|
Saker (cannon)
The saker was a medium cannon, slightly smaller than a culverin, developed during the early 16th century and often used by the English. It was named after the saker falcon, a large falconry bird native to the Middle East. A saker's barrel was approximately long, had a caliber, calibre of , and weighed approximately . It could fire List of cannon projectiles, round shot weighing approximately using of black powder. The shot was intended to bounce along the ground to cause as much damage as possible, the explosive shell (projectile), shell being rare before the 19th century. Tests performed in France during the 1950s show that a saker's range was over when fired at a 45-degree angle. Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII amassed a Inventory of Henry VIII of England, large arsenal of sakers in the early 16th century as he expanded the Royal Navy and came into conflict with France. Henry's foundries used so much bronze that there was a world shortage of tin. According to the inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saker
Saker may refer to: * Saker falcon (''Falco cherrug''), a species of falcon * Saker (cannon), a type of cannon * Saker Baptist College, an all-girls secondary school in Limbe, Cameroon * Grupo Saker-Ti, a Guatemalan writers group formed in 1947 * Changwon LG Sakers, a South Korean basketball team * Saker Cars, a sports car designed in New Zealand * HMS Saker, HMS ''Saker'', a Royal Navy ship * Saker LSV, a British Army light vehicle People * Alan Saker (1921–2001), Australian rules footballer * Alfred Saker (1814–1880), British Christian missionary to West Africa * Annie Saker (1882–1932), English actress * David Saker (born 1966), Australian first-class cricketer * Dora Saker (1888–1926), cheese-maker for Somerset County Council * Edward Saker (1838–1883), British actor-manager * Frank Saker (1907–1980), Canadian flatwater canoeist * Neil Saker (born 1984), English cricketer * Rivka Saker, Israeli philanthropist and art collector * Sardar Saker (1904–1973), Indian fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William III Of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 1650 – 8 March 1702), also known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht, Guelders, and Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from 1672, and List of English monarchs, King of England, Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland, and List of Scottish monarchs, Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. He ruled Great Britain and Ireland with his wife, Queen Mary II, and their joint reign is known as that of William and Mary. William was the only child of William II, Prince of Orange, and Mary, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange, Mary, Princess Royal, the daughter of King Charles I of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His father died a week before his birth, making William III the prince of Orange from birth. In 1677, he Cousin marriage, married his first cousin Mary, the elder daughter of his maternal u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Richards (engineer)
Michael Richards (1673–1721) was an Irish military engineer who rose to become Chief Engineer of Great Britain and Surveyor-General of the Ordnance. He was the son of Jacob Richards, also a leading military engineer, and the grandson of Solomon Richards. The family were Irish Protestants who owned land in County Wexford. His elder brothers Jacob and John Richards both pursued military careers. He was commissioned in 1692 (although he may have seen earlier service in the Williamite War in Ireland) and served in Flanders Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ... in the Nine Years War. He accompanied an expedition to Newfoundland in 1697. He played a role in rebuilding the town of St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's which had been destroyed in a French a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
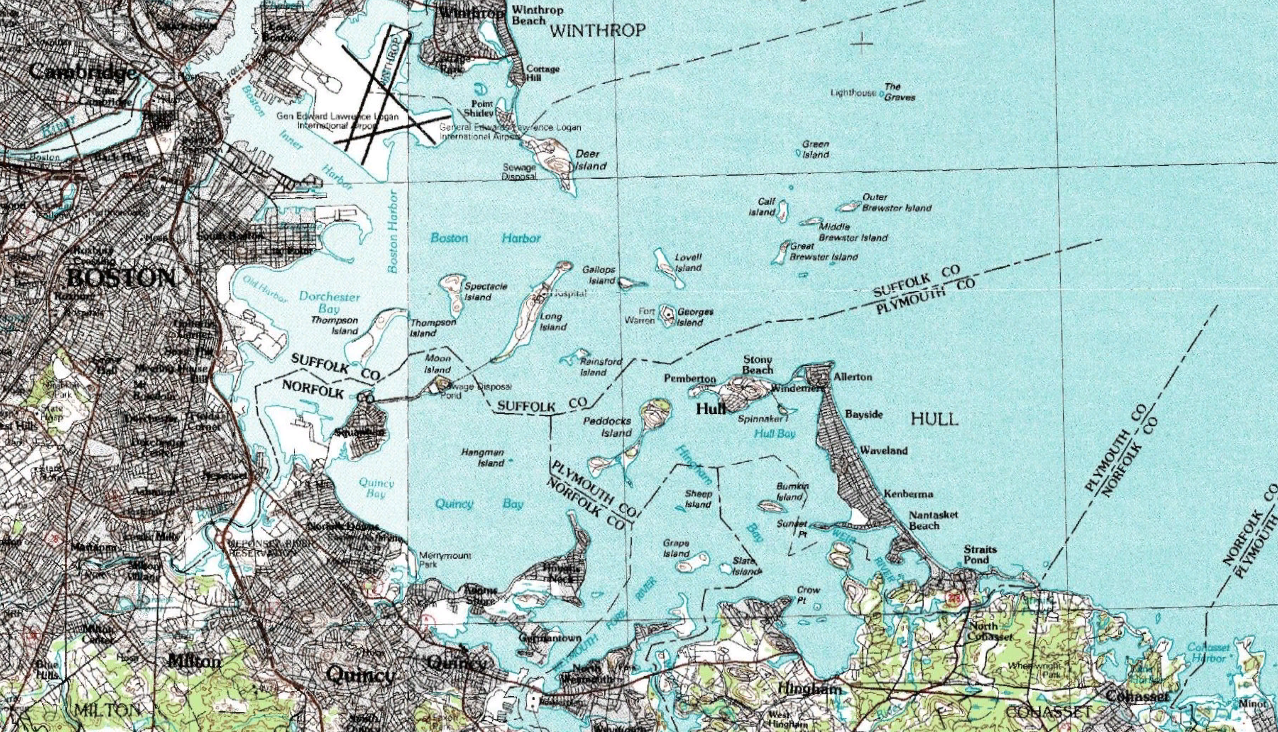
Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, located adjacent to Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the Northeastern United States. History 17th century Since its discovery by Europeans by John Smith in 1614, Boston Harbor has been an important port in American history. Boston Harbor was recognized by Europeans as one of the finest natural harbors in the world due to its depth and natural defense from the Atlantic as a result of the many islands that dot the harbor. It was also favored due to its access to the Charles River, Neponset River, and Mystic River, which made travel from the harbor deeper into Massachusetts far easier. By 1660, almost all imports came to the greater Boston area and the New England coast through the waters of Boston Harbor. A rapid influx of people transformed Boston into an exploding city. 18th century On December 16, 1773, Boston Harbor was the site of the Boston Tea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Island (Massachusetts)
Castle Island is a peninsula in South Boston on the shore of Boston Harbor. In 1928, Castle Island was connected to the mainland by a narrow strip of land and is thus no longer an island. It has been the site of a fortification since 1634, and is currently a recreation site and the location of Fort Independence (Massachusetts), Fort Independence. History 17th century In 1632, a fortification was constructed on Fort Hill to defend the town. In 1634, Boston sought defenses farther out in the harbor, on one of the numerous islands which protected the port. In July 1634, the town decided to build a fortification on Castle Island. Deputy Governor Roger Ludlow and Captain John Mason (c. 1600–1672), John Mason of Dorchester supervised construction of the fort. After a structure was built on the northeast side of the island, the General Court resolved that the fort at Castle Island should be completed before any other fortification was begun. The fort was later known as Castle Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Independence (Massachusetts)
Fort Independence is a granite bastion fort that provided harbor defenses for Boston, Massachusetts, located on Castle Island. Fort Independence is one of the oldest continuously fortified sites of English origin in the United States.Wilson, 312. The first primitive fortification was called "The Castle", placed on the site in 1634. It was rebuilt twice, then replaced around 1692 with a more substantial structure known as Castle William.Roberts, pp. 402-404 It was abandoned by the British during the American Revolution, but the Americans renamed it Fort Adams and then Fort Independence. The existing granite fort was constructed between 1833 and 1851. Today it is preserved as a state park and fires occasional ceremonial salutes. Fort Independence was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1970.Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation History Castle William The site of Fort Independence has been occupied by various fortifications since 1634.Wilso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on the '' Mayflower'' at a location that had previously been surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement served as the capital of the colony and developed as the town of Plymouth, Massachusetts. At its height, Plymouth Colony occupied most of what is now the southeastern portion of Massachusetts. Many of the people and events surrounding Plymouth Colony have become part of American folklore, including the American tradition of Thanksgiving and the monument of Plymouth Rock. Plymouth Colony was founded by a group of Protestant Separatists initially known as the Brownist Emigration, who came to be known as the Pilgrims. The colony established a treaty with Wampanoag chief Massasoit which helped to ensure its success; in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reached what is today the United States, dropping anchor near the tip of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, on , 1620. Differing from their contemporary Puritans (who sought to reform and purify the Church of England), the Pilgrims chose to separate themselves from the Church of England, which forced them to pray in private. They believed that its resistance to reform and Roman Catholic past left it beyond redemption. Starting in 1608, a group of English families left England for the Netherlands, where they could worship freely. By 1620, the community determined to cross the Atlantic for America, which they considered a "new Promised Land", where they would establish Plymouth Colony. The Pilgrims had originally hoped to reach America by early October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim Fathers
The Pilgrims, also known as the Pilgrim Fathers, were the English settlers who travelled to North America on the ship ''Mayflower'' and established the Plymouth Colony at what now is Plymouth, Massachusetts, United States. John Smith had named this territory New Plymouth in 1620, sharing the name of the Pilgrims' final departure port of Plymouth, Devon, England. The Pilgrims' leadership came from religious congregations of Brownists or Separatists who had fled religious persecution in England for the tolerance of 17th-century Holland in the Netherlands. These Separatists held many of the same Calvinist religious beliefs as Puritans, but unlike Puritans (who wanted a purified established church), Pilgrims believed that their congregations should separate from the Church of England, which led to their being labelled Separatists. After several years of living in exile in Holland, they determined to establish a new settlement in the New World and arranged with investors to fund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (often known as Invincible Armada, or the Enterprise of England, ) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by Alonso de Guzmán, Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, join with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas. The Spanish were opposed by an English fleet based in Plymouth. Faster and more manoeuvrable than the larger Spanish galleons, its ships were able to attack the Armada as it sailed up the Channel. Several subordinates advised Medina Sidonia to anchor in the Solent and occupy the Isle of Wight, but he refused to deviate from his instructions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, and vessels used for piracy are called pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples of such areas include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its History of the Republic of Venice, 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the ''Dogado'' area (a territory currently comparable to the Metropolitan City of Venice), during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and eastern Ionian Sea, Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed Crete, Cyprus, the Peloponnese, a number of List of islands of Greece, Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |