|
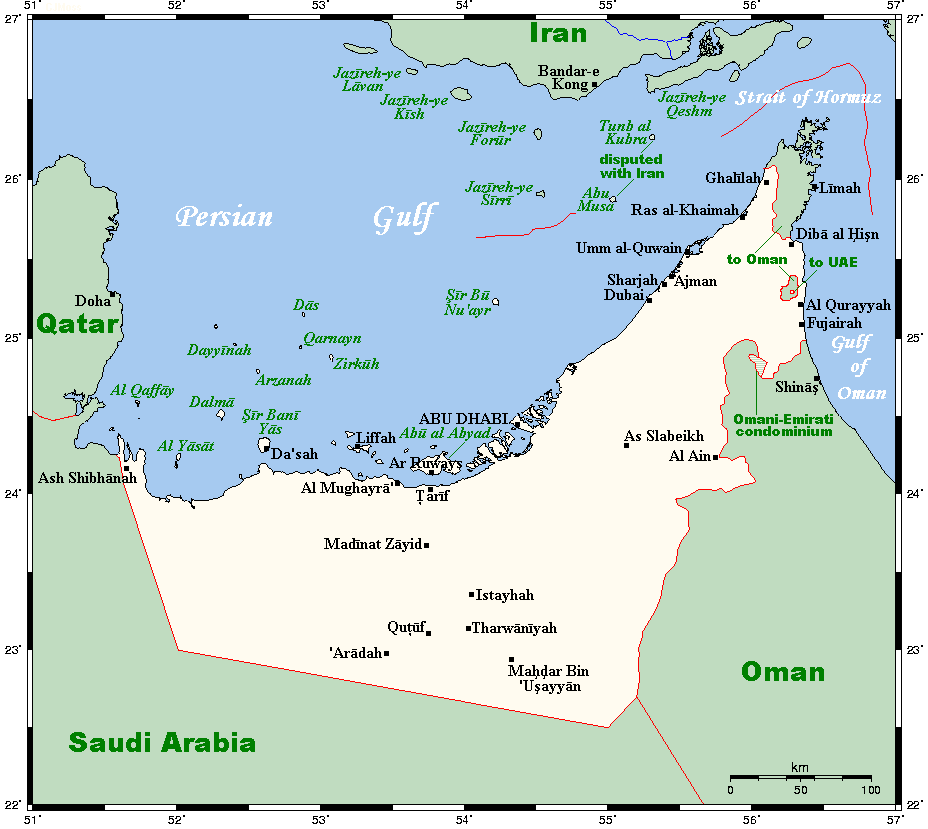
Saudi Arabia–United Arab Emirates Border
The Saudi Arabia–United Arab Emirates border is 457 km (284 mi) in length and runs from the Persian Gulf coast in the west to the tripoint with Oman in the east. The governments of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates signed the Treaty of Jeddah (1974), Treaty of Jeddah in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, on 21 August 1974 between Faisal of Saudi Arabia and Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan apparently ending a long-running boundary dispute, but according to the UAE the dispute has not been settled due to discrepancies between the oral agreement before the treaty's signing and the final text of the treaty itself. According to the UAE, the government did not notice this discrepancy until 1975 as a result of the absence of lawyers, technicians, and geographers on its negotiation team. The UAE has attempted to bring Saudi Arabia back to the negotiating table ever since. The provisions of the 1974 treaty were not publicly disclosed until 1995, when it was lodged with the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violet Line (1914)
The Violet Line was a boundary line agreed between the United Kingdom and the Ottoman Empire in March 1914.{{citation , url= https://www.dur.ac.uk/ibru/publications/view/?id=49, title=The Iraq-Kuwait boundary dispute: historical background and the UN decisions of 1992 and 1993, author=Harry Brown, publisher=IBRU Boundary and Security Bulletin, date=October 1994, accessdate= 1 April 2020 It started from the termination of the Blue Line agreed to at the Anglo-Ottoman Convention of 1913 and extended to the border between the Ottoman Yemen Vilayet and the British Aden Protectorates. Together with the Blue Line, the Violet Line effectively divided the Arabian peninsula in two. This boundary between the Ottoman and British empires is what eventually led to the border between North Yemen and South Yemen South Yemen, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, abbreviated to Democratic Yemen, was a country in South Arabia that existed in what is now southeast Yemen from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ras Tanura
Ras Tanura (, presumably due to the unusual heat prevalent at the cape that projects into the sea) is a city and semi-governorate in the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia located on a peninsula extending into the Persian Gulf, Even though the closest governorate is Qatif and geographically it can be considered part of Qatif, the city is de facto under the administration of the Jubail governorate, The name Ras Tanura applies both to a Gated community, gated Saudi Aramco employee compound (also referred to as "Najmah") and to an industrial area further out on the peninsula that serves as a major Petroleum, oil port and oil operations center for Aramco, the largest oil company in the world. Today, the compound has about 3,200 residents, with a few Americans and British expats. Geographically, the Ras Tanura complex is located south of the modern industrial port city of Jubail and north across Tarout Bay from the old port city of Dammam. Although Ras T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has a history of use in West Asia, East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the modern era, when used as a formal monarchical title, it is roughly synonymous with "prince", applicable both to a son of a hereditary monarch, and to a reigning monarch of a sovereign principality, namely an emirate. The female, feminine form is emira ( '), with the same meaning as "princess". Prior to its use as a monarchical title, the term "emir" was historically used to denote a "commander", "general", or "leader" (for example, Amir al-Mu'min). In contemporary usage, "emir" is also sometimes used as either an honorary or formal title for the head of an Islamic, or Arab (regardless of relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Ain Region
The Eastern Region (), officially known as Al Ain Region (), is one of three Municipal Regions in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. It forms the southeastern part of the United Arab Emirates. Its main settlement is the eponymous city of Al Ain, located on the country's border with Oman, about from the city of Abu Dhabi, the capital of the Emirate and country. Compared to the Western Region, it is also a rather remote region of the Emirate, but smaller by area, and is not known to hold reserves of gas or petroleum, but is agriculturally important. History and prehistory The city of Al-Ain, part of a historical region which also includes the adjacent Omani town of Al-Buraimi, is noted for its forts, oases, '' aflāj'' (underground water channels), and archaeological sites such as those of Hili and Rumailah. Sites outside the city include Jebel Hafeet and Al-A'ankah Fort. Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan had been the Ruler's Representative in this region, before becoming the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Buraimi Governorate
Al Buraimi Governorate () is one of the 11 governorates of Oman. The area was part of Ad Dhahirah Region until October 2006, when a new governorate was created from the wilayats (provinces) of Al Buraymi and Mahdah. A third wilayat, As- Sunaynah, was created from parts of the two. Dr. Hamad bin Ahmed Al Busaidi has been governor since 2020. The town of Al-Buraimi is an oasis town in northwestern Oman, on the border of the United Arab Emirates. Al Ain is an adjacent city on the UAE side of the border. Both settlements are part of the historical region of Tawam or Al-Buraimi Oasis. For many decades, there had been an open border between Al-Buraimi located in Oman and Al-Ain. In September 2006, this border was relocated to an area near Hilli which is around from the traditional open border. The traditional border near Al-Ain City is now closed to all except to those with valid visas ( GCC nationals require no visa). Climate Al Buraimi has a hot desert climate (Köppen clim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Ain
Al Ain () is a city in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, and the seat of the administrative division of the Al Ain Region. The city is Oman–United Arab Emirates border, bordered to the east by the Omani town of Al-Buraimi. Al Ain is the largest inland city in the Emirates, the List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, fourth-largest city (after Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah), and the second-largest in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. The Controlled-access highway, freeways connecting Al Ain, Abu Dhabi, and Dubai form a geographic triangle in the country, each city being roughly from the others. Climate and geography Al Ain is known as the "Garden City" () of Abu Dhabi, the UAE or the Persian Gulf, Gulf, due to its greenery, particularly with regard to the city's oases, parks, tree-lined avenues and decorative roundabouts, with strict height controls on new buildings, to no more than seven floors. According to one author, the oases around Al Ain and Al-Ahsa Oasis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Abu Dhabi
The Emirate of Abu Dhabi is one of seven Emirates of the United Arab Emirates, emirates that constitute the United Arab Emirates. It is the largest emirate, accounting for 87% of the nation's total land area or . Abu Dhabi also has the second-largest population of the seven emirates. In mid-2016, the emirate had a population of 2,908,000, with 551,500 being Emirati citizens, accounting for around 19% of the population. In 2023, the emirate's population had grown to 3,789,860. The city of Abu Dhabi, after which the emirate is named, is the capital of both the emirate and the federation. In the early 1970s, two important developments influenced the status of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. The first was the establishment of the United Arab Emirates in December 1971, with Abu Dhabi as its initially temporary political and administrative capital. The second was the sharp increase in oil prices following the Yom Kippur War, which accompanied a change in the relationship between the oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Dhafra, Abu Dhabi
Al Dhafra Region (), known until 2017 as Al Gharbia or the Western Region (), is one of three Municipal Regions in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. Forming the western part of the United Arab Emirates, it is by far the largest region by area, occupying 71 % of the Abu Dhabi emirate's total area, yet the smallest by population and population density, and thus a rather remote region of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, similar to the Eastern Region. The capital of Al Dhafra Region is Madinat Zayed (Bida Zayed). The new official name was already the historical name of the westernmost region of former Trucial Oman, which was ''Dhafrah''. It is significant for its natural resources, particularly gas and petroleum. Its reserves of hydrocarbons account for 90% of the Emirate's reserves, which in turn account for 90% of the country's reserves, and are important for the local economy. Demographics The Region had a population of 202,154 as of the Census of 2010 (including Islands Region with 17,64 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Aramco
Saudi Aramco ( ') or Aramco (formerly Arabian-American Oil Company), officially the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, is a majority state-owned petroleum and natural gas company that is the national oil company of Saudi Arabia. , it is the fourth- largest company in the world by revenue and is headquartered in Dhahran. Saudi Aramco has both the world's second-largest proven crude oil reserves, at more than , and largest daily oil production of all oil-producing companies. Saudi Aramco operates the world's largest single hydrocarbon network, the Master Gas System. In 2024, its oil production total was 12.7 million barrels of oil equivalent per day, and it manages over one hundred oil and gas fields in Saudi Arabia, including 288.4 trillion standard cubic feet (scf) of natural gas reserves. Along the Eastern Province, Saudi Aramco most notably operates the Ghawar Field (the world's largest onshore oil field) and the Safaniya Field (the world's largest offshore oil field). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted as 1876, although a few sources give it as 1880. According to British author Robert Lacey's book ''The Kingdom'', a leading Saudi historian found records that show Ibn Saud in 1891 greeting an important tribal delegation. The historian reasoned that a 10 or 11-year-old child (as given by the 1880 birth date) would have been too young to be allowed to greet such a delegation, while an adolescent of 15 or 16 (as given by the 1876 date) would likely have been allowed. When Lacey interviewed one of Ibn Saud's sons prior to writing the book, the son recalled that his father often laughed at records showing his birth date to be 1880. Ibn Saud's response to such records was reportedly that "I swallowed four years of my life." p. 561" – 9 November 1953), known in the Western world as Ibn Saud (; ''Ibn Suʿūd''),''Ibn Saud'', meaning "son of Saud" (see Arabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |