|
Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset
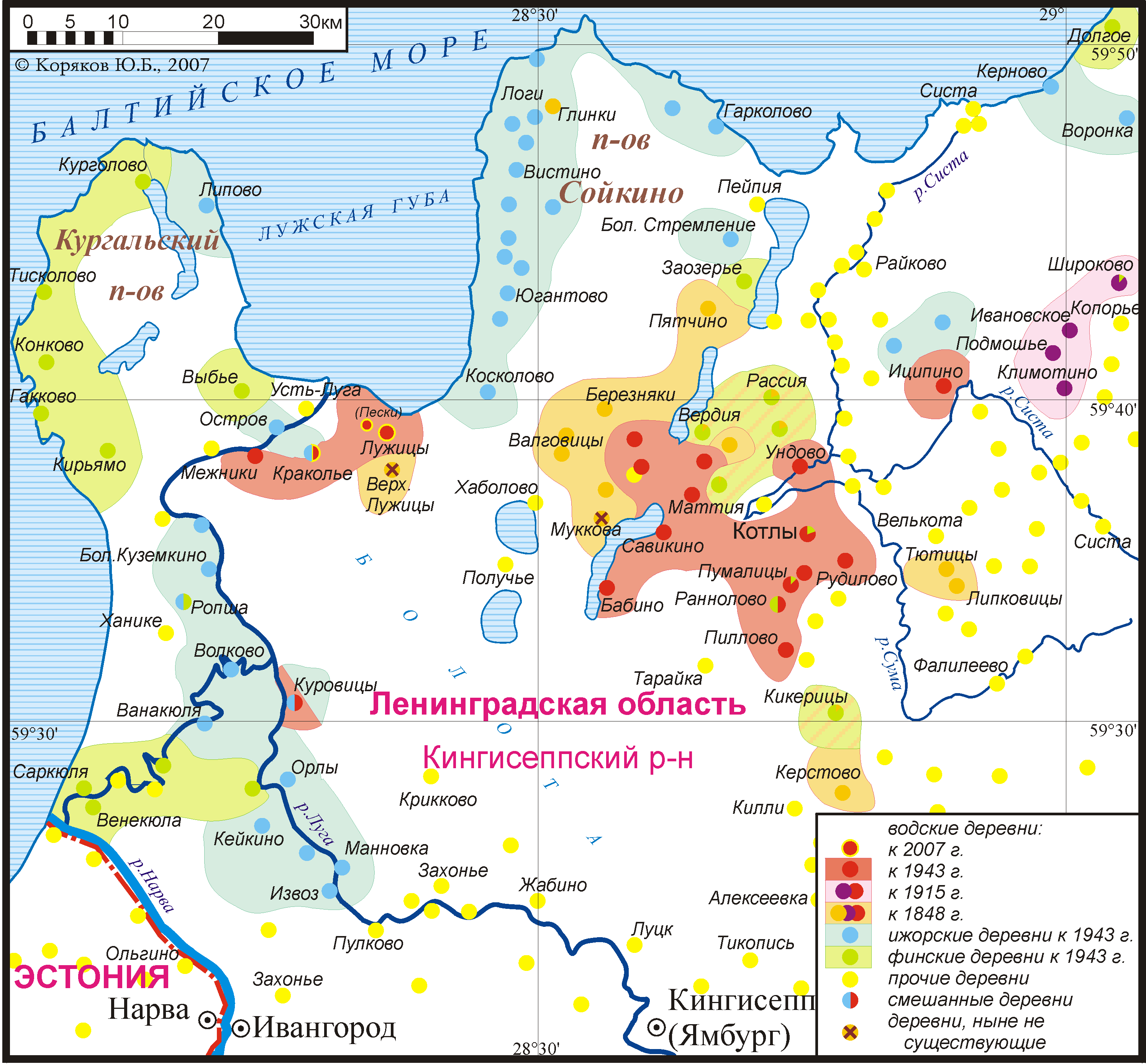
The Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset or, as the Russians call them, Evrimeiset (Russian: –≠–≤―Ä–Β–Φ–Β–Ι―¹―΄), were a Finnish language-speaking people who lived in the Saint Petersburg Oblast and earlier also on the Finnish part of the Karelian Isthmus. Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset were one of the two groups of Ingrian Finns, the Finnish speaking groups in St. Petersburg Oblast, the other being the Savakot. Most of the Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset are Lutherans. The name Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset (ΟΛkrΟΛmΟΕiset) comes from the ancient county of Ο³yrΟΛpΟΛΟΛ (Ο³krΟΛpΟΛΟΛ) in the Western part of the Karelian Isthmus - which was a part of the kingdom of Sweden after 1323 AD. In earlier times existed as well an agricultural deity called Ο³krΟΛs (Ο³grΟΛs), the god of beans, peas and hemp and the mythological forefather of the Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset. The Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset made up the majority of the population of the Province of Ingria, when it was established in the 17th century. The Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset did not mix with the immigrants from Savonia, but by the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savakot
Savakot (plural; singular: Savakko; ) were one of the two main subgroups of Ingrian Finns, the other being the Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset. The Savakot descended from Finnish ( Savonian) peasants who had migrated to Swedish Ingria (now part of Russia) from Savonia in Eastern Finland during the 17th century.–ß–Η―¹―²―è–Κ–Ψ–≤ –ê.–°. –≠―²–Ϋ–Η―΅–Β―¹–Κ–Η–Β –≥―Ä―É–Ω–Ω―΄ –Η–Ϋ–≥–Β―Ä–Φ–Α–Ϋ–Μ–Α–Ϋ–¥―¹–Κ–Η―Ö ―³–Η–Ϋ–Ϋ–Ψ–≤ –≤ 18-19 –≤–≤. // –ü–Β―²–Β―Ä–±―É―Ä–≥―¹–Κ–Η–Β ―΅―²–Β–Ϋ–Η―è 97. –ü–Β―²–Β―Ä–±―É―Ä–≥ –Η –†–Ψ―¹―¹–Η―è. –Γ–ü–±., 1997, as cited in"Savakots"(retrieved November 12, 2015) According to German-born Russian ethnographer Peter von KΟΕppen (known in Russia as Petr Keppen), in the middle of the 19th century there were 43,000 Savakot on the Karelian Isthmus. In 1929, in Leningrad Oblast, there were about 115,000 "Leningrad Finns", which included both Savakot and Ο³yrΟΛmΟΕiset and excluded "Finland Finns" (whose number was estimated at 13,000).''–ù–Α―Ü–Η–Ψ–Ϋ–Α–Μ―¨–Ϋ―΄–Β –Φ–Β–Ϋ―¨―à–Η–Ϋ―¹―²–≤–Α –¦–Β–Ϋ–Η–Ϋ– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingrian Finns
Ingrian Finns (, ; ) are the Finnish people, Finnish population of Ingria (now the central part of Leningrad Oblast in Russia), descending from Lutheranism, Lutheran Finnish immigrants introduced into the area in the 17th century, when Finland and Ingria were both parts of the Swedish Empire. Before and after World War II, most of them were relocated to other parts of the Soviet Union or killed, in Soviet campaigns directed towards their Deportations of the Ingrian Finns, forced deportation and Genocide of the Ingrian Finns, genocide. Today the Ingrian Finns constitute the largest part of the Finnish population of the Russian Federation. According to some records, some 25,000 Ingrian Finns have returned or still reside in the region of Saint Petersburg. They are also referred to as Ingrians, although the term can also refer to the Izhorians or the Baltic Finnic residents of Ingria in general. History Origins Ingrian Finns are the indigenous minority of Europe. Finnish-speakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Finnic languages, Finnic language of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish language, Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and MeΟΛnkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. Kven language, Kven, which like MeΟΛnkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norway, Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent. Finnish is morphological typology, typologically agglutinative language, agglutinative and uses almost exclusively Suffix, suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, Numeral (linguistics), numerals and verbs are inflection, inflected depending on their role in the Sentence (linguistics), sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subjectβÄ™verbβÄ™object word order, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 ( 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the south, Pskov Oblast in the southwest, and the federal city of Saint Petersburg in the wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about . The smaller part of the isthmus to the southeast of the old Russia-Finland border is considered historically as Northern Ingria, rather than part of the Karelian Isthmus itself. The rest of the isthmus was historically a part of Finnish Karelia. This was conquered by the Russian Empire during the Great Northern War in 1712 and included within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland (1809βÄ™1917) of the Russian Empire. When Finland became independent in 1917, the isthmus (excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Saint Petersburg, Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 1517. The Lutheran Churches adhere to the Bible and the Ecumenical Creeds, with Lutheran doctrine being explicated in the Book of Concord. Lutherans hold themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic church and affirm the writings of the Church Fathers and the first four ecumenical councils. The schism between Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism, which was formalized in the Edict of Worms of 1521, centered around two points: the proper source of authority in the church, often called the formal principle of the Reformation, and the doctrine of justification, the material principle of Lutheran theology. Lutheranism advocates a doctrine of justification "by Grace alone through faith alone on the basis of Scripture alone", the doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ο³yrΟΛpΟΛΟΛ
Baryshevo (; ) is a rural locality on Karelian Isthmus, in Vyborgsky District of Leningrad Oblast. It is situated on the southern shore of Vuoksi River. Until the Winter War and Continuation War, it had been the administrative center of the Ο³yrΟΛpΟΛΟΛ municipality of the Viipuri Province of Finland Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, .... See also * Battle of Vuosalmi Rural localities in Leningrad Oblast Karelian Isthmus {{LeningradOblast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ο³krΟΛs
Ο³krΟΛs or Ο³yrΟΛs is a haltija or god of various plants in Finnish mythology. She was first mentioned in writing by Mikael Agricola in 1551: "Egres created peas, beans, rutabagas / Brought forth cabbages, flax, hemp" (''Egres hernet Pawudh Naurit loi / Caalit Linat ia Hamput edestoi''). She was also later associated with potatoes. She was known widely from Western Finland to Karelia, and there are many similar beliefs as those associated with Ο³krΟΛs in traditions around Europe. Similar beliefs also exist among Udmurts. Name The spelling "Egres", as mentioned by Agricola, was quoted in all writings until 1761. Vicar in LeppΟΛvirta, I.D. Alopaeus, said this name in LeppΟΛvirta and Kuopio was "Ο³crΟΛs". Terms such as ''ΟΛkrΟΛs rutabaga'' refer to a rutabaga with two ends growing from the same core (or conjoined rutabagas). Similar terminology has also been used in relation to potatoes and flax. In North Ostrobothnia, the name has been known in the form Ο³yrΟΛs. In Karelia, differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Ingria
Swedish Ingria (, βĉland of IngriansβÄô) was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1583 to 1595 and then again from 1617 to 1721 in what is now the territory of Russia. At the latter date, it was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Nystad, at the end of the Great Northern War between the two empires. History Ingria had fallen to Sweden in the 1580s and as a consequence of the Treaty of Plussa (1583), Sweden kept the Ingrian towns of Ivangorod (Ivanslott), Jamburg (Jama/Jamo) and Koporye (Kaprio) together with their hinterland. Russia only kept a narrow passage to the Baltic Sea at the estuary of the Neva River, between Strelka and Sestra Rivers. The region was returned to Russia by the Treaty of Teusina (1595), and again ceded together with the remainder of Ingria and the County of Kexholm to Sweden in the Treaty of Stolbovo (1617) that concluded the Ingrian War. The area ran along the basin of the Neva River, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |