|
Saint-Quentin, Aisnes
Saint-Quentin (; ; ) is a city in the Aisne department, Hauts-de-France, northern France. It has been identified as the ''Augusta Veromanduorum'' of antiquity. It is named after Saint Quentin of Amiens, who is said to have been martyred there in the 3rd century. Administration Saint-Quentin is a sub-prefecture of Aisne. Although Saint-Quentin is by far the largest city in Aisne, the capital is the third-largest city, Laon. Mayors The mayor of Saint-Quentin is Frédérique Macarez, a member of the centre-right LR Party. History The city was founded by the Romans, in the Augustean period, to replace the ''oppidum'' of Vermand (11 km away) as the capital of ''Viromandui'' (Celtic Belgian people who occupied the region). It received the name "''Augusta Viromanduorum''", ''Augusta'' of the ''Viromandui'', in honor of the emperor Augustus. The site is that of a ford across the River Somme. During the late Roman period, it is possible that the civitas capital was transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôtel De Ville, Saint-Quentin
The (, ''City hall (administration), City Hall'') is a municipal building in Saint-Quentin, Aisne, northern France, standing on Place l'Hôtel de Ville. It was designated a ''monument historique'' by the French government in 1984. History The first town hall in Saint-Quentin was the Maison du Plaid or Maison de la Paix which served as the meeting place of the provost and aldermen from the mid-13th century. The provost assembled the bourgeoisie of the town there to consider pleas in 1332. The building contained two rooms: the Chambre du Haut Banquet (the banqueting hall) and the Chambre de Jugement (courtroom), and there was a square tower at the rear, which was used to store the municipal archives. In the late 15th century, the aldermen decided to demolish the existing building and to commission a new town hall. Construction of the new town hall started in the late 15th century. It was designed by Colard Noël from Valenciennes (who was also involved in rebuilding part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Le Meur
Daniel Le Meur was a French politician. He was the deputy for Aisne's 2nd constituency from 1973 to 1993 (including the 8th legislature (1986-1988), when deputies were elected by proportional representation by department) and the Mayor of Saint-Quentin, Aisne from 1977 to 1983 and from 1989 to 1995. He was a member of the French Communist Party The French Communist Party (, , PCF) is a Communism, communist list of political parties in France, party in France. The PCF is a member of the Party of the European Left, and its Member of the European Parliament, MEPs sit with The Left in the .... Biography He worked as a metallurgical worker at Motobécane, where he was a CGT delegate in 1965. He joined the Communist Party in 1956 and was part of the office of the Aisne federation. He was an alternate member of the central committee in February 1976 (XXIIth congress). He was a Communist deputy for Aisne from 1973 to 1993 and mayor of Saint-Quentin from 1977 to 1983 and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Franks, Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Pippinids, Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and ''dux et princeps Francorum'' hereditary, and becoming the ''de facto'' rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans in the West in over three centuries. Nearly every monarch of France from Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious until the pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermandois
Vermandois was a French county that appeared in the Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: St Quentin (Aisne) and Péronne ( Somme). In today's times, the Vermandois county would fall in the Picardy region of northern France. Pepin I of Vermandois, the earliest of its hereditary counts, was descended in direct male line from the emperor Charlemagne. More famous was his grandson Herbert II (902–943), who considerably increased the territorial power of the house of Vermandois, and kept the lawful king of France, the unlucky Charles the Simple, prisoner for six years. Herbert II was son of Herbert I, lord of Péronne and St Quentin, who was killed in 902 by an assassin in the pay of Baldwin II, Count of Flanders. His successors, Albert I, Herbert III, Albert II, Otto and Herbert IV, were not as historically significant. In 1077, the last count of the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of Saint-Quentin
The Basilica of Saint-Quentin (), formerly the Collegiate Church of Saint-Quentin () is a Catholic church in the town of Saint-Quentin, Aisne, France. There have been religious buildings on the site since the 4th century AD, which were repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during the Early Middle Ages. The present basilica was constructed in stages between the 12th and 15th centuries. It was severely damaged in World War I (1914–18), and was only reopened in 1956 after extensive reconstruction. Origins The town of Saint-Quentin has been identified with the Roman city of Augusta Veromandurorum, a commercial center at an important crossroads. It takes its present name from the Christian missionary Saint Caius Quintinus, who was beheaded there in 287 AD. Legend says the body was found many years later in the nearby marches of the River Somme by a Roman widow named Eusebia. She reburied the remains at the top of the hill at the center of the present town and built a small shri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitas
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by Roman law, law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on the one hand and rights of citizenship on the other. The agreement () has a life of its own, creating a or "public entity" (synonymous with ), into which individuals are born or accepted, and from which they die or are Exile, ejected. The is not just the collective body of all the citizens, it is the contract binding them all together, because each of them is a . is an abstract formed from . Claude Nicolet traces the first word and concept for the citizen at Rome to the first known instance resulting from the synoecism of Romans and Sabines presented in the legends of the Roman Kingdom. According to Livy, the two peoples participated in a ceremony of union after which they were named Quirites after the Sabine town of Cures, Sabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Somme
The Somme ( , ; ) is a river in Picardy, northern France. The river is in length, from its source in the high ground of the former at Fonsomme near Saint-Quentin, to the Bay of the Somme, in the English Channel. It lies in the geological syncline which also forms the Solent. This gives it a fairly constant and gentle gradient where several fluvial terraces have been identified. Name The Somme river was known in ancient times as ''Samara''. It presumably means 'the summery river', that is to say the 'quiet river', stemming from an adjective *''sam-aro''- ('summery') itself derived from the Celtic root *''samo''- ('summer')., s.v. ''Samara'' and ''Samarobriva Ambianorum.'' The city of Amiens was also known as '' Samarobriva'' (Gaulish: 'bridge on the Samara'). It is attested by the early 1st century BC as the chief town of the Ambiani, an ancient Gallic tribe of the region. The modern department of Somme was named after this river. History left, '' King_Edward_III. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Ford
A ford is a shallow place with good footing where a river or stream may be crossed by wading, on horseback, or inside a vehicle getting its wheels wet. A ford may occur naturally or be constructed. Fords may be impassable during high water. A low-water crossing is a low bridge that allows crossing over a river or stream when water is low but may be treated as a ford when the river is high and water covers the crossing. The word ''ford'' is both a noun (describing the water crossing itself) and a verb (describing the act of crossing a ford). Description A ford is a much cheaper form of river crossing than a bridge, and it can transport much more weight than a bridge, but it may become impassable after heavy rain or during flood conditions. A ford is therefore normally only suitable for very minor roads (and for paths intended for walkers and horse riders etc.). Most modern fords are usually shallow enough to be crossed by cars and other wheeled or tracked vehicles (a process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viromandui
The Viromanduī or Veromanduī (Gaulish: *''Uiromanduoi'') were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the modern Vermandois region (Picardy) during the Iron Age and Roman periods. During the Gallic Wars (58–50 BC), they belonged to the Belgic coalition of 57 BC against Caesar. Name They are mentioned as ''Viromanduos'' and ''Viromanduis'' (var. ''vero''-) by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Viromanduos'' by Livy (late 1st c. BC), ''Veromandui'' (var. ''uir''-) by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''(Ou̓i)romándues'' () by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), and as ''Veromandi'' by Orosius (early 5th c. AD). The ethnonym ''Viromanduī'' is a latinized form of Gaulish *''Uiromanduoi'' (sing. ''Uiromanduos''), which literally means 'horse-men' or 'male ponies'. It derives from the stem *''uiro-'' ('man') attached to ''mandos'' ('pony'). It should perhaps be interpreted as the 'Centaurs' or as the ' envirile in owning ponies'. Pierre-Yves Lambert has also proposed the meaning 'those who trample upon men', by comparing the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
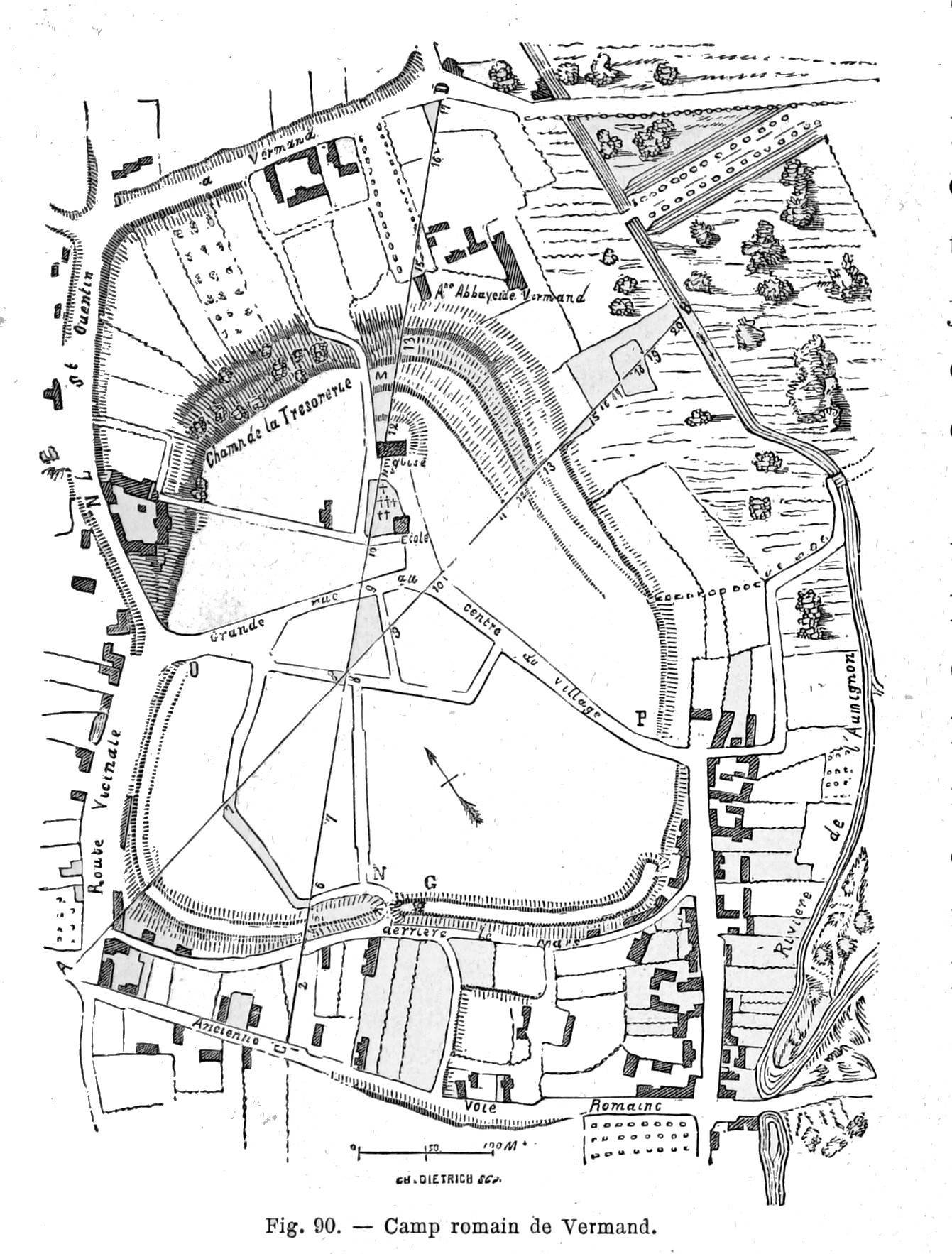
Vermand
Vermand (; Picard: ''Vermind'') is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. History Vermand was probably the original capital of the Viromandui, after whom the region of Vermandois is named. It was later displaced by the Roman settlement of Augusta Viromanduorum, modern Saint-Quentin.Jean-Luc Collart and Michèle Gaillard"Vermand /Augusta Viromanduorum (Aisne)" ''Supplément à la Revue archéologique du centre de la France'', 25, 1 (2004): 493–96. Population See also *Communes of the Aisne department The following is a list of the 796 communes in the French department of Aisne. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Communes of Aisne [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |