|
Sava Temišvarac
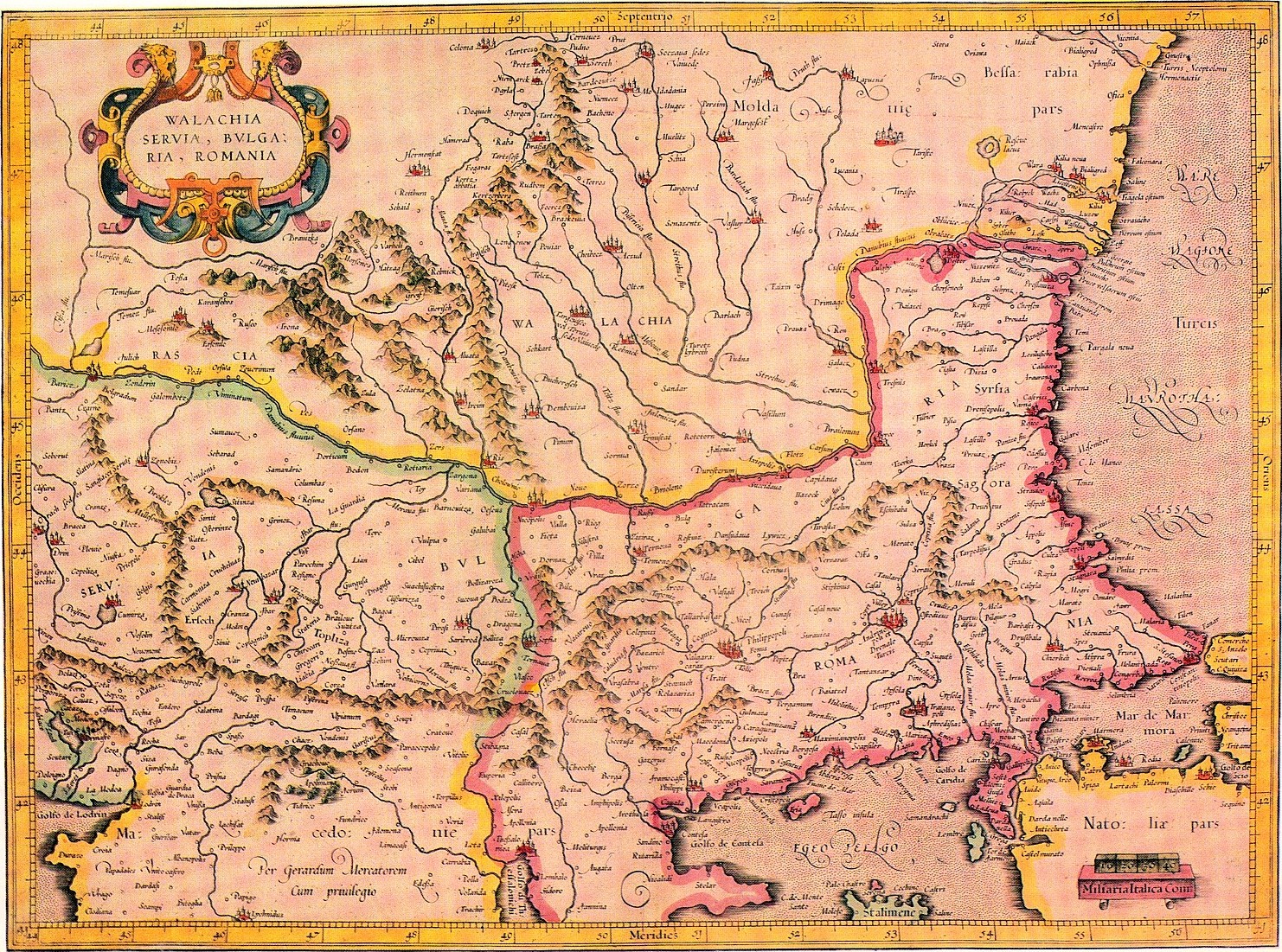
Sava Temišvarac ( sr-cyr, Сава Темишварац, "Sava of Timișoara"; 1594–1612) was a Serb military commander (''vojvoda'') in the service of the Transylvania and then the Holy Roman Empire. He was active during the Long Turkish War, having led the Uprising in Banat (1594) and then joined the Transylvanian Army with other notable Serb leaders. Uprising in Banat Bishop Teodor of Vršac and Sava Temišvarac led the Uprising in Banat (1594). The rebels had, in the character of a holy war, carried war flags with the icon of Saint Sava. After initial success, the rebels had by March 1594 expelled the Ottomans from almost the entire territory of Banat and Körös. On 27 April, in an act of retaliation, Grand Vizier Koca Sinan Pasha had the relics of Saint Sava incinerated at Vračar; made to discourage the Serbs, it instead intensified the rebellion. Đorđe Palotić, the Ban of Lugos, stole armament which he sent to the rebels, and encouraged them to continue to figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rascians
Rascians ( / ''Raši, Rašani''; ) was a historical term for Serbs. The term was derived from the Latinized name for the central Serbian region of Raška (; sr-Cyrl, Рашка). In medieval and early modern Western sources, exonym ''Rascia'' was often used as a designation for Serbian lands in general, and consequently the term ''Rasciani'' became one of the most common designations for Serbs. Because of the increasing migratory concentration of Serbs in the southern Pannonian Plain, since the late 15th century, those regions also became referred to as ''Rascia'', since they were largely inhabited by ''Rasciani'' (Rascians). Among those regions, term ''Rascia'' (Raška) was most frequently used for territories spanning from western Banat to central Slavonia, including the regions of Syrmia, Bačka, and southern Baranja. From the 16th to the 18th century, those regions were contested between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, and today they belong to several modern coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Đorđe Palotić
Đorđe ( sr-Cyrl, Ђорђе; transliterated Djordje) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, common in Serbian. It is derived from Greek ''Georgios'' (''George'' in English). Other variants include: Đurđe, Đurađ, Đura, Đuro, Georgije. Notable people with the name A-J * Đorđe Andrejević Kun (1904–1964), Serbian painter * Đorđe Babalj (born 1981), Serbian footballer * Đorđe Bajić (footballer) (born 1977), Serbian footballer * Đorđe Bajić (novelist) (born 1975), Serbian writer, literary and film critic * Đorđe Balašević (1953–2021), Serbian recording artist and singer-songwriter * Đorđe Bašanović (born 1996), Serbian footballer * Đorđe Bašić (1946–2007), Serbian politician * Đorđe Bodinović ( 1113-1131), King of Duklja and Travunija * Đorđe Bogić (1911–1941), Serbian Orthodox protopresbyter and priest * Đorđe Božović (1955–1991), Serbian criminal and paramilitary commander * Đorđe Branković (1461–1516), Serbian ruler * Đ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teiuș
Teiuș (, ; ) is a town in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania, with a population of 6,308 inhabitants as of 2021. The town, declared as such in 1994, administers four villages: Beldiu (''Marosbéld''), Căpud (''Magyarkapud''), Coșlariu Nou (''Újkoslárd''), and Pețelca (''Pacalka''). The town is located near the confluence of the Geoagiu River with the Mureș River. Teiuș is a junction point on the Cluj-Napoca–Sighișoara railway. It has several old churches, the most notable being the 17th century Uniate church and the Roman Catholic church, built for John Hunyadi in 1449 and rebuilt (1701–1704) in a simple Gothic style. Demographics At the 2011 census, Teiuș had 6,695 inhabitants, of which 83.57% were Romanians, 7.63% Roma, and 3.87% Hungarians. At the 2021 census, the town had a population of 6,308; of those, 80.83% were Romanians, 7.13% Roma, and 2.79% Hungarians. Natives * Ioan Bălan (1880–1959), Romanian bishop of the Greek-Catholic Church * Nori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ineu
Ineu (; ) is a town in Arad County, western Transylvania, Romania. It is situated at a distance of from the county capital, Arad, it occupies a surface at the contact point of Crișul Alb Basin and Crișurilor Plateau. Ineu is the main entrance gate into the (''Țara Zarandului''). The town administers one village, Mocrea (''Apatelek''). Ineu was first attested in documents in 1214 under the name "Villa Ieneu". It was a sanjak centre in the Temeşvar and Varat eyalets and it was known as "Yanova" during the Ottoman rule between 1564 and 1595 and again between 1658 and 1693. Population At the 2021 census, Ineu had a population of 8,807. At the 2011 census, the town had 9,078 inhabitants; of those, 86.49% were Romanians, 6.57% Hungarians, 5.98% Roma, 0.34% Germans, 0.08% Slovaks, and 0.1% are of other or undeclared nationalities. Natives * Mona Nicoară, film director and producer *Radu Theodoru (born 1924), writer, far-right politician and general Tourist attractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zrenjanin
Zrenjanin ( sr-Cyrl, Зрењанин, ; ; ; ; ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Central Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The city urban area has a population of 67,129 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 105,722 inhabitants (2022 census data). The old name for Zrenjanin is Veliki Bečkerek or ''Nagybecskerek'' as it was known under Austria-Hungary up until 1918. After World War I and the liberation of Veliki Bečkerek the new name of the city was Petrovgrad, in honor of His Majesty Peter I of Serbia, King Peter I the Great Liberator, the King of Serbia and the King of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Zrenjanin is the 2nd largest city in the Serbian part of the Banat geographical region, and the 4th largest city in Vojvodina (after Novi Sad, Subotica and Pancevo). The city was designated European City of Sport 2021. Name The city was named after Žarko Zrenjanin (1902–1942) in 1946 in honour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budin Eyalet
Budin Eyalet (also known as Province of Budin/Buda or Pashalik of Budin/Buda, ) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire in Central Europe and the Balkans. It was formed on the territories that Ottoman Empire conquered from the medieval Kingdom of Hungary and Serbian Despotate. The capital of the Budin Province was Budin (Hungarian: Buda). Population of the province was ethnically and religiously diverse and included Hungarians, Croats, Serbs, Slovaks, Muslims of various ethnic origins (living mainly in the cities) and others (Jews, Romani, etc.). The city of Buda itself became majority Muslim during the seventeenth century, largely through the immigration of Balkan Muslims. History In the 16th century the Ottoman Empire had conquered the southern "line of fortresses" (végvár) of the Kingdom of Hungary. After the Battle of Mohács where the Kingdom of Hungary was heavily defeated, and the turmoil caused by the defeat, the influence was spread on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beylerbey
''Beylerbey'' (, meaning the 'commander of commanders' or 'lord of lords’, sometimes rendered governor-general) was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Anatolian Seljuks and the Ilkhanids to Safavid Iran and the Ottoman Empire. Initially designating a commander-in-chief, it eventually came to be held by senior provincial governors. In Ottoman usage, where the rank survived the longest, it designated the governors-general of some of the largest and most important provinces, although in later centuries it became devalued into a mere honorific title. The title is originally Turkic and its equivalents in Arabic were ''amir al-umara'', and in Persian, ''mir-i miran''. Early use The title originated with the Seljuks, and was used in the Sultanate of Rum initially as an alternative for the Arabic title of ''malik al-umara'' ("chief of the commanders"), designating the army's commander-in-chief. Among the Mongol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasan Pasha Of Temeşvar
Hasan Pasha ( 1593–1594) was the Beylerbey of the Temeşvar Eyalet. During the Uprising in Banat (1594), he received aid from the Grand Vizier Koca Sinan Pasha Koca Sinan Pasha (, "Sinan the Great", ; c. 1506 – 3 April 1596) was an Albanian-born Ottoman Grand Vizier, military figure, and statesman. From 1580 until his death he served five times as Grand Vizier. Early life Sinan Pasha, also known ... and the Pasha of Budin, thus appeared with an army numbering 20,000 soldiers and attacked Becskerek (Zrenjanin), in the hands of 4,300 rebels, ending in a decisive Ottoman victory. Subsequently, Sinan Pasha took an army of 30,000 soldiers which suppressed the badly armed Serbs. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Hasan Pasha of Temesvar Governors of the Ottoman Empire by eyalet 16th-century Ottoman military personnel Temeşvar Eyalet 16th-century births Year of death unknown 16th-century governors of the Ottoman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyulafehérvár
Alba Iulia (; or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; ; ) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the river Mureș in the historical region of Transylvania, it has a population of 64,227 (). During ancient times, the site was the location of the Roman camp Apulum. Since the High Middle Ages, the city has been the seat of Transylvania's Roman Catholic diocese. Between 1526 and 1570 it was the capital of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged by the Treaty of Speyer in 1570 and it was the capital of the Principality of Transylvania until 1711. At one point it also was a center of the Eastern Orthodox Metropolitan of Transylvania with suffragan to Vad diocese.Maksym Mayorov. Metropolitan of Kiev and other Eastern Orthodox Churches before 1686 (Київська митрополія та інші православні церкви перед 1686 роком ) Likbez. 16 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbdom
Serbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, under the influence of Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Serbian statesman Ilija Garašanin. Serbian nationalism was an important factor during the Balkan Wars which contributed to the decline of the Ottoman Empire, during and after World War I when it contributed to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and again during the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s. After 1878, Serbian nationalists merged their goals with those of Yugoslavists, and emulated the Piedmont's leading role in the '' Risorgimento'' of Italy, by claiming that Serbia sought not only to unite all Serbs in one state, but that Serbia intended to be a South Slavic Piedmont that would unite all South Slavs in one state known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knyaz
A , also , ''knjaz'' or (), is a historical Slavs, Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English language, English as 'prince', 'king' or 'duke', depending on specific historical context and the potentially known Latin equivalents at the time; the word was originally derived from the Proto-Germanic language, common Germanic ('king'). Feminine forms of the word may be divided into two groups: * "Princess", be it princess consort (wife of a reigning prince), princess regnant (reigning princess ''suo jure''), or princess regent (reigning on behalf of an underage prince, usually her son after her husband's death) ** Belarusian language, Belarusian: ''kniahinia'' (княгіня) ** Bulgarian language, Bulgarian and Russian language, Russian: () ** Slovene language, Slovene, Serbo-Croatian, and Macedonian language, Macedonian: (in Serbian Cyrillic alphabet, Serbian and Macedonian alphabet, Macedonian Cyrillic: ) ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |