|
Saint Gregory Of Nyssa Church, Trabzon
Saint Gregory of Nyssa ( el, Εκκλησία Αγίου Γρηγορίου Νύσσης) was a church and monastery of Trabzon. It's believed the church was built around 1280-1297 by the wife of John III, Emperor of Trabzon. After 1665, St Gregory became the cathedral of the city of Trabzon. The church is dedicated to Saint Gregory of Nyssa (c. 330–395), a Christian bishop and saint. Nyssa (current day Nevşehir) is a city located in Cappadocia. Georgian traveler Timote Gabashvili Timote (Timothy) Gabashvili (Georgian: ტიმოთე გაბაშვილი) (1703–1764) was a Georgian travel writer, traveler, diplomat, cartographer, religious and public figure. He was the first to describe the Georgian antiquit ... visited the church in the late 1750s and included this event in his writings. In 1863, the Metropolitan Constantius of Trabzon rebuilt the church. In 1930 the church was dynamited to make way for the City Club.A. Bryer and D. Winfield, ''The Byzantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabzon Saint Gregory Of Nyssa Cathedral (destroyed 1930)
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. Trabzon, located on the historical Silk Road, became a melting pot of religions, languages and culture for centuries and a trade gateway to Persia in the southeast and the Caucasus to the northeast. The Venetian and Genoese merchants paid visits to Trabzon during the medieval period and sold silk, linen and woolen fabric. Both republics had merchant colonies within the city – Leonkastron and the former "Venetian castle" – that played a role to Trabzon similar to the one Galata played to Constantinople (modern Istanbul). Trabzon formed the basis of several states in its long history and was the capital city of the Empire of Trebizond between 1204 and 1461. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III Of Trebizond
John III Megas Komnenos or Grand Comnenus ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Mégas Komnēnós''; – 1362) was emperor of Trebizond from September 4, 1342, to May 3, 1344. He was a son of Emperor Michael of Trebizond (who had reigned for a day in 1341) and Acropolitissa, a daughter of Constantine Acropolites. John lived most of his life in Constantinople where his father had lived since . When Michael became Emperor of Trebizond for a day in 1341 and was quickly deposed and imprisoned by '' megas doux'' John the Eunuch, John was still in Constantinople. However, in 1342 the leaders of the ''Scholarioi'', Niketas Scholares and Gregory Meitzomates, visited him there and persuaded the young man to come with them to Trebizond and take the throne. With the approval of the Byzantine government, the group set out for Trebizond in September 1342 after enlisting the support of three Genoese galleys, bringing their little fleet to a total of five ships. After a short but fierce fight John and his sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Gregory Of Nyssa
Gregory of Nyssa, also known as Gregory Nyssen ( grc-gre, Γρηγόριος Νύσσης; c. 335 – c. 395), was Bishop of Nyssa in Cappadocia from 372 to 376 and from 378 until his death in 395. He is venerated as a saint in Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, Anglicanism, and Lutheranism. Gregory, his elder brother Basil of Caesarea, and their friend Gregory of Nazianzus are collectively known as the Cappadocian Fathers. Gregory lacked the administrative ability of his brother Basil or the contemporary influence of Gregory of Nazianzus, but he was an erudite Christian theologian who made significant contributions to the doctrine of the Trinity and the Nicene Creed. Gregory's philosophical writings were influenced by Origen. Since the mid-twentieth century, there has been a significant increase in interest in Gregory's works from the academic community, particularly involving universal salvation, which has resulted in challenges to many traditional i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyssa (Cappadocia)
Nyssa ( grc, Νύσσα) was a small town and bishopric in Cappadocia, Asia Minor. It is important in the history of Christianity due to being the see of the prominent 4th century bishop Gregory of Nyssa. Today, its name continues to be used as a titular see in the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church. Site and location The Antonine Itinerary places it on the road from Ancyra to Caesarea, between Parnassos and Asiana, 24 Roman miles from Parnassus and 32 from Asiana. Ptolemy's ''Geography'' places it at 68°20' 38°40 (in his degrees) in the Prefecture of Murimene ( grc, Στρατηγίας Μουριμηνῆς). The Synecdemus and the ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' indicate that Nyssa was in the Roman province of Cappadocia Prima. The site of Nyssa has been identified as near the modern town of Harmandalı, Ortaköy district, Aksaray province, in south-central Turkey.Talbert, Richard. ''Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World'', Princeton Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevşehir
Nevşehir (from the Persian compound ''Now-shahr'' meaning "new city"), formerly Neapolis (Ancient Greek: Νεάπολις) and Muşkara, is a largely modern city and the capital district of Nevşehir Province in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. According to the 2020 census, the population of the city is 82,110. It is from the capital Ankara and lies within the historical region of Cappadocia. The town lies at an elevation of and has a continental climate, with heavy snow in winter and great heat in summer. Although Nevşehir is close to the underground cities, fairy chimneys, monasteries, caravanserais and rock-hewn churches of Cappadocia, and has a few hotels, the modern town is not itself a tourist centre. In 2015 a huge underground city was discovered underneath its centre following demolition works intended to clear the central hillside of ramshackle modern housing. Founded in 2007, Nevşehir University was renamed Nevşehir Hacı Bektaş Veli University in 2013. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revolt (499 BC), the Cappadocians were reported as occupying a region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine (Black Sea). Cappadocia, in this sense, was bounded in the south by the chain of the Taurus Mountains that separate it from Cilicia, to the east by the upper Euphrates, to the north by Pontus, and to the west by Lycaonia and eastern Galatia. Van Dam, R. ''Kingdom of Snow: Roman rule and Greek culture in Cappadocia.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002, p.13 The name, traditionally used in Christian sources throughout history, continues in use as an international Tourism in Turkey, tourism concept to define a region of exceptional natural wonders, in particular characterized by fairy chimneys and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timote Gabashvili
Timote (Timothy) Gabashvili (Georgian: ტიმოთე გაბაშვილი) (1703–1764) was a Georgian travel writer, traveler, diplomat, cartographer, religious and public figure. He was the first to describe the Georgian antiquities of Jerusalem on his visit to the Holy Land in the 1750s. Timote Gabashvili was a highly educated Georgian figure who was well versed in philosophy, theology and the history of religion. He also knew Russian, Greek and Turkish. Author of an essay in the memoir genre - "Mimosvla", which provides historical, ethnographic, geographical information. Biography Very little information is available about Timote Gabashvili and his life and work can not be fully restored. The first to write about Timothe was Ioane Batonishvili. Only the part of Ioane Batonishvili's information that is collected from the "Mimosvla" is reliable. The first attempt to write a biography of Timote Gabashvili belongs to Platon Ioseliani. But this biographical essay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Architecture In Trabzon
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
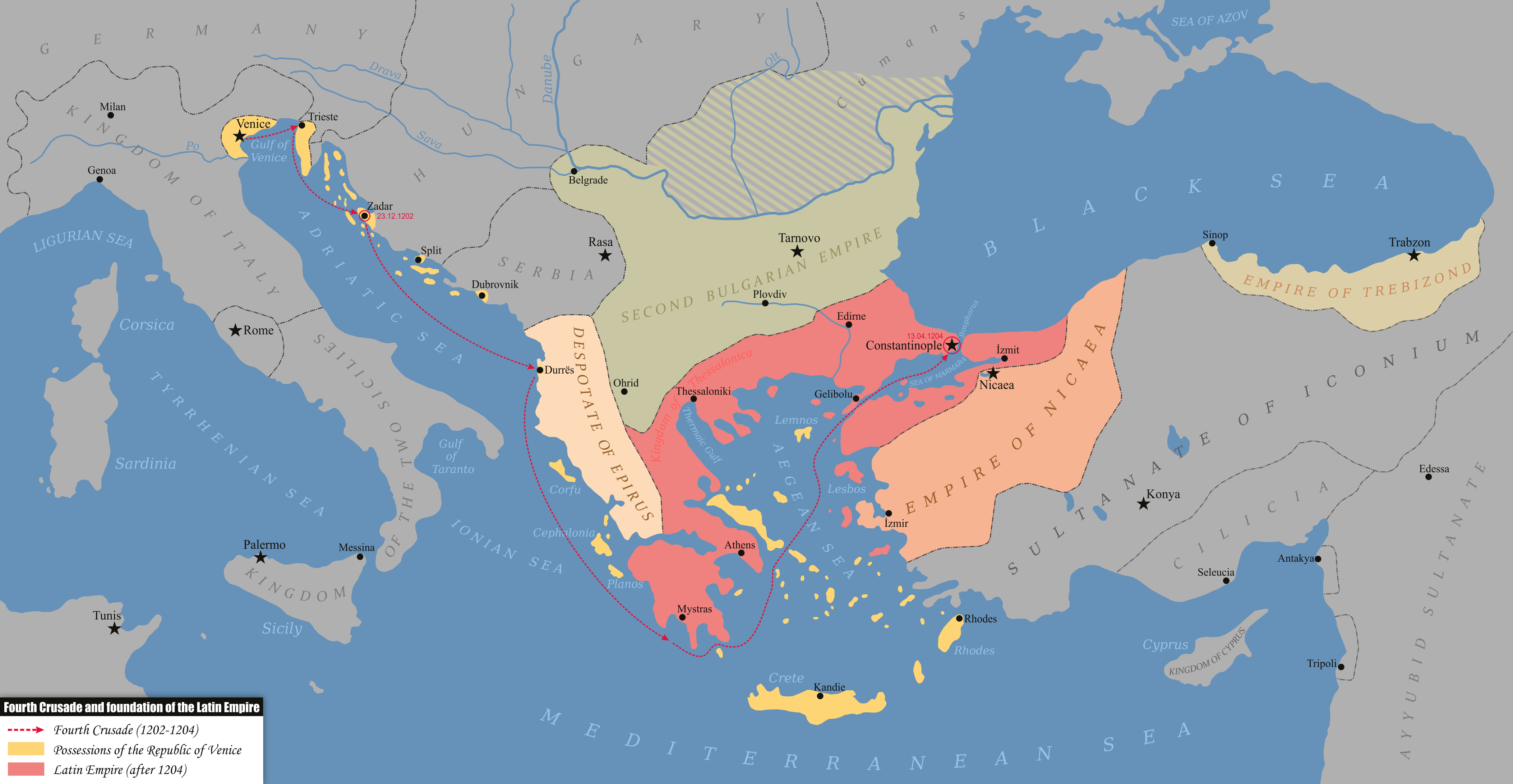
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Eastern Orthodox Church Buildings
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)