|
Salassi
The Salassi or Salasses were a Gallic or Ligurian tribe dwelling in the upper valley of the Dora Baltea river, near present-day Aosta, Aosta Valley, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''dià Salassō̃n'' (διὰ Σαλασσῶν) by Polybius (2nd c. BC) and Strabo (early 1st c. AD), as ''Salassi'' by Livy (late 1st c. BC), as ''Salassos'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), as ''Salasíon'' (Σαλασίον) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), as ''Salassoí'' (Σαλασσοί) by Appian (2nd c. AD)., s.v. ''Salassi''. The origin of the ethnic name ''Salassi'' remains unclear. If Celtic, it may derive from the root ''sal''-, with various possible explanations regarding the word-formation. According to Cato the Elder and Strabo, the Salassi were a Ligurian tribe. Geography The Salassi lived in the upper valley of the Dora Baltea river, where they controlled the Great and Little St Bernard passes in the Alps, collecting road tolls, and gold and iron mines. Thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aosta
Aosta ( , , ; ; , or ; or ) is the principal city of the Aosta Valley, a bilingual Regions of Italy, region in the Italy, Italian Alps, north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel and the Great St Bernard Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Dora Baltea, and at the junction of the Great St Bernard Pass, Great and Little St Bernard Pass routes. History Aosta was settled in proto-historic times and later became a centre of the Salassi, many of whom were killed or sold into slavery by the Ancient Rome, Romans in 25 BC. The campaign was led by Aulus Terentius Varro Murena, Terentius Varro, who then founded the Ancient Rome, Roman colony of ''Augusta Praetoria Salassorum'', housing 3,000 retired veterans. After 11 BC Aosta became the capital of the Alpes Poeninae, Alpes Graies province of the Roman Empire, Empire. Its position at the confluence of two rivers, at the end of the Great St Bernard Pass, Great and the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy (Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and Gallic invasion of the Balkans, into the Balkans, leading to Battle of Thermopylae (279 BC), war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veragri
The Veragrī (Gaulish: *''Ueragroi'', 'super-warriors'; Greek: ) were a Gallic tribe dwelling around present-day Martigny, in the Pennine Alps, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Along with the Nantuates, Seduni and Uberi, they were part of the Vallenses, a group of tribes living between Lake Geneva and the Pennine Alps, in the modern Canton of Valais (Switzerland). Name They are mentioned as ''Veragros'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''uer agri'' by Livy (late 1st c. BC), ''Ou̓áragroi'' (Οὐάραγροι) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Varagri'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), Pliny. ''Naturalis Historia''3:20 ''Ouarágrous'' (Οὐαράγρους) by Cassius Dio (3rd c. AD), and as ''Veragros'' (var. ''beragros'', ''ueragres'') by Orosius (early 5th c. AD)., s.v. ''Veragri'' and ''Octodurus''. The ethnonym ''Veragrī'' is a Latinized form of Gaulish ''Ueragroi'' (sing. ''Ueragros''). It has been translated as 'super-warriors'. It stems from the Celtic root *''uer(o) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acitavones
The Acitavones were a small Gallic tribe dwelling in the Alps during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Acitavones'' (var. ''agitabo''-) by Pliny (1st c. AD), Pliny. ''Naturalis Historia''3:20 and as ''Acitavones'' on the Tropaeum Alpium., s.v. ''Acitavones''. The etymology of the name ''Acitauones'' is unclear. The first element, ''acito''-, could mean 'field' (cf. Old Irish ''ached'', ''achad'')'','' or else be a variant of ''agido''- ('face, appearance'). Geography According to historian Guy Barruol, they may have dwelled in the Aosta Valley, near the Little St Bernard Pass. Their territory was located north of the Medulli and Segusini, south of the Veragri, west of the Salassi, and east of the Ceutrones., Map 17: Lugdunum Lugdunum (also spelled Lugudunum, ; modern Lyon, France) was an important Colonia (Roman), Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon, France, Lyon. The Roman city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great St Bernard Pass
The Great St Bernard Pass (, , ; ) is the third highest road pass in Switzerland, at an elevation of . It connects Martigny in the canton of Valais in Switzerland with Aosta in the region Aosta Valley in Italy. It is the lowest pass lying on the ridge between the two highest mountains of the Alps, Mont Blanc and Monte Rosa. It is located on the main watershed that separates the basin of the Rhône from that of the Po. Great St Bernard is one of the most ancient passes through the Western Alps, with evidence of use as far back as the Bronze Age and surviving traces of a Roman road. In 1800, Napoleon's army used the pass to enter Italy, an event depicted in Jacques-Louis David's '' Napoleon at the Saint-Bernard Pass'' and Paul Delaroche's '' Bonaparte Crossing the Alps'', both notable oil paintings. Having been bypassed by easier and more practical routes, particularly the Great St Bernard Tunnel, a road tunnel which opened in 1964, its value today is mainly historical and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Antistius Vetus (consul 30 BC)
Gaius Antistius Vetus was a Roman politician and general who was consul suffectus in 30 BC as the colleague of Augustus, succeeding Marcus Licinius Crassus. Biography Vetus was a descendant of the Plebeian Roman house of the Antistii Veteres. He was probably the son of Gaius Antistius Vetus, praetor in 70, and governor in 69 BC in Hispania Ulterior, under whom Julius Caesar served as quaestor. Initially a supporter of Caesar, Vetus was appointed ''Quaestor pro praetore'' of Syria by Caesar, a position which he held in 45 BC. He was forced to fight against Quintus Caecilius Bassus, the former governor and an opponent of Caesar, who refused to relinquish his post. Vetus besieged him until the Parthians came to relieve Bassus; during this time Vetus was hailed as ''imperator''. On his way back to Rome in 44 BC, he was intercepted by Brutus, one of Caesar's leading assassins, who persuaded him not only to hand over the province's revenues which he was taking to Rome, but also to j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
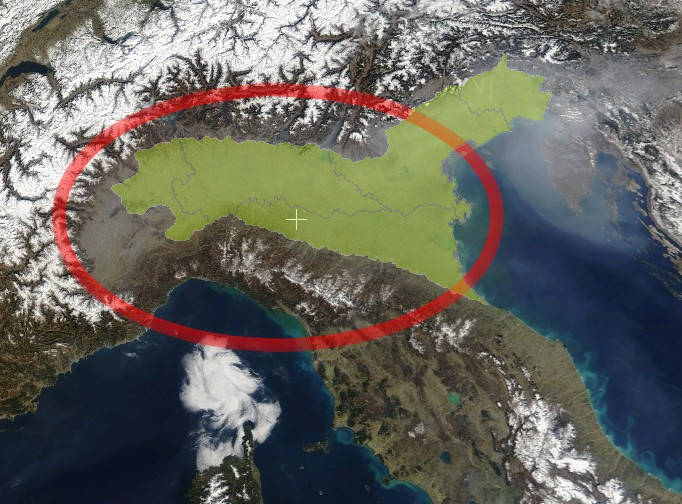
Aosta Valley
The Aosta Valley ( ; ; ; or ), officially the Autonomous Region of Aosta Valley, is a mountainous Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region in northwestern Italy. It is bordered by Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France, to the west; by Valais, Switzerland, to the north; and by Piedmont, Italy, to the south and east. The regional capital is Aosta. Covering an area of and with 122,714 inhabitants as of 2025, it is the smallest, least populous, and least densely populated region of Italy. The province of Aosta having been dissolved in 1945, the Aosta Valley region was the first region of Italy to abolish provincial subdivisions, followed by Friuli-Venezia Giulia in 2017 (where they were reestablished later). Provincial administrative functions are provided by the regional government. The region is divided into 74 (). Italian language, Italian and Aostan French, French are the official languages, and the Valdôtain dialect of Franco-Provençal is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 BC, recording in detail events in Italy, Iberia, Greece, Macedonia, Syria, Egypt and Africa, and documented the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars among many others. Polybius' ''Histories'' is important not only for being the only Hellenistic historical work to survive in any substantial form, but also for its analysis of constitutional change and the mixed constitution. Polybius' discussion of the separation of powers in government, of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", all influenced Montesquieu's '' The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's '' Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurini
The Taurini were a Ligurian or Celto-Ligurian tribe dwelling in the upper valley of the river Po, around present-day Turin, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''Taurĩnoí'' (Ταυρῖνοί) by Polybius (2nd c. BC), ''Taurini'' by Livy (late 1st c. BC), ''Taurinoí'' (Ταυρινοί) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Taurinorum'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Taurínōn'' (Ταυρίνων; var. Ταυρικῶν, Ταυρινῶν) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD)., s.v. ''Taurini''. The ethnic name ''Taurini'' can be translated as 'the tribe of the bull'. It is either an older form of the metathesized Celtic noun ''taruos'' ('bull'), or a non-Celtic Ligurian form. Geography The Taurini lived between the Dora Riparia and the upper Po river and the lower Dandrune river. Their territory was located east of the Iemerii, west of the Libicii and Iadatini., Map 39: Mediolanum. Their original capital, Taurasia, was destroyed by the Carthagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isère (river)
The Isère ( , ; ; ) is a river in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southeastern France. Its source, a glacier known as the ''Sources de l'Isère'', lies in the Vanoise National Park in the Graian Alps of Savoie, near the ski resort in Val-d'Isère on the border with Italy. An important left-bank tributary of the Rhône, the Isère merges with it a few kilometers north of Valence. Many riverside communes have incorporated the Isère's name into their own, for example, Sainte-Hélène-sur-Isère and Romans-sur-Isère. The department of Isère is likewise named after the river. Etymology The name ''Isère'' was first recorded under the form ''Isara'', which means "the impetuous one, the swift one." Not originally a Celtic word, it was very likely assimilated by the Celts in ancient times. This word is related to the Indo-European ''*isərós'', meaning "impetuous, quick, vigorous," which is similar to the Sanskrit ''isiráḥ'' इसिरः อิสิระ with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain (, , or ) is a major geographical feature of northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetian Plain, Venetic extension not actually related to the Po (river), Po basin; it runs from the Western Alps to the Adriatic Sea. The flatlands of Veneto and Friuli are often considered apart since they do not drain into the Po, but they effectively combine into an unbroken plain, making it the largest in Southern Europe. It has a population of 17 million, or a third of Italy's total population. The plain is the surface of an in-filled system of ancient canyons (the "Apennine Foredeep") extending from the Apennine Mountains, Apennines in the south to the Alps in the north, including the northern Adriatic. In addition to the Po and its affluents, the contemporary surface may be considered to include the Savio (river), Savio, Lamone (river), Lamone and Reno (river), Reno to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |