|
Saint Marys Bay, New Zealand
Saint Marys Bay is an inner List of suburbs of Auckland, suburb of Auckland, New Zealand. Demographics Saint Marys Bay covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Saint Marys Bay had a population of 2,049 in the 2023 New Zealand census, a decrease of 156 people (−7.1%) since the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census, and a decrease of 237 people (−10.4%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census. There were 987 males, 1,059 females and 6 people of non-binary gender, other genders in 915 dwellings. 7.2% of people identified as LGBTQ, LGBTIQ+. The median age was 48.7 years (compared with 38.1 years nationally). There were 189 people (9.2%) aged under 15 years, 378 (18.4%) aged 15 to 29, 984 (48.0%) aged 30 to 64, and 495 (24.2%) aged 65 or older. People could identify as more than one ethnicity. The results were 86.5% European New Zealanders, European (Pākehā); 7.3% Māori people, Māori; 2.8% Pasifika New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westhaven Marina
Westhaven Marina in Auckland, New Zealand, is the largest yacht marina in the Southern Hemisphere. The marina has nearly two thousand berths and swing moorings, and tends to be continually booked. Auckland, known as 'City of Sails', is generally known for its maritime passions. It is owned by Auckland Council, as successor to the Auckland City Council, which bought it from Ports of Auckland in 2004 for NZ$46 million. In 2008, it received its second-time-running international 'Blue Flag award' for its water quality, environmental management and safety standards. It is one of 640 marinas worldwide (and the only marina in New Zealand) to have received the award. Construction During the 1950s the foreshore of St. Mary's Bay disappeared under the approaches to the Auckland Harbour Bridge pened 1959 For over a century St Mary's Bay had been the location of several small commercial boatyards mixed in with the private moorings from houses set on the harbour cliffs above the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBTQ
LGBTQ people are individuals who are lesbian, Gay men, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or questioning (sexuality and gender), questioning. Many variants of the initialism are used; LGBTQIA+ people incorporates intersex, Asexuality, asexual, Aromanticism, aromantic, agender, and other individuals. The group is generally conceived as broadly encompassing all individuals who are part of a Sexual and gender minorities, sexual or gender minority, including all Sexual orientation, sexual orientations, romantic orientations, gender identities, and sex characteristics that are Non-heterosexual, not heterosexual, heteroromantic, cisgender, or endosex, respectively. Scope and terminology A broad array of sexual and gender minority identities are usually included in who is considered LGBTQ. The term ''gender, sexual, and romantic minorities'' is sometimes used as an alternative umbrella term for this group. Groups that make up the larger group of LGBTQ people include: * People with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In New Zealand
Irreligion in New Zealand refers to atheism, agnosticism, deism, religious scepticism and secular humanism in New Zealand society. Post-war New Zealand has become a highly secular country, meaning that religion does not play a major role in the lives of most people. Although New Zealand has no established religion, Christianity had been the most common religion since widespread European settlement in the 19th century. Demographics Statistics New Zealand gathers information on religious affiliation in the five-yearly census. Completing a census form is compulsory by law for every person in New Zealand on census night but respondents are able to object to answering the question of religious affiliation, and around 6% do object. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism In New Zealand
New Zealand Jews, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion, form with Hawaii (8,000–10,000), the joint-second largest (7,500–10,000) Jewish community in Oceania, behind Australia (118,000). The Jewish community in New Zealand is composed predominantly of Ashkenazi Jews. Other Jewish ethnic divisions are also represented and include Sephardi Jews, Mizrahi Jews, and Bene Israel. A number of converts to Judaism make up the New Zealand Jewish community, which manifests a wide range of Jewish cultural traditions and the Jewish religious movements#Ashkenazic movements, full spectrum of Jewish religious observance. Though they are a small minority, they have had an open presence in the country since the first Jewish immigrants began arriving in 1829. New Zealand has had three Jewish Prime Ministers or premiers, Julius Vogel (1873–1875), Francis Bell (New Zealand politician), Francis Bell and John Key (2008–2016). The first Jewish settlers in New Zealand were Anglo-Jewish t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars consider it a religious movement, its adherents typically see it as spiritual or as a unification of mind, body, and spirit, and rarely use the term ''New Age'' themselves. Scholars often call it the New Age movement, although others contest this term and suggest it is better seen as a Social environment, ''milieu'' or ''zeitgeist''. As a form of Western esotericism, the New Age drew heavily upon esoteric traditions such as the occultism of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, including the work of Emanuel Swedenborg and Franz Mesmer, as well as Spiritualism (movement), Spiritualism, New Thought, and Theosophy (Blavatskian), Theosophy. More immediately, it arose from mid-20th-century influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest religion after Christianity and Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the mid-1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. Buddhism grew significantly as a religion in New Zealand during the 1970s and 1980s with the arrival of Southeast Asian immigrants and refugees, coinciding with increased interest in Buddhist teaching from Western communities. Buddhist associations began forming, such as the Zen Society of New Zealand in 1972 (originally known as the Denkyo-ji Society), often fundraising to organise In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In New Zealand
Islam is the third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion in New Zealand (1.5%) after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity (32.3%) and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism (2.9%). Small numbers of Muslim immigrants from South Asia and eastern Europe settled in New Zealand from the early 1900s until the 1960s. Large-scale Muslim immigration began in the 1970s with the arrival of Indo-Fijians, Indian Fijians, followed in the 1990s by refugees from various war-torn countries. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, there are 75,144 Muslim New Zealanders, representing 1.5% of the total population. The first Islamic centre in New Zealand opened in 1959 and there are now several mosques and two Islamic schools. The majority of Muslims in New Zealand are Sunni, with significant Shia and Ahmadiyya minorities. The Ahmadiyya Community has translated the Qur'an into the Māori language. History Early migration, 19th century The earliest Muslim presence in New Zealand dates bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In New Zealand
Hinduism is the second largest religion in New Zealand. It is also one of the fastest-growing religions in the country. According to the 2023 census, Hindus form 2.9% of the population of New Zealand. There are about 153,534 Hindus in New Zealand. Hindus from all over India continue to immigrate today, with the largest Indian ethnic subgroup being Gujaratis, Haryanvi and Dravidians. A later wave of immigrants also includes Hindu immigrants who were of Indian descent from nations that were historically under European colonial rule, such as Fiji. Today there are Hindu temples in all major New Zealand cities. History Early settlement In 1836 the missionary William Colenso saw Māori women near Whangārei using a broken bronze bell to boil potatoes. The inscription is in very old Tamil script. This discovery has led to speculation that Tamil-speaking Hindus may have visited New Zealand hundreds of years ago. However, the first noted settlement of Hindus in New Zealand da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Sign Language
New Zealand Sign Language or NZSL () is the main language of the deaf community in New Zealand. It became an official language of New Zealand in April 2006 under the New Zealand Sign Language Act 2006. The purpose of the act was to create rights and obligations in the use of NZSL throughout the legal system and to ensure that the Deaf community had the same access to government information and services as everybody else. According to the 2013 Census, over 20,000 New Zealanders know NZSL. New Zealand Sign Language has its roots in British Sign Language (BSL), and may be technically considered a dialect of British, Australian and New Zealand Sign Language (BANZSL). There are 62.5% similarities found in British Sign Language and NZSL, compared with 33% of NZSL signs found in American Sign Language. Like other natural sign languages, it was devised by and for deaf people, with no linguistic connection to a spoken or written language. NZSL uses the same two-handed manual alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
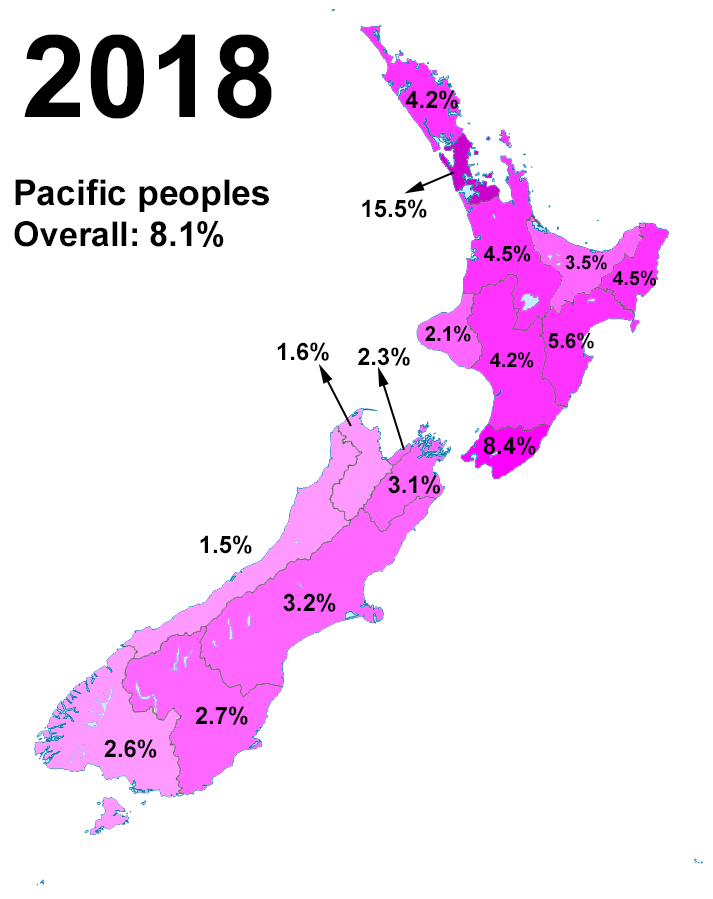
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |