|
Savatije Milošević
Savatije Milošević ( sr-cyr, Саватије Милошевић; 1876 – 1905), known as Vojvoda Savatije, was a Serbian hajduk and Chetnik commander. Life Early life Savatije Miličević Milošević (Саватије Миличевић Милошевић) was born in Pavlica, Raška, at the time part of the Ottoman Empire (today Serbia). At the age of 25, Milošević murdered Pavle Jasnić, a chief of a ''srez'' (municipality) in Raška, because of a blood feud, and joined the hajduks (brigands) with whom he was active in the Ottoman Empire. He found refuge in Peć, Kosovo Vilayet, at the house of Albanian kachak Mula Zeka. name="SrejovićGavrilović1983">cite book, author1=Dragoslav Srejović, author2=Slavko Gavrilović, author3=Sima M. Ćirković, title=Istorija srpskog naroda: knj. Od Berlinskog kongresa do Ujedinjenja 1878-1918 (2 v.), url=https://books.google.com/books?id=L75BAAAAYAAJ, year=1983, publisher=Srpska književna zadruga, quote=Међутим, по изве ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
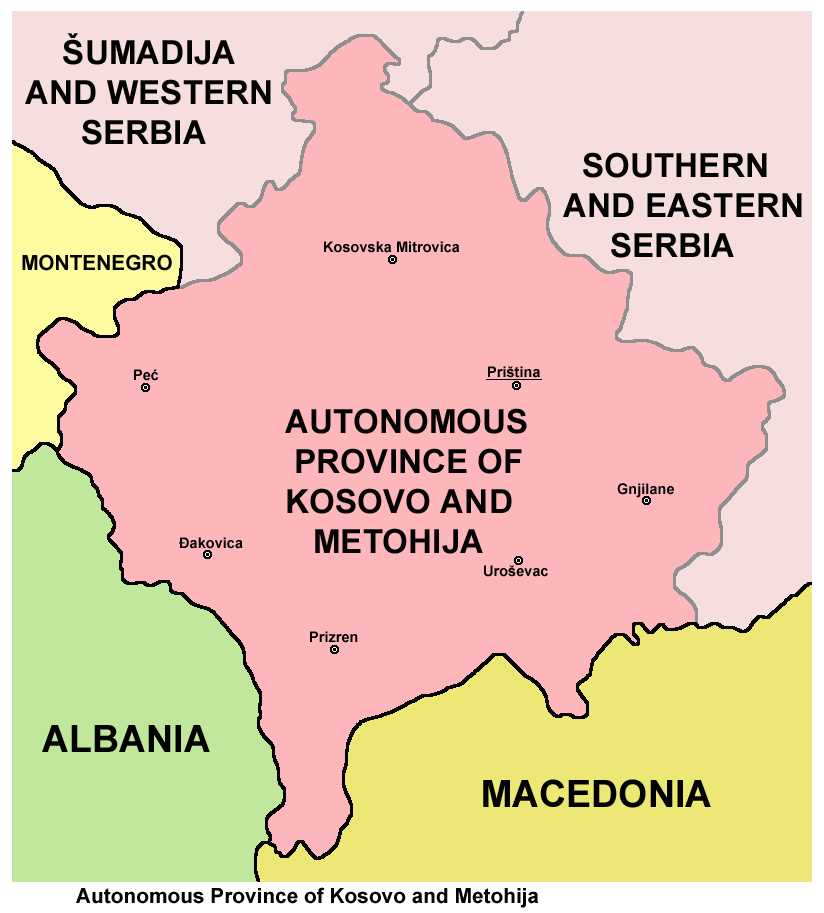
Autonomous Province Of Kosovo And Metohija
The Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija (APKM) (; ), commonly known as Kosovo (; ) and abbreviated to Kosmet (from ''Kosovo (region), Kosovo'' and ''Metohija, Metohija''; ) or KiM (), is an autonomous province that occupies the southernmost corner of Serbia, as defined by the Constitution of Serbia, country's constitution. The territory is the subject of an ongoing Political status of Kosovo, political and territorial dispute between the Republic of Serbia and the partially recognised Kosovo, Republic of Kosovo, with the APKM being viewed as the ''de jure'' interpretation of the territory under Serbian law; however, the Serbian government currently does not control the territories because they are administered by the Republic of Kosovo. Its claimed administrative capital and largest city is Pristina. The territory of the province, as defined by Serbian laws, lies in the southern part of Serbia and covers the regions of geography of Kosovo, Kosovo and Metohija. The capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Raška, Serbia
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Serbian People
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1905 Deaths
As the second year of the massive Russo-Japanese War begins, more than 100,000 die in the largest world battles of that era, and the war chaos leads to the 1905 Russian Revolution against Nicholas II of Russia (Dmitri Shostakovich, Shostakovich's Symphony No. 11 (Shostakovich), 11th Symphony is subtitled ''The Year 1905'' to commemorate this) and the start of Revolution in the Kingdom of Poland (1905–07), Revolution in the Kingdom of Poland. Canada and the U.S. expand west, with the Alberta and Saskatchewan provinces and the founding of Las Vegas. 1905 is also the year in which Albert Einstein, at this time resident in Bern, publishes his four Annus Mirabilis papers, ''Annus Mirabilis'' papers in ''Annalen der Physik'' (Leipzig) (March 18, May 11, June 30 and September 27), laying the foundations for more than a century's study of theoretical physics. Events January * January 1 – In a major defeat in the Russo-Japanese War, Russian General Anatoly Stessel su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1876 Births
Events January * January 1 ** The Reichsbank opens in Berlin. ** The Bass Brewery Red Triangle becomes the world's first registered trademark symbol. *January 27 – The Northampton Bank robbery occurs in Massachusetts. February * February 2 ** The National League of Professional Base Ball Clubs is formed at a meeting in Chicago; it replaces the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players. Morgan Bulkeley of the Hartford Dark Blues is selected as the league's first president. ** Third Carlist War (Spain): Battle of Montejurra – The new commander General Fernando Primo de Rivera marches on the remaining Carlist stronghold at Estella, where he meets a force of about 1,600 men under General Carlos Calderón, at nearby Montejurra. After a courageous and costly defence, Calderón is forced to withdraw. * February 14 – Alexander Graham Bell applies for a U.S. patent for the telephone, as does Elisha Gray. * February 19 – Third Carlist War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chetnik Voivodes
This is a list of Chetnik voivodes. is a Slavic as well as Romanian title that originally denoted the principal commander of a military force. It derives from the word , which in early Slavic meant the , i.e. the military commander of an area, but it usually had a greater meaning. Among the first modern-day voivodes was Kole Rašić, a late 19th-century Serb revolutionary and guerrilla fighter, who led a cheta of 300 men between Niš and Leskovac in Ottoman areas during the Serbo-Turkish War (1876–1878). The others were Rista Cvetković-Božinče, Čerkez Ilija, Čakr-paša, and Spiro Crne. Jovan Hadži-Vasiljević, who knew Spiro Crne personally, wrote and published his biography, ''Spiro Crne Golemdžiojski'', in 1933. Commanders of Old Serbia and Macedonia (1903–1912), Balkan Wars * Jovan Atanacković * Mihailo Ristić (diplomat) * Svetislav Simić * Denko Krstić * Dimitrije Dimitrijević (Chetnik) * Nikola Omoranski * Rista Ognjanović * Cene Marković ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raška (town)
Raška may refer to: Geography * Raška (region), geographical and historical region in modern Serbia * Raška (river), river in southwestern part of Serbia * Raška, Serbia, town and municipality in Serbia History and administration * Eparchy of Raška, a medieval diocese (eparchy) of the Serbian Orthodox Church * Catepanate of Raška, variant designation for the ''Catepanate of Ras'', a short lived Byzantine province (971–976) in central Serbian lands * Grand Principality of Raška, variant designation for the Grand Principality of Serbia, in the 11th and 12th century * Kingdom of Raška, variant designation for the medieval Kingdom of Serbia, in the 13th and 14th century * Raška architectural style, architectural style in medieval Serbia, in the 12th and 13th century * Despotate of Raška, variant designation for the Despotate of Serbia, in the 15th century * Little Raška, a region inhabited by Serbs (Rascians) in southern regions of Pannonian plain, from the 16th to 18th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvezdara
Zvezdara ( sr-cyr, Звездара, ) is a municipality of the city of Belgrade. The municipality is geographically hilly and with many forests. According to the 2022 census results, the municipality has a population of 172,625 inhabitants. The municipality of Zvezdara is located east of Belgrade and occupied almost the entire eastern urban section of the city. It borders the municipalities of Palilula on the north-west, north and north-east, Grocka on the east and south-east, Voždovac on the south and south-west and Vračar on the west. History Historically, Zvezdara hill was known as Great Vračar. Vračаr area at that time occupied much wider area that it does today and was divided into West Vračar, East Vračar and Great Vračar. Turkish source from 1621 describes it as "a hill and a big field". In the 17th and 18th century, the area was covered in vineyards, orchards and lush oriental gardens, a major excursion ground for the wealthy Belgrade Turks which called the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kachaks
Kachaks (, / ''kačaci'') is a term used for the Albanians, Albanian rebels active in the late 19th and early 20th century in northern Albania, Montenegro, Kosovo and Macedonia (region), Macedonia, and later as a term for the militias of Albanians, Albanian revolutionary organizations against the Kingdom of Serbia (1910–18) Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–24), called the "Kachak Movement". Etymology The word is derived from Turkish ''wikt:kaçak, kaçak'' for "outlaw". Background History 1920–24 Kachak movement The Committee for the National Defence of Kosovo, Committee for the National Defense of Kosovo () was created in Shkodër, under Hasan Prishtina, in 1918. The committee organizationally and financially supported the kachaks in Albanian-populated areas of Yugoslavia, in Kosovo and Skopje (the former Kosovo vilayet). Kachaks were also active around Ohrid and Bitola. On 6 May 1919 the Committee called for a general uprising in Kosovo and other Albanian-inhabited regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besa (Albanian Culture)
Besa ( Albanian indefinite form: ) is an Albanian cultural precept, usually translated as "pledge of honor", "solemn faith" or "solemn oath", that means "to keep the promise" and "word of honor", regarded as something sacred and inviolable. ''Besa'' is of prime importance as a cornerstone of personal and social conduct in the Albanian traditional customary law ('' Kanun''), which has directed all the aspects of Albanian tribal society. The Albanian adjective ''besnik'', derived from besa, means "faithful", "trustworthy", i.e. one who keeps his ''word''. Besnik for men and Besa for women continue to be popular names among Albanians. Etymology The Albanian word ''besa'' is an Indo-European cognate and shares similarities with the Classical Latin word ''fides''. In Late Antiquity and the Medieval period, Latin ''fides'' took on the Christian meaning of 'faith' or '(religious) belief,' a sense that persists in modern Romance languages and was borrowed into Albanian as '' feja''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |