|
Santosh Gupta (journalist)
Santosh Gupta (9 January 1925 – 6 August 2004) was a Bangladeshi journalist and writer. He was awarded Ekushey Padak in 1997 and Independence Day Award in 2015 by the Government of Bangladesh. He wrote sometimes under the pen name ''Aniruddha''. Career Gupta started his career as journalist in 1957. Later he served as the senior assistant editor of The Sangbad. He wrote 18 books and edited some 30 books. Awards * Ekushey Padak * Independence Day Award The Independence Award (), formally known as the Independence Day Award or Swadhinata Padak (), is the highest state award given by the government of Bangladesh. Introduced in 1977 by President Ziaur Rahman, this award is bestowed upon Banglade ... * Sher-e-Bangla Padak * Maulana Tarkabagish Padak * Jahur Hossain Memorial Padak References Further reading * 4 {{DEFAULTSORT:Gupta, Santosh Recipients of the Ekushey Padak Bangladeshi Hindus Bengali Hindus Recipients of the Independence Award 1925 births 2004 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhalokati District
Jhalokathi District officially Jhalakathi District, () is a district in southern Bangladesh. It is located in the Barisal Division and covers an area of 758.06 km2. It is bounded by Barisal district to the north, Barguna district to the east and the Bishkhali river in the south, and Pirojpur district to the west. The main rivers in this district are the Bishkhali, Dhanshiri, Gabkhan, Sugandha, Jangalia, Bamanda and Bajitpur. "''পেয়ারা আর শীতলপাটি, এই নিয়ে ঝালকাঠি"'' "''(Jhalokathi, The land of tasty Guava and Shitolpati)"'' is the official motto of the district. History Jhalokati subdivision was established in 1972, shortly after the Liberation of Bangladesh. It was turned into a district in 1984. The 2021 Bangladesh ferry fire occurred on the Sugandha River near the town. Subdivisions The district is administratively subdivided into 4 upazilas, these are: # Jhalokati Sadar Upazila # Kathalia Upazila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal until 1937, later the Bengal Province, was the largest of all three presidencies of British India during Company rule in India, Company rule and later a Provinces of India, Province of British India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the West Bengal, Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, India, Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the governor of Bengal was concurrently the governor-general of India and Calcutta was the capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in the Bengal Subah, Bengal province during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (EIC), a British Indian monopoly with a royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757, the East India Company set up "factories" (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century three ''Presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India, 1757–1858, the Company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "Presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government oversight, in effect sharing sovereig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekushey Padak
Ekushey Padak () is the second highest civilian award in Bangladesh, introduced in memory of martyrs of the Bengali language movement of 1952. The award is given to recognize contributions in a number of fields, including culture, education, and economics. The Ministry of Cultural Affairs administers the award. The award consists of an 18-carat gold medal weighing 3 Tola (unit), tolas, a certificate of honour and a cash award. The medal was designed by the artist Nitun Kundu. The amount of the cash reward was originally ৳ 25,000, but it was increased to ৳ 100,000 in 2015, to ৳ 200,000 in 2017 and to ৳ 400,000 as of November 2019. Etymology The name ''Ekushey'' is important to Bengali nationalism, referring to 21 February 1952, commemorated as Language Movement Day and International Mother Language Day, when students campaigning for official status of the Bengali language within Pakistan were killed by law enforcement. Method of giving In the case of Ekushey Padak, followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence Day Award
The Independence Award (), formally known as the Independence Day Award or Swadhinata Padak (), is the highest state award given by the government of Bangladesh. Introduced in 1977 by President Ziaur Rahman, this award is bestowed upon Bangladeshi citizens or organizations in recognition of substantial contributions to one of many fields, including the War of Liberation, the Language Movement, education, literature, journalism, public service, science and technology, medical science, social science, song, games and sports, fine arts, rural development, and other areas. Each awardee receives a gold medal, a certificate of honour, and 500,000 Bangladeshi takas (US$4109). A cabinet committee on national awards prepares the list of each year's nominees and forwards the list to the head of the government for final approval. The award is traditionally presented on the eve of Independence Day An independence day is an annual event memorialization, commemorating the anniversary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Daily Star (Bangladesh)
''The Daily Star'' is a Bangladeshi English-language daily newspaper. It is by far the largest circulating English-language newspaper in the country. Founded by Syed Mohammed Ali on 14 January 1991, as Bangladesh transitioned and restored parliamentary democracy, the newspaper became popular for its outspoken coverage of politics, corruption, and foreign policy. It is considered a newspaper of record for Bangladesh. The newspaper has been described as having a "reputation for journalistic integrity and liberal and progressive views - a kind of Bangladeshi ''New York Times''". Mahfuz Anam serves as the editor and publisher of ''The Daily Star.'' ''The Daily Star'' is owned by Mediaworld, in which a major share is held by the Transcom Group. ''Star Business,'' the business edition of the paper, is highly popular. The newspaper serves its Bengali readership digitally through its website. History In the late 1980s, plans for a major English newspaper in Bangladesh were drawn up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pen Name
A pen name or nom-de-plume is a pseudonym (or, in some cases, a variant form of a real name) adopted by an author and printed on the title page or by-line of their works in place of their real name. A pen name may be used to make the author's name more distinctive, to disguise the author's gender, to distance the author from their other works, to protect the author from retribution for their writings, to merge multiple persons into a single identifiable author, or for any of several reasons related to the marketing or aesthetic presentation of the work. The author's real identity may be known only to the publisher or may become common knowledge. In some cases, such as those of Elena Ferrante and Torsten Krol, a pen name may preserve an author's long-term anonymity. Etymology ''Pen name'' is formed by joining pen with name. Its earliest use in English is in the 1860s, in the writings of Bayard Taylor. The French-language phrase is used as a synonym for "pen name" ( means 'pen') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Sangbad
''The Sangbad'' () is a Bengali-language daily newspaper, founded in 1951 and published from Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is the oldest newspaper in Bangladesh. History The Sangbad was founded in 1951 and published from Dhaka, Bangladesh. Its first owner was Nasiruddin Ahmad and its first editor was Khairul Kabir. During the 1950s and 1960s, the newspaper expressed strong views opposed to the Ayub Khan government of Pakistan, and was accordingly repressed. Its offices and printing pressed were burned during the crackdown in March 1971, and it remained closed during the entire Bangladesh Liberation War The Bangladesh Liberation War (, ), also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, was an War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which res .... On 31 October 2017, a journalist of the Sangbad was arrested under the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Act. He had sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
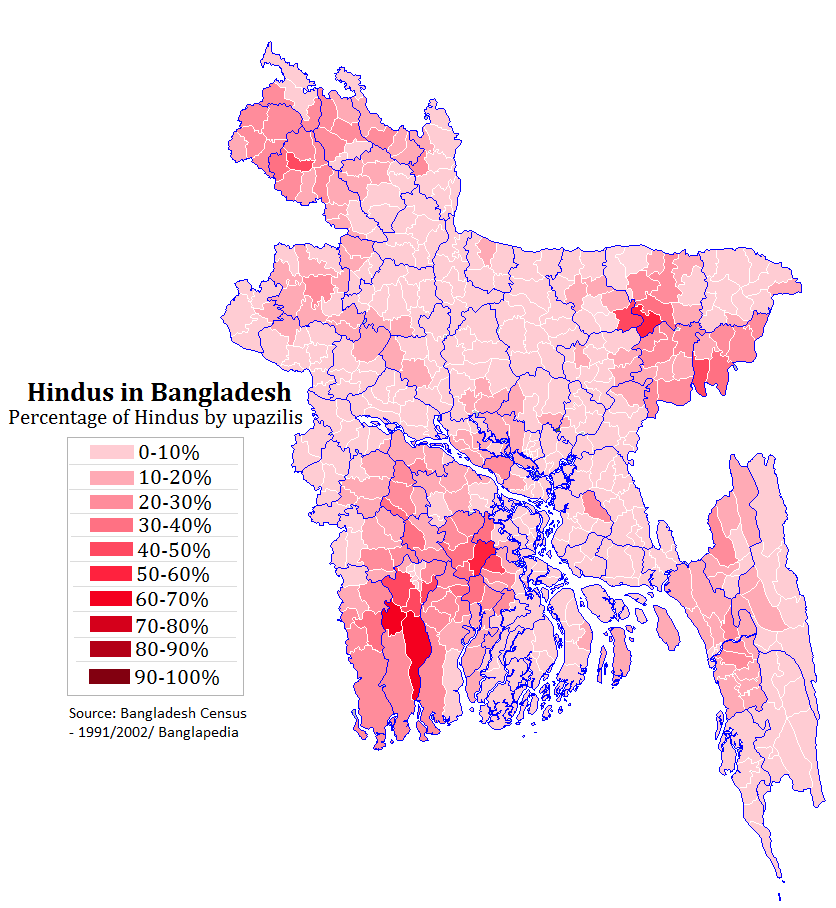
Bangladeshi Hindus
Hinduism is the second largest religion in Bangladesh, as according to the 2022 Census of Bangladesh, approximately 13.1 million people responded as Hindus, constituting 7.95% of the nation. Bangladesh is the third-largest Hindu populated country in the world, after India and Nepal. Hinduism is the second-largest religion in 61 of 64 districts in Bangladesh, but there are no Hindu majority districts in Bangladesh. Demographics According to the 2001 Bangladesh census, there were around 11.82 million Hindus in Bangladesh constituting 9.6% of the population, which at the time was 123.15 million. The Bangladesh 2011 census states, that approximately 12.73 million people responded that they were Hindus, constituting 8.54% of the total 149.77 million. While 2022 Census of Bangladesh, put the number of Hindus in Bangladesh at 13.1 million out of total 165.1 million population, thus constituting 7.95% of the population. According to a report published by a local daily newspa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Hindus
Bengali Hindus () are adherents of Hinduism who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. They make up the majority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Assam's Barak Valley region and make up the largest minority in Bangladesh. Comprising about one-third of the global Bengali population, they are the largest ethnic group among Hindus. Bengali Hindus speak Bengali, which belongs to the Indo-Aryan language family and adhere to Shaktism (majority, the Kalikula tradition) or Vaishnavism (minority, Gaudiya Vaishnavism and Vaishnava-Sahajiya) of their native religion Hinduism with some regional deities. There are significant numbers of Bengali-speaking Hindus in different Indian states. Around the 8th century, the Bengali language branched off from Magadhi Prakrit, a derivative of Sanskrit that was prevalent in the eastern region of the Indian Subcontinent at that time. During the Sena period (11th – 12t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |