|
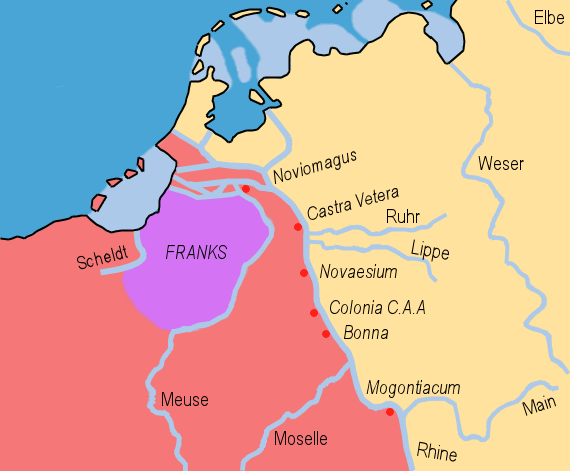
Salic Code
The Salic law ( or ; ), also called the was the ancient Frankish civil law code compiled around AD 500 by Clovis, the first Frankish King. The name may refer to the Salii, or " Salian Franks", but this is debated. The written text is in Late Latin, and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Dutch. It remained the basis of Frankish law throughout the early Medieval period, and influenced future European legal systems. The best-known tenet of the old law is the principle of exclusion of women from inheritance of thrones, fiefs, and other property. The Salic laws were arbitrated by a committee appointed and empowered by the King of the Franks. Dozens of manuscripts dating from the sixth to eighth centuries and three emendations as late as the ninth century have survived. Salic law provided written codification of both civil law, such as the statutes governing inheritance, and criminal law, such as the punishment for murder. Although it was originally intended as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childebert III
Childebert III (or IV), called the Just () ( 678/679 – 23 April 711), was the son of Theuderic III and Chrothildis (or Doda) and sole king of the Franks (694–71 He was seemingly but a puppet of the mayor of the palace, Pepin of Heristal, though his '' placita'' show him making judicial decisions of his own will, even against the Arnulfing clan. His nickname has no comprehensible justification except possibly as a result of these judgements, but the '' Liber Historiae Francorum'' calls him a "famous man" and "the glorious lord of good memory, Childebert, the just king."''Monumenta Germaniae Historica, Scriptorum rerum Merovingicarum'' vol. II, pp. 323–324 He had a son named Dagobert, who succeeded him, as Dagobert III but his wife was not Edonne, the invention of later fantasists. It is possible, though not likely, that Chlothar IV was also his son. He spent almost his entire life in a royal villa on the Oise. In 708, during his reign of sixteen years, the bishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consisted of two sovereign states with a single monarch who was titled both the Emperor of Austria and the King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War, following wars of independence by Hungary in opposition to Habsburg rule. It was dissolved shortly after Dissolution of Austria-Hungary#Dissolution, Hungary terminated the union with Austria in 1918 at the end of World War 1. One of Europe's major powers, Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe (after Russian Empire, Russia) and the third-most populous (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Foederatus
Frankish may refer to: * Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture ** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties * Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany * East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany * West Francia, the successor state to Francia in France * Crusaders * Levantines (Latin Christians) Family name * Ernest Frankish (1876–1962), New Zealand cricketer * Keith Frankish (born 1962), British philosopher * Kevin Frankish, Canadian television presenter and media personality * Pat Frankish, British psychologist and psychotherapist * Ronald Frankish (1925–2013), Australian cricketer * Stanley Frankish (1872–1909), New Zealand cricketer See also * Farang, Persian for 'Franks', later used for Western or Latin Europeans; in Arabic 'Faranj' * Franconian (other) * Franks (other) * Name of the Franks * Franks * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salic Law
The Salic law ( or ; ), also called the was the ancient Frankish Civil law (legal system), civil law code compiled around AD 500 by Clovis I, Clovis, the first Frankish King. The name may refer to the Salii, or "Salian Franks", but this is debated. The written text is in Late Latin, and contains some of the earliest known instances of Old Dutch. It remained the basis of Frankish law throughout the early Medieval period, and influenced future History of Western law, European legal systems. The best-known tenet of the old law is the principle of exclusion of women from inheritance of thrones, fiefs, and other property. The Salic laws were arbitrated by a committee appointed and empowered by the King of the Franks. Dozens of manuscripts dating from the sixth to eighth centuries and three emendations as late as the ninth century have survived. Salic law provided written codification of both civil law, such as the statutes governing inheritance, and criminal law, such as the punishme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (Holy Roman Empire)
The Kingdom of Italy ( or ; ; ), also called Imperial Italy (; ), was one of the constituent kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire, along with the kingdoms of Germany, Bohemia, and Burgundy. It originally comprised large parts of northern and central Italy. Its original capital was Pavia until the 11th century. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and the brief rule of Odoacer, Italy was ruled by the Ostrogoths and later the Lombards. In 773, Charlemagne, the king of the Franks, crossed the Alps and invaded the Lombard kingdom, which encompassed all of Italy except the Duchy of Rome, the Republic of Venice and the Byzantine possessions in the south. In June 774, the kingdom collapsed and the Franks became masters of northern Italy. The southern areas remained under Lombard control, as the Duchy of Benevento was changed into the independent Principality of Benevento. Charlemagne called himself king of the Lombards and in 800 was crowned emperor in Rome. Membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from the High Middle Ages to 1848 during its dissolution. It was also an early French colonial empire, colonial power, with colonies in Asia and Africa, and the largest being New France in North America geographically centred around the Great Lakes. The Kingdom of France was descended directly from the West Francia, western Frankish realm of the Carolingian Empire, which was ceded to Charles the Bald with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ('king of the Franks') well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ('King of France') was Philip II of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatic Succession
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritance of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male kin. This is sometimes distinguished from cognate kinship, through the mother's lineage, also called the spindle side or the distaff side. A patriline ("father line") is a person's father, and additional ancestors, as traced only through males. In the Bible In the Bible, family and tribal membership appears to be transmitted through the father. For example, a person is considered to be a priest or Levite, if his father is a priest or Levite, and the members of all the Twelve Tribes are called Israelites because their father is Israel (Jacob). In the first lines of the New Testament, the descent of Jesus Christ is counted through the male lineage from Abraham through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France, Wallachia, southern Romania, Spain, Turkey, and Vatican City. Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them with very different types of climates (mainly subtropics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon (, ) ;, ; ; . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona (later Principality of Catalonia) and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Iberian Peninsula, parts of what is now Northern Catalonia, southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy (from 1442), and parts of Greece (until 1388). The component realms of the Crown were not united politically except at the level of the king, who ruled over each autonomous polity according to its own laws, raising funds under each tax structure, dealing separately with each ''Corts'' or ''Cortes'', particularly in the Kingdom of Aragon, the Principality of Catalonia, and the Kingdom of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historic States Of Italy
Italy, up until its unification in 1861, was a conglomeration of city-states, republics, and other independent entities. The following is a list of the various Italian states during that period. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the arrival of the Middle Ages (in particular from the 11th century), the Italian Peninsula was divided into numerous states. Many of these states consolidated into major political units that balanced the power on the Italian Peninsula: the Papal States, the Venetian Republic, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Milan, the Kingdom of Naples and the Kingdom of Sicily. Unlike all the other Italian states of the medieval and early modern period, the republics of Venice and Genoa, thanks to their maritime power, went beyond territorial conquests within the Italian Peninsula, conquering various regions across the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Ancient Italy The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as Italic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of the region, due to political, economic, historical, cultural, and geographical considerations. Sovereign state, Sovereign states and territories that may be included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (alternatively placed in Central Europe), Greece (alternatively placed in the broader region of Southern Europe), Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania (alternatively placed in Eastern Europe), Serbia, and the East Thrace, European part of Turkey (alternatively placed in the broader region of Southern Europe, also in West Asia, Western Asia with the rest of the country). Sometimes, Cyprus (most often placed in West Asia), Hungary (most often placed in Central Europe), Moldova (most often placed in Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of southeastern Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In the 19th century the term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia, the parts of Europe that were provinces of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |