|
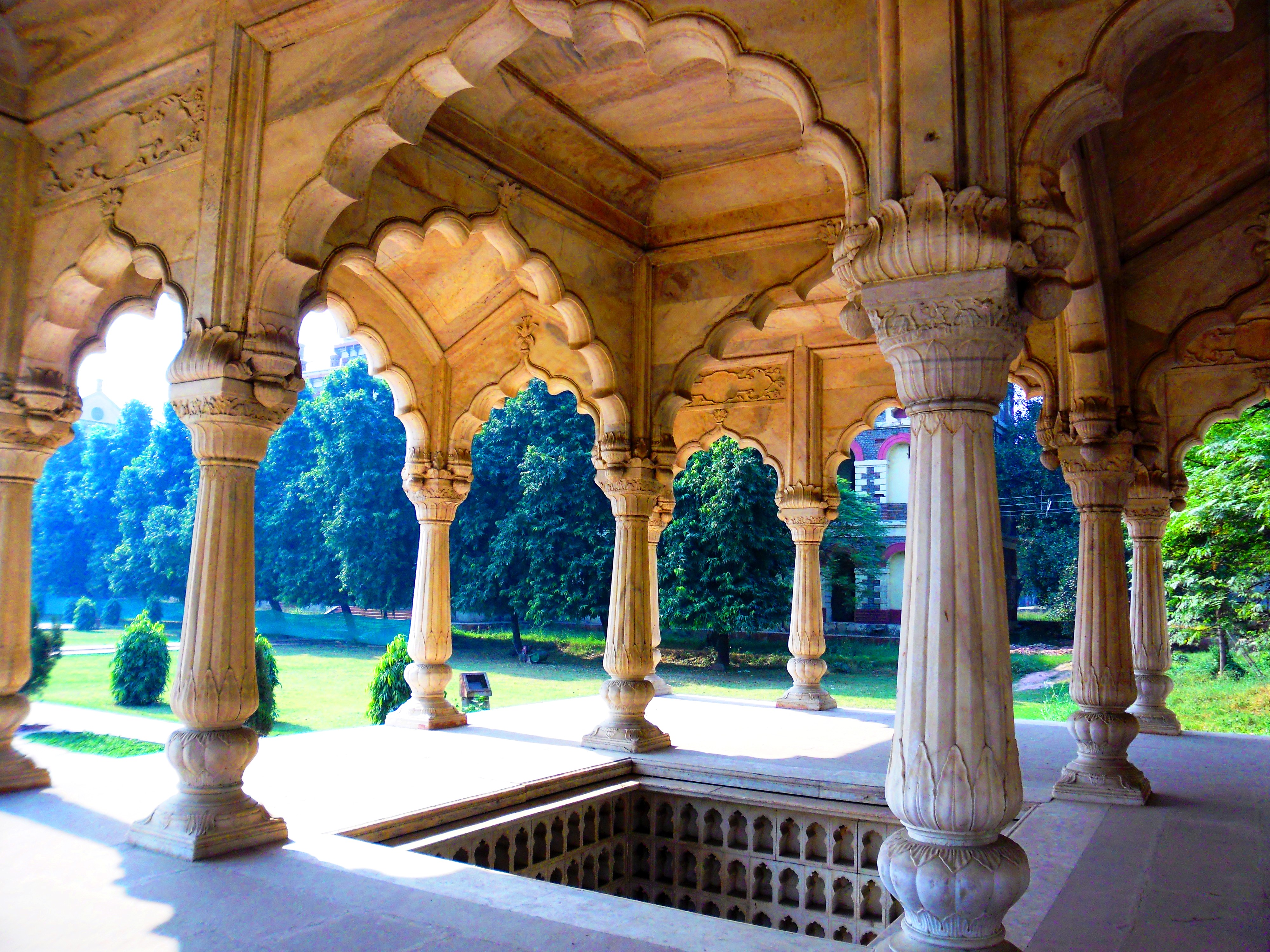
Sala (Thai Architecture)
A sala ( ), also known as a Sala Thai, is an open pavilion, used as a meeting place and to give people shade. With etymological roots in the Sanskrit ''Śālā, sala'', the word in Thai connotes buildings for specific purposes, such as ''sala klang'' ('provincial hall'). Most are open on all four sides. They are found throughout Thailand in Buddhist temple areas, or wats, although they can also be at other places. A person who builds a sala at a temple or in a public place gains religious merit. A sala located in a temple is called a ''salawat'' (ศาลาวัด), it's a transliteration from the Khmer word "sala wat", means a house for gathering to study, meeting in a wat. Some temples have large salas where laity can hear sermons or receive religious instruction. These are called ''sala kan parian'' (ศาลาการเปรียญ), meaning 'pavilion where monks learn for the Parian examination'. The city halls or offices of the province governors are called ''sala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
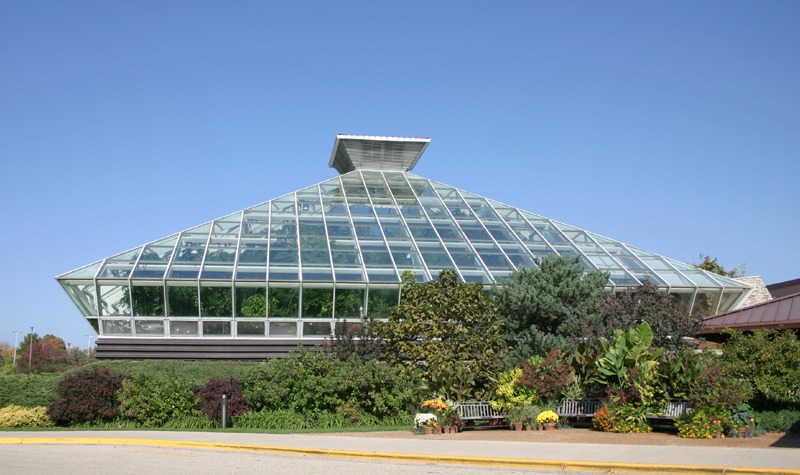
Thai Sala At Olbrich Botanical Gardens
Thai or THAI may refer to: * Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia. ** Thai people, Siamese people, Central/Southern Thai people or Thai noi people, an ethnic group from Central and Southern Thailand. ** , Thai minority in southern Myanmar. ** , Bamar with Thai ancestry in Central Myanmar. ** Sukhothai language, a kind of Thai topolect, by the end of the 18th century, they gradually diverged into regional variants, which subsequently developed into the modern Central Thai and Southern Thai. *** Central Thai language or Siamese language, the sole official language in Thailand and first language of most people in Central Thailand, including Thai Chinese in Southern Thailand. *** Southern Thai language, or Southern Siamese language, or Tambralinga language, language of Southern Thailand first language of most people in Southern Thailand *** Thai script *** Thai (Unicode block) People with the name * Thai (surname), a Vietnamese version of Cai, including a list of people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Architecture In Thailand
The architecture of Thailand () is a major part of the country's cultural legacy and reflects both the challenges of living in Thailand's sometimes extreme climate as well as, historically, the importance of architecture to the Thai people's sense of community and religious beliefs. Influenced by the architectural traditions of many of Thailand's cultures, it has also developed significant regional variation within its vernacular and religious buildings. Although Siam urged to identify themselves as a modernized state, Western culture and influence was undesirable and inevitable. In an attempt to become distinguished, Thailand's ruling elite gravitated toward selective Modernization to avoid the undesired Western influence. History Dvaravati era (7th–11th century CE) The architecture of Dvaravati appears in the central region of Thailand. It used clay bricks and sometimes laterite. The construction of pagodas had a square base and an inverted-bell shape topped with a spire. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
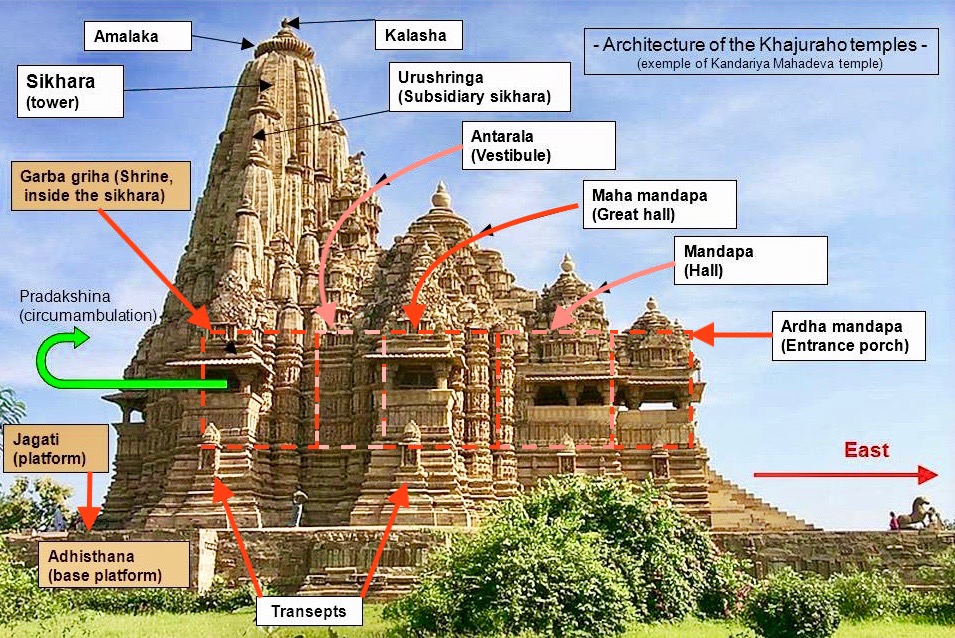
Hindu Architecture
Hindu architecture is the traditional system of Indian architecture for structures such as temples, monasteries, statues, homes, market places, gardens and town planning as described in Hindu texts. The architectural guidelines survive in Sanskrit manuscripts and in some cases also in other regional languages. These texts include the Vastu shastras, Shilpa Shastras, the ''Brihat Samhita'', architectural portions of the Puranas and the Agamas, and regional texts such as the Manasara among others. By far the most important, characteristic and numerous surviving examples of Hindu architecture are Hindu temples, with an Hindu temple architecture, architectural tradition that has left surviving examples in stone, brick, and Indian rock-cut architecture, rock-cut architecture dating back to the Gupta Empire. These architectures had influence of Ancient Persian and Hellenistic influence on Indian art, Hellenistic architecture. Far fewer secular Hindu architecture have survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pavilions
In architecture, ''pavilion'' has several meanings; * It may be a subsidiary building that is either positioned separately or as an attachment to a main building. Often it is associated with pleasure. In palaces and traditional mansions of Asia, there may be pavilions that are either freestanding or connected by covered walkways, as in the Forbidden City ( Chinese pavilions), Topkapi Palace in Istanbul, and in Mughal buildings like the Red Fort. * As part of a large palace, pavilions may be symmetrically placed building ''blocks'' that flank (appear to join) a main building block or the outer ends of wings extending from both sides of a central building block, the '' corps de logis''. Such configurations provide an emphatic visual termination to the composition of a large building, akin to bookends. The word is from French (Old French ) and it meant a small palace, from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zayat
A zayat (; ; from ) is a Burmese building found in almost every village. It serves primarily as a shelter for travelers, at the same time, is also an assembly place for religious occasions as well as meeting for the villagers to discuss the needs and plans of the village. Theravada Buddhist monks use zayats as their dwelling place while they are exercising precepts on Uposatha days. Buddhist monasteries may have one or more zayats nearby. Donors mostly build Zayats along main roads aiming to provide the exhausted travelers with water and shelter. Beginning with Adoniram Judson's construction of one in 1818 Christian missionaries have also adopted their use. Contributions, in money or labor, towards the construction, running or elaboration of a zayat are seen as dāna (meritorious charity). Thus zayats are generally built in a more durable and costly manner than most private houses. The labor is normally provided by locals, while the financing may be local or remote. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ordination Hall
The ordination hall (Pali: ''sīmā'') is a Buddhist building specifically consecrated and designated for the performance of the Buddhist ordination ritual (''upasampadā'') and other ritual ceremonies, such as the recitation of the Pāṭimokkha. The ordination hall is located within a boundary () that defines "the space within which all members of a single local community have to assemble as a complete Sangha () at a place appointed for ecclesiastical acts ()." The constitution of the ''sīmā'' is regulated and defined by the Vinaya and its commentaries and sub-commentaries. Burmese ordination halls In Burmese, ordination halls are called ''thein'' (), derived from the Pali term , meaning "boundary". The ''thein'' is a common feature of Burmese monasteries ('' kyaung''), although the ''thein '' may be not necessarily be located on the monastery compound itself. Shan ordination halls, called ''sim'' (သိမ်ႇ)'','' are exclusively used for events limited to the monkhoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Architecture Of Thailand
The architecture of Thailand () is a major part of the country's cultural legacy and reflects both the challenges of living in Thailand's sometimes extreme climate as well as, historically, the importance of architecture to the Thai people's sense of community and religious beliefs. Influenced by the architectural traditions of many of Thailand's cultures, it has also developed significant regional variation within its vernacular and religious buildings. Although Siam urged to identify themselves as a modernized state, Western culture and influence was undesirable and inevitable. In an attempt to become distinguished, Thailand's ruling elite gravitated toward selective Modernization to avoid the undesired Western influence. History Dvaravati era (7th–11th century CE) The architecture of Dvaravati appears in the central region of Thailand. It used clay bricks and sometimes laterite. The construction of pagodas had a square base and an inverted-bell shape topped with a spire. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Westpark (Munich)
The Westpark is a large urban public park in Munich, Germany. It was designed by landscape architect Peter Kluska and completed in 1983. It hosted the International Garden Expo 83 that same year. The park covers an area of (178 acres) extending 2.6 km from east to west. The Garmischer Straße divides the park into an eastern and western section. Sights and attractions Rose garden The rose garden is made up of more than 20,000 roses and 500 different rose species. There also are two popular Biergarten, beer gardens. Lake stage The western lake features a stage area (''Seebühne'') hosting open air movie screenings, live music and theater shows during the summer season. Asian gardens Four of the originally 23 national gardens of the exhibit are preserved. The very first authentic Chinese garden in Europe is a walled garden that might have been constructed for an historic scholar. Around a pond the walkways leads along the four seasons and four parts of a lifetime. The Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ueno Zoo
The is a zoo, managed by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, and located in Taitō, Tokyo, Japan. It is Japan's oldest zoo, opened on March 20, 1882. It is served by Ueno Station, Keisei Ueno Station and Nezu Station, with convenient access from several public transportation networks (JR East, Tokyo Metro and Keisei Electric Railway). The Ueno Zoo Monorail, the first monorail in the country, connected the eastern and western parts of the grounds, however the line was suspended from 2019 onwards due to ageing infrastructure until being announced as closing permanently on 27 December 2023. The zoo is in Ueno Park, a large urban park that is home to museums, a small amusement park, and other attractions. The zoo is closed on Mondays (Tuesday if Monday is a holiday). History The zoo started life as a menagerie attached to the National Museum of Natural History. In 1881, responsibility for this menagerie was handed to naturalist and civil servant Tanaka Yoshio, who oversaw its tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
East–West Center
The East–West Center (EWC), or the Center for Cultural and Technical Interchange Between East and West, is an education and research organization established by the U.S. Congress in 1960 to strengthen relations and understanding among the peoples and nations of Asia, the Pacific, and the United States as part of Cold War diplomatic efforts. James K. Scott serves as the Center’s interim president and chief executive, where it is headquartered in Honolulu at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa. History The East-West Center was established to facilitate Cold War-era diplomacy between the United States and its allies through technical interchange. Hawaii had become an important site for U.S. cultural diplomacy, military training, research, and as a staging ground for the U.S. war in Vietnam. In its early stages, the East-West Center only admitted students from countries deemed friendly to the United States. "The East–West Center originated as a University of Hawaiʻi a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Olbrich Botanical Gardens
Olbrich Botanical Gardens is a 16-acre outdoor botanical garden and 10,000-square-foot conservatory in Madison, Wisconsin. Founded in 1952 and named for its founder, Michael Olbrich, the gardens are owned and operated jointly by the City of Madison Parks and the non-profit Olbrich Botanical Society. Noteworthy additions to the gardens were the Bolz Conservatory in 1991, and a Thai sala, a gift to the University of Wisconsin–Madison from the Thai Chapter of the Wisconsin Alumni Association and the government of Thailand through its king, Bhumibol Adulyadej. Opened in 2002, it is one of only six sala outside of Thailand and one of two in the United States (the other is located in Hawaii). Gardens and grounds The gardens are made up of several separate areas. The Sunken Garden is in the form of a traditional English garden. Surrounded by limestone terraces and hedges, it contains an long reflecting pool – designed to connect the garden thematically with nearby Lake M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |