Kaavi) is a retired male javelin thrower from Finland. He set his personal best (87.82 metres) on 24 June 1995 in Kuortane Kuortane is a municipality of Finland. It is located in the South Ostrobothnia region. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . The neighboring municipalities of Kuortane are .... Seasonal bests by year *1986 – 60.38 *1987 – 63.88 *1988 – 65.78 *1989 – 70.06 *1992 – 83.46 *1993 – 84.36 *1994 – 85.46 *1995 – 87.82 *1996 – 87.44 *1997 – 86.48 *1998 – 85.34 *1999 – 85.00 *2000 – 85.65 *2001 – 83.67 *2002 – 80.56 *2003 – 77.52 *2004 – 74.60 *2005 – 74.11 *2006 – 71.34 *2007 – 72.07 *2008 – 72.11 *2009 – 70.55 *2010 – 65.46 *2011 – 61.20 *2012 – 61.85 Achievements ReferencesIAAF Profile [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juhan Af Grann
Juhan af Grann (3 December 1944 – 14 January 2023) was a Finnish film director and producer known for his UFO documentaries. His most notable documentary is ''Mankind's Last Exodus'', released in 1998 and sold in over 120 countries. Grann is noted for his interest in the topic of unidentified flying object An unidentified flying object (UFO) is an object or phenomenon seen in the sky but not yet identified or explained. The term was coined when United States Air Force (USAF) investigations into flying saucers found too broad a range of shapes ...s, but he is also known for outlandish promotion. __NOTOC__ Filmography Director * ''Kun maailma paloi'' (1969) * ''Ihminen tundrassa'' (1972) * ''UKK – Luova valtiomies'' (1975) * ''Luonnon luomaa'' (1977) * ''A la Finlandia'' (1985) * ''Visitors from Space'' (1992) * ''UFOs & Paranormal Phenomena'' (1995) * ''The New Apocalypse – Mankind's Last Exodus'' (1998) * ''Intruders - They Have Always Been Here and Somebody Knows T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannu Aravirta
Hannu Aravirta (born 26 March 1953) is a former Finnish ice hockey player and an ice hockey coach for the Finnish national men's team, SM-liiga and Elitserien. Career as player Aravirta was born in Savonlinna, and made his first professional appearance in the 1973–1974 season, playing 35 games for TuTo in the SM-liiga. In the following season Aravirta played for his hometown team SaPKo in the Suomi-sarja for one season (1974–1975). Aravirta then headed to Kärpät for a three-season stint. Kärpät gained promotion from the first division to the SM-liiga after the 1976–1977 season and Aravirta played for the team in the 1977–1978 season. Aravirta left Oulu and Finland as he went to Södertälje SK to play in Swedish Allsvenskan. Aravirta stayed in Södertälje for a total of 3 seasons (1978–1980), and then played in Kiruna AIF for 1980–1981, his last season in Sweden. Aravirta returned to Finland and played for Kärpät for two seasons (1981–1983) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juhani Aho
Juhani Aho, originally Johannes Brofeldt (11 September 1861 – 8 August 1921), was a Finnish author and journalist. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature sixteen times. Early life Juhani Aho was born at Lapinlahti in 1861. His parents were Henrik Gustaf Theodor Brofeldt and Karolina Fredrika Emelie "Emma" Brofeldt (née Snellman). The Brofeldts were a priestly family: Theodor was a relatively well-known revivalist preacher whose sermons were published in 1917 as ''Rovasti H. G. Th. Brofeldtin saarnoja'' ("Reverend H. G. Th. Brofeldt's Sermons") and his father had been a chaplain and his grandfather a vicar. Juhani had two younger brothers Kaarlo Kustaa Brofeldt (1865–1936) and Petter Fredrik Brofeldt (1864–1945) who, following Juhani's example, adopted the Finnish names Kalle and Pekka as well as the surname Aho. From 1872 to 1880 Juhani Aho attended the Kuopion Lyseo, one of the few upper secondary schools offering education in Finnish. During his time a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminutive
A diminutive is a word obtained by modifying a root word to convey a slighter degree of its root meaning, either to convey the smallness of the object or quality named, or to convey a sense of intimacy or endearment, and sometimes to belittle something or someone. A ( abbreviated ) is a word-formation device used to express such meanings. A is a diminutive form with two diminutive suffixes rather than one. Purpose Diminutives are often employed as nicknames and pet names when speaking to small children and when expressing extreme tenderness and intimacy to an adult. The opposite of the diminutive form is the augmentative. In some contexts, diminutives are also employed in a pejorative sense to denote that someone or something is weak or childish. For example, one of the last Western Roman emperors was Romulus Augustus, but his name was diminutivized to "Romulus Augustulus" to express his powerlessness. Formation In many languages, diminutives are word forms that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surname
In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several given names and surnames are possible in the full name. In modern times most surnames are hereditary, although in most countries a person has a right to name change, change their name. Depending on culture, the surname may be placed either at the start of a person's name, or at the end. The number of surnames given to an individual also varies: in most cases it is just one, but in Portuguese-speaking countries and many Spanish-speaking countries, two surnames (one inherited from the mother and another from the father) are used for legal purposes. Depending on culture, not all members of a family unit are required to have identical surnames. In some countries, surnames are modified depending on gender and family membership status of a person. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Äyrämöiset
The Äyrämöiset or, as the Russians call them, Evrimeiset (Russian: Эвремейсы), were a Finnish language-speaking people who lived in the Saint Petersburg Oblast and earlier also on the Finnish part of the Karelian Isthmus. Äyrämöiset were one of the two groups of Ingrian Finns, the Finnish speaking groups in St. Petersburg Oblast, the other being the Savakot. Most of the Äyrämöiset are Lutherans. The name Äyrämöiset (äkrämöiset) comes from the ancient county of Äyräpää (Äkräpää) in the Western part of the Karelian Isthmus - which was a part of the kingdom of Sweden after 1323 AD. In earlier times existed as well an agricultural deity called Äkräs (Ägräs), the god of beans, peas and hemp and the mythological forefather of the Äyrämöiset. The Äyrämöiset made up the majority of the population of the Province of Ingria, when it was established in the 17th century. The Äyrämöiset did not mix with the immigrants from Savonia, but by the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
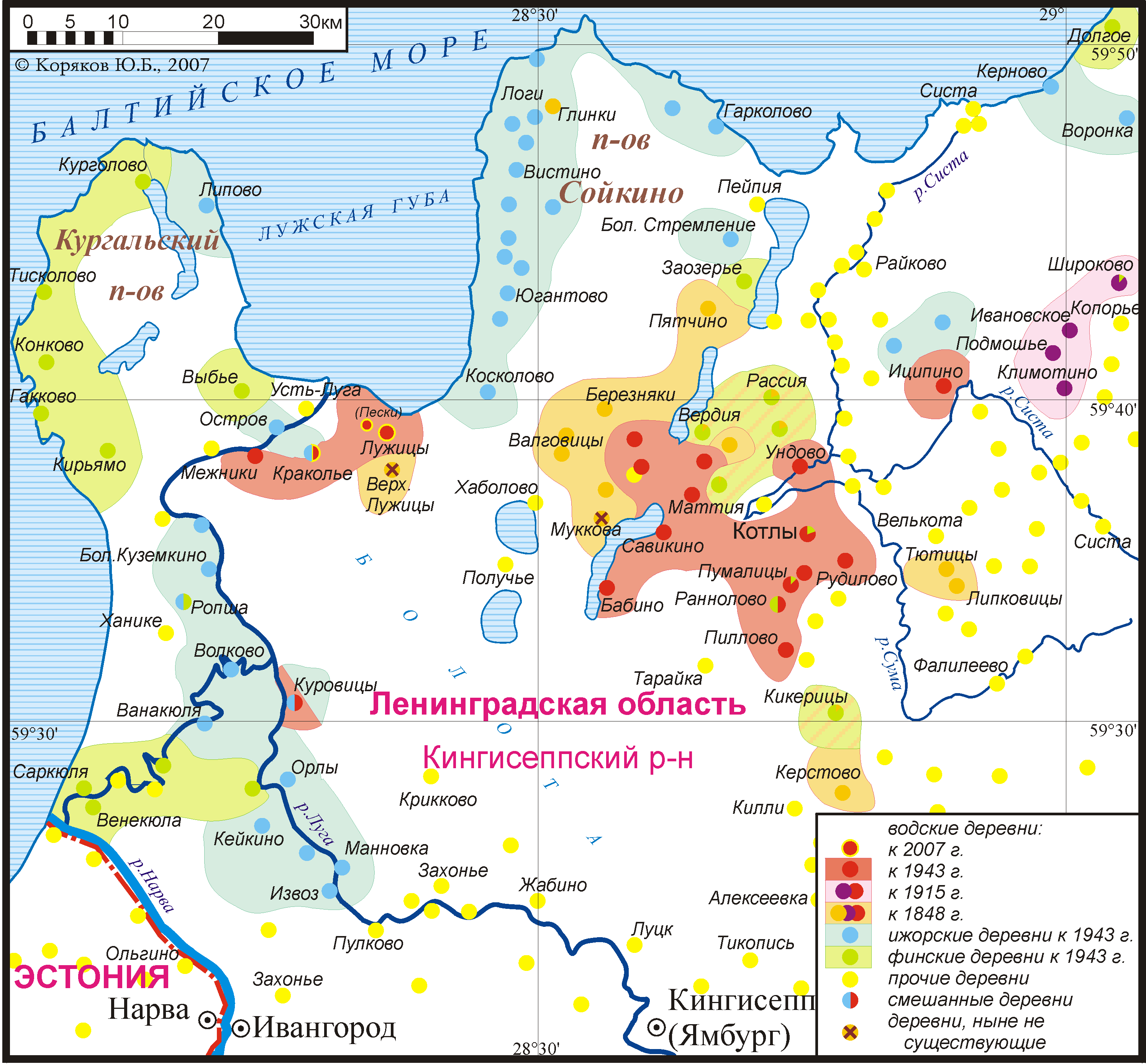
Ingrian Finns
Ingrian Finns (, ; ) are the Finnish people, Finnish population of Ingria (now the central part of Leningrad Oblast in Russia), descending from Lutheranism, Lutheran Finnish immigrants introduced into the area in the 17th century, when Finland and Ingria were both parts of the Swedish Empire. Before and after World War II, most of them were relocated to other parts of the Soviet Union or killed, in Soviet campaigns directed towards their Deportations of the Ingrian Finns, forced deportation and Genocide of the Ingrian Finns, genocide. Today the Ingrian Finns constitute the largest part of the Finnish population of the Russian Federation. According to some records, some 25,000 Ingrian Finns have returned or still reside in the region of Saint Petersburg. They are also referred to as Ingrians, although the term can also refer to the Izhorians or the Baltic Finnic residents of Ingria in general. History Origins Ingrian Finns are the indigenous minority of Europe. Finnish-speakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savakot
Savakot (plural; singular: Savakko; ) were one of the two main subgroups of Ingrian Finns, the other being the Äyrämöiset. The Savakot descended from Finnish ( Savonian) peasants who had migrated to Swedish Ingria (now part of Russia) from Savonia in Eastern Finland during the 17th century.Чистяков А.Ю. Этнические группы ингерманландских финнов в 18-19 вв. // Петербургские чтения 97. Петербург и Россия. СПб., 1997, as cited in"Savakots"(retrieved November 12, 2015) According to German-born Russian ethnographer Peter von Köppen (known in Russia as Petr Keppen), in the middle of the 19th century there were 43,000 Savakot on the Karelian Isthmus. In 1929, in Leningrad Oblast, there were about 115,000 "Leningrad Finns", which included both Savakot and Äyrämöiset and excluded "Finland Finns" (whose number was estimated at 13,000).''Национальные меньшинства Ленин� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Ingria
Swedish Ingria (, ‘land of Ingrians’) was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1583 to 1595 and then again from 1617 to 1721 in what is now the territory of Russia. At the latter date, it was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Nystad, at the end of the Great Northern War between the two empires. History Ingria had fallen to Sweden in the 1580s and as a consequence of the Treaty of Plussa (1583), Sweden kept the Ingrian towns of Ivangorod (Ivanslott), Jamburg (Jama/Jamo) and Koporye (Kaprio) together with their hinterland. Russia only kept a narrow passage to the Baltic Sea at the estuary of the Neva River, between Strelka and Sestra Rivers. The region was returned to Russia by the Treaty of Teusina (1595), and again ceded together with the remainder of Ingria and the County of Kexholm to Sweden in the Treaty of Stolbovo (1617) that concluded the Ingrian War. The area ran along the basin of the Neva River, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |