|
Salisbury Plain Training Area
The Salisbury Plain Training Area is a large expanse of land on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, which is managed by the Defence Infrastructure Organisation on behalf of the Ministry of Defence. History The British Army's Salisbury Plain Training Area covers roughly half of the plain (and makes up about 11% of Wiltshire). The army first conducted exercises on the plain in 1898. From that time, the Ministry of Defence bought up large areas of land until the Second World War. The MoD now own of land, making it the largest military training area in the United Kingdom. Much of this land is let to farmers or grazed under licence, while around (12,000 ha) are used for live firing, where public access is greatly restricted or permanently closed. The land and facilities are managed by the MoD's Defence Infrastructure Organisation. The largest camps and barracks in or near the training area are at Larkhill, Bulford, Tidworth, Trenchard Lines (Upavon) and Waterloo Lines (War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in southern England covering . It is part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England formed by the rocks of the Chalk Group and largely lies within the county of Wiltshire, but stretches into Hampshire. The plain is famous for its rich archaeology, including Stonehenge, one of England's best known landmarks. Large areas are given over to military training; thus, the sparsely populated plain is the biggest remaining area of calcareous grassland in northwest Europe. Additionally, the plain has arable land, and a few small areas of beech trees and coniferous woodland. Its highest point is Easton Hill. A large amount of land is set aside for military use as Salisbury Plain Training Area. Physical geography The boundaries of Salisbury Plain have never been truly defined, and there is some difference of opinion as to its exact area. The river valleys surrounding it, and other downland, downs and plains beyond them loo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amesbury And Military Camp Light Railway
The Amesbury and Military Camp Light Railway (also known as the Bulford Camp Railway) was a branch line in Wiltshire, England, constructed under a light railway order, the Amesbury and Military Camp Light Railway Order 1898, dated 24 September 1898. It was opened for military traffic from Amesbury to the east-facing Newton Tony Junction (on the London and South Western Railway main line from Andover to Salisbury, part of the West of England line) on 1 October 1901. A west-facing junction, Amesbury Junction, where the branch burrowed under the main line, opened on 2 June 1902. The line closed in 1963. Previous proposals Although the line did not open until the early 1900s, various other proposals had been put forward, but none had succeeded in being built. Before the Bulford Camp branch opened, all nearby railway routes had skirted Salisbury Plain, but none led through it.Harding, Peter. ''The Bulford Branch Line''. Binfield Printers, 1991, pp.4-5 Bristol and London & South Wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Wiltshire
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BFBS
The British Forces Broadcasting Service (BFBS) provides radio and television programmes for His Majesty's Armed Forces, and their dependents worldwide. Editorial control is independent of the Ministry of Defence and the armed forces themselves. It was established by the British War Office (now the Ministry of Defence) in 1943. In 1944, it was managed by Gale Pedrick. History Originally known as the Forces Broadcasting Service (FBS), it was initially under the control of the British Army Welfare Service, its first effort, the Middle East Broadcasting Unit, being headquartered in Cairo. Before and after the end of the Second World War various radio stations were set up, some using the FBS name, others using the name British Forces Network (BFN), but by the early 1960s these had all adopted the BFBS name. From 1982 until 2020, BFBS formed part of the Services Sound and Vision Corporation (SSVC), a registered charity which is also responsible for the British Defence Film L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westland WAH-64 Apache
The AgustaWestland Apache is a Licensed production, licence-built version of the Boeing AH-64 Apache, Boeing AH-64D Apache Longbow attack helicopter for the British Army Army Air Corps (United Kingdom), Air Corps. The first eight helicopters were built by Boeing Integrated Defense Systems, Boeing; the remaining 59 were assembled by Westland Helicopters (later AgustaWestland) at Yeovil, Somerset in England from Boeing-supplied kits. Changes from the AH-64D include Rolls-Royce Turbomeca Rolls-Royce Turbomeca RTM322, RTM322 engines, a new electronic defensive aids suite and a folding blade mechanism allowing the British version to operate from ships. The helicopter was initially designated WAH-64 by Westland Helicopters and was later British military aircraft designation systems, given the designation Apache AH Mk 1 (also written as "Apache AH1") by the Ministry of Defence (UK), Ministry of Defence. The Apache was a valued form of close air support in the conflict in Afghanistan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Air Corps Middle Wallop
Middle Wallop Flying Station is a British Army airfield located near the Hampshire village of Middle Wallop. It is the Headquarters for the Army Air Corps, and the 1st Aviation Brigade Combat Team, and is also used for Army Air Corps training. The base hosts 2 (Training) Regiment AAC and 7 (Training) Regiment AAC under the umbrella of the Army Aviation Centre. 2 Regiment performs ground training; 7 Regiment trains aircrew on AAC aircraft after they complete basic training at RAF Shawbury. The base is notable for having previously served as both a Royal Navy (as HMS ''Flycatcher'') and a Royal Air Force (as RAF Middle Wallop) controlled airfield, as well as an Army one initially as Middle Wallop Airfield. History Early use The base was opened as RAF Middle Wallop, a training school for new pilots in 1940. It was originally intended for bomber use; however, with the Battle of Britain being fought, No. 609 Squadron RAF, flying the Supermarine Spitfire Ia, and No. 238 Sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boscombe Down
MOD Boscombe Down ' is the home of a military aircraft testing site, on the south-eastern outskirts of the town of Amesbury, Wiltshire, England. The site is managed by QinetiQ, the private defence company created as part of the breakup of the Defence Evaluation and Research Agency (DERA) in 2001 by the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD). The base was originally conceived, constructed, and operated as Royal Air Force Boscombe Down, more commonly known as RAF Boscombe Down, and since 1939, has evaluated aircraft for use by the British Armed Forces. The airfield has one active runway in length. The airfield's evaluation centre is currently home to Rotary Wing Test and Evaluation Squadron (RWTS), Fast Jet Test Squadron (FJTS), Heavy Aircraft Test Squadron (HATS), Handling Squadron, and the Empire Test Pilots' School (ETPS). It will be home to an anti-jamming test facility by 2026. History First World War An aerodrome opened at the Boscombe Down site in October 1917 and operated as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porton Down
Porton Down is a science and defence technology campus in Wiltshire, England, just north-east of the village of Porton, near Salisbury. It is home to two British government facilities: a site of the Ministry of Defence's Defence Science and Technology Laboratory – known for over 100 years as one of the UK's most secretive and controversial military research facilities, occupying – and a site of the UK Health Security Agency. Since 2018, part of the campus has housed Porton Science Park, which is owned and operated by Wiltshire Council and has private sector companies in the health, life science and defence and security sectors. Location Porton Down is just north-east of the village of Porton, near Salisbury, in Wiltshire, England. To the north-west lies the MoD Boscombe Down airfield operated by Qinetiq. On some maps, the land surrounding the complex is identified as a "Danger Area". History of government use Porton Down opened in 1916 as the War Department Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defence Science And Technology Laboratory
The Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl) is an executive agency of the Ministry of Defence of the United Kingdom. Its stated purpose is "to maximise the impact of science and technology for the defence and security of the UK". The agency is headed by Paul Hollinshead as its chief executive, with the board being chaired by Adrian Belton. Ministerial responsibility lies with the Minister of State for Defence Procurement and Industry. History Dstl was formed from the July 2001 split of the Defence Evaluation and Research Agency (DERA). Dstl was established to carry out and retain the science and technology work that is best done within government, while work that could be done by industry (forming the majority of DERA's activities) was transferred to Qinetiq, a government-owned company that was later floated on the stock exchange. Dstl absorbed the Home Office's Centre for Applied Science and Technology (CAST) in April 2018, taking on CAST's role to apply science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keevil Airfield
Royal Air Force Keevil or more simply RAF Keevil is a former Royal Air Force station, now controlled by the Army Air Corps. It lies between the villages of Keevil and Steeple Ashton, about east of the town of Trowbridge, in Wiltshire, England. The airfield was built on a site previously earmarked for the purpose in the mid-1930s. With three long concrete runways, the airfield was used by the Royal Air Force and the United States Army Air Forces Eighth and Ninth Air Forces. Although no longer a RAF station and now known as Keevil Airfield, it is maintained for military use and used for training purposes, predominantly by aircraft from RAF Brize Norton and Joint Aviation Command. History Spitfire assembly After air raids in 1940 on the Supermarine Spitfire production plants near Southampton, the Trowbridge area was one of several chosen for dispersal of production. At first parts were made, and later complete aircraft after completion of a purpose-built factory at Bradl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day (military term), D-Day) with the Normandy landings (Operation Neptune). A 1,200-plane Airborne forces, airborne assault preceded an amphibious warfare, amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake cross-channel landings in 1944 was made at the Washington Conference (1943), Trident Conference in Washington, D.C., Washington in May 1943. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and British General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
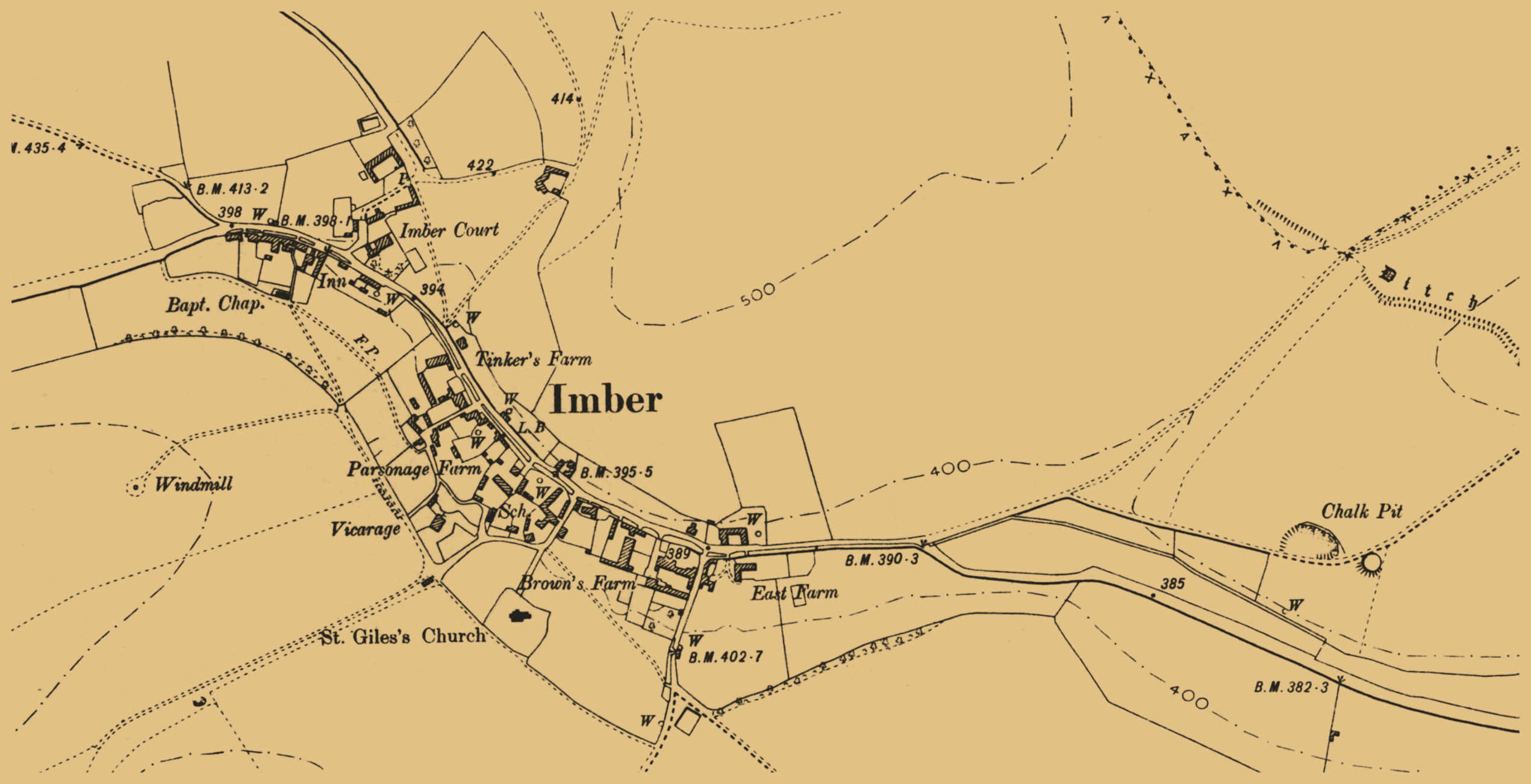
Imber
Imber is an uninhabited village and former civil parish within the British Army's Salisbury Plain Training Area, training area, now in the parish of Heytesbury, on Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England. It lies in an isolated area of the Plain, about west of the A360 road between Tilshead and West Lavington, Wiltshire, West Lavington. A linear village, its main street follows the course of a stream. Recorded in the ''Domesday Book'' of 1086, Imber was always an isolated community, several miles from any market town, and most of its men worked in agriculture or related trades. Beginning in the 1890s, the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence slowly bought up the village and in 1943 the whole population of about 150 was evicted to provide an exercise area for American troops preparing for the invasion of Europe during the Second World War. After the war, the villagers were not allowed to return to their homes. It remains under the control of the Ministry of Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |