|
Saint-Michel–Notre-Dame Station
Saint-Michel–Notre-Dame () is a station on line B and line C of the Réseau Express Régional (RER) in Paris. Located in the 5th arrondissement, the station is named after the nearby Saint-Michel area and Notre-Dame Cathedral. The station opened, as Pont Saint-Michel and with platforms on the line that is now RER line C, in 1900. It gained its current name in 1988 with the opening of the line B platforms. Location The main entrance to the station is in Place Saint-Michel on the Rive Gauche of the Seine. There is also a satellite entrance to the line B platforms on Place Notre-Dame, which is on the Île de la Cité across the Seine from Place Saint-Michel. The line C platforms run parallel to the Seine at just above river level and are provided by natural light through 28 large windows that are designed to withstand flooding from the river. The line B platforms pass underneath the Seine and are at right-angles under the RER C platforms. The station is linked by undergr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RATP Group
The RATP Group () is a French state-owned enterprise (Établissement public à caractère industriel et commercial, EPIC) that operates public transport systems primarily in Paris, France. Headquartered in Paris, it originally operated under the name (). Its logo represents the Seine's meandering path through the Ile de France, Paris Region stylised as the face of a person looking up. The company had described itself as the fourth-largest presence in public transport. RATP Group was established in 1949 with the express purpose of operating Paris's public transport system. During the twentieth century, it focused solely on the provision of the capital's various forms of transit, from the Paris Métro, Tramways in Île-de-France, Île-de-France tram, and the RATP bus network, as well as part of the Réseau Express Régional, regional express rail (RER) network. However, since 2002, RATP Group's operations have no longer been geographically restricted; it has competitively pursued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank). It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy (region), Burgundy, is negotiable by large barges and most tour boats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; Bateaux Mouches, excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in the capital city, Paris. There are 37 List of bridges in Paris#Seine, bridges in Paris across the Seine (the most famous of which are the Pont Alexandre III and the Pont Neuf) and dozens List of crossings of the River Seine, more outside the city. A notable bridge, which is also the last along the course of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversal Rive Gauche
RER C is one of the five lines in the Réseau Express Régional (English: Regional Express Network), a hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system serving Paris and its suburbs. The line crosses the region from north to south. Briefly, between September 1979 and May 1980, the line was known as the ''Transversal Rive Gauche''. The line is operated by SNCF. The line runs from the northern termini Pontoise (C1), Versailles-Château-Rive-Gauche (C5) and Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines (C7) to the southern termini Massy-Palaiseau (C2), Dourdan-la-Forêt (C4) and Saint-Martin d'Étampes (C6). The RER C line is the second-longest in the network, created from an amalgamation and renovation of several old SNCF commuter lines, unlike RER A and B which had newer sections owned and constructed by RATP. Each day, over 531 trains run on the RER C alone, and carries over 540,000 passengers daily, 150,000 passengers more than the entirety of the TGV network. It is the most popular RER line f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invalides (Paris Métro And RER)
The Hôtel des Invalides (; ), commonly called (; ), is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as well as a hospital and an old soldiers' retirement home, the building's original purpose. The buildings house the Musée de l'Armée, the museum of the Army of France, the Musée des Plans-Reliefs, and the Musée d'Histoire Contemporaine. The complex also includes the Cathedral of Saint-Louis-des-Invalides, the national cathedral of the French military. It is adjacent to the Royal Chapel known as the , the tallest church building in Paris at a height of 107 meters. The latter has been converted into a shrine to some of France's leading military figures, most notably the tomb of Napoleon. History Louis XIV initiated the project by an order dated 24 November 1670 to create a home and hospital for aged and disabled () soldiers, the veterans of his many military campaig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée D'Orsay Station
Musée d'Orsay () is a station in line C of the Paris Region's Réseau Express Régional (RER) rapid transit system, named after the Musée d'Orsay, housed in the former Gare d'Orsay. It is in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, on the Quai Anatole-France. It was one of several stations attacked during the 1995 Paris Métro and RER bombings. History The Gare d'Orsay was opened in 1900 by the Chemin de Fer de Paris à Orléans (Paris–Orléans Railway, PO) as a mainline railway station for the 1900 Exposition Universelle. It became the PO company's new central terminus station, after the company extended its line from the Gare d'Austerlitz in the 13th arrondissement. The line made use of the new technology at the time, 550 V DC third rail electric traction, and it was constructed in a cut-and-cover tunnel along the left bank of the Seine from Austerlitz to the Quai d'Orsay. By the late 1930s, SNCF mainline trains had grown too long for the platforms at Gare d'Orsay, and ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
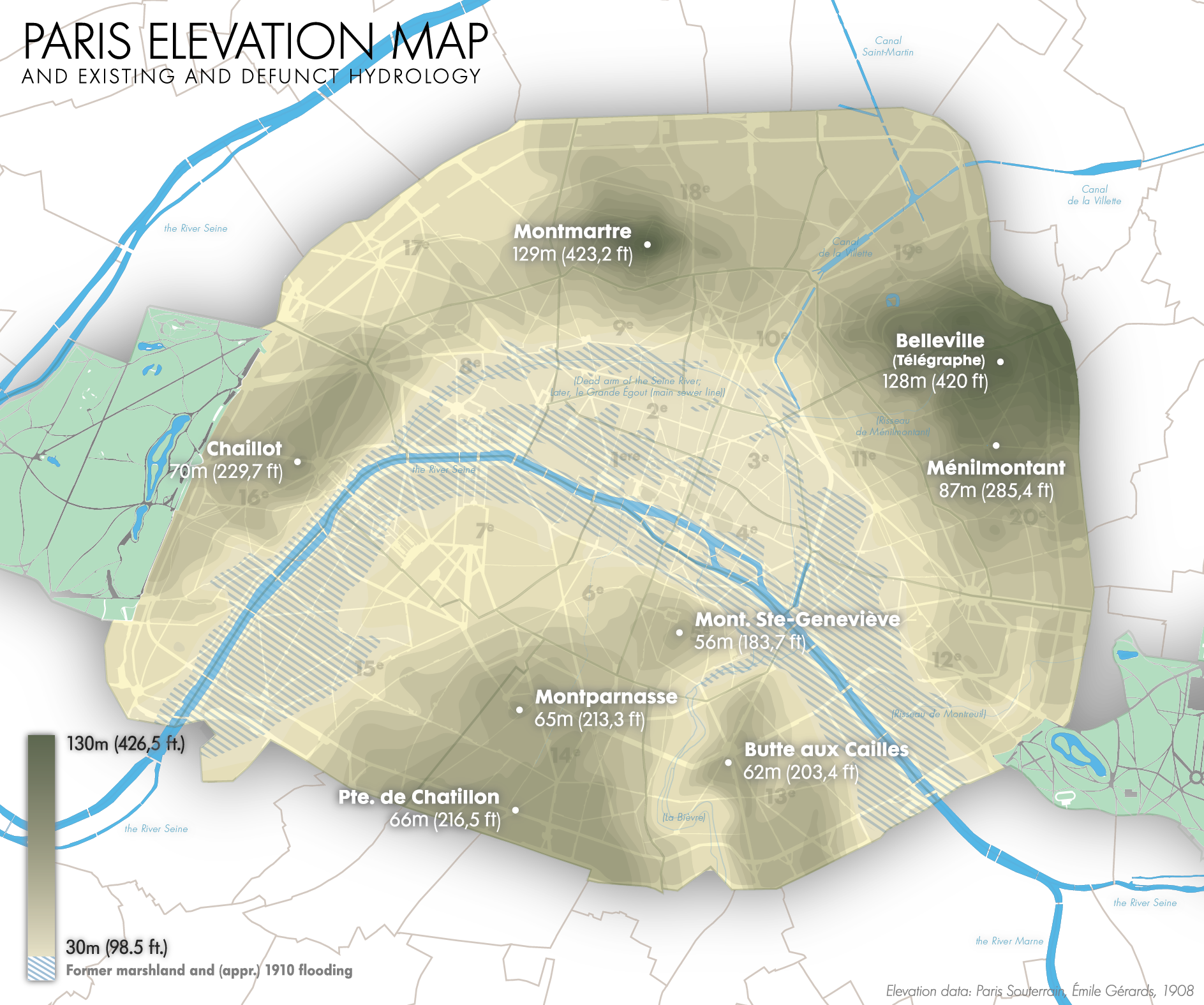
1910 Great Flood Of Paris
The 1910 Great Flood of Paris () was a catastrophe in which the Seine River, carrying winter rains from its tributaries, flooded the conurbation of Paris, France. The Seine water level rose eight meters (more than 26 feet) above the ordinary level. Chronology In the winter of 1909–1910, Paris and the surrounding area experienced higher than normal rainfall, which saturated the ground and caused rivers to overflow. In January 1910, Parisians were focused on daily life and lulled into a false sense of security because the Seine's water level had risen and fallen again in December. As a result, they largely ignored reports of mudslides and flooding occurring upriver. They were also slow to notice warnings signs within the city as the Seine's water level rose above normal; its water began to flow much faster than usual, and large amounts of debris appeared. By late January, water pushed upwards from overflowing Paris sewers, sewers and Paris subway, subway tunnels, then seepin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Curve
In civil engineering, a reverse curve (or "S" curve) is a section of the horizontal alignment of a highway or rail route in which a curve to the left or right is followed immediately by a curve in the opposite direction. On highways in the United States of America, United States reverse curves are often announced by the posting of a W1-4L sign (left–right reverse curve) or a W1-4R sign (right–left reverse curve), as called for in the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices. On rail routes, reverse curves can cause Buffers and chain coupler#Buffer-locking, buffer-locking. On the Northeast Corridor in the United States, these also hinder the development of High-speed rail in the United States, high-speed rail. See also *S bridge *Road curve *Track geometry References Railway track layouts {{engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gare D'Orsay
The Gare d'Orsay () is a former Paris railway station and hotel, built in 1900 to designs by Victor Laloux, Lucien Magne and Émile Bénard; it served as a terminus for the Chemin de Fer de Paris à Orléans (Paris–Orléans railway). It was the first electrified urban terminal station in the world, opened 28 May 1900, in time for the 1900 Exposition Universelle. After its closure as a station, it reopened in December 1986 as the Musée d'Orsay, an art museum. The museum is currently served by the eponymous RER station. History Palais d'Orsay In the early 19th century, the site was occupied by military barracks and the , a governmental building originally built for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The palace was erected over a period of 28 years, from 1810 to 1838, by the architects Jacques-Charles Bonnard and later Jacques Lacorné. After completion, the building was occupied by the Cour des Comptes and the Council of State. After the fall of the French Second Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gare D'Austerlitz
Gare d'Austerlitz ( English: ''Austerlitz station''), officially Paris Austerlitz, is one of the seven large Paris railway terminal stations. The station is located on the left bank of the Seine in the southeastern part of the city, in the 13th arrondissement. It is the start of the Paris–Bordeaux railway; the line to Toulouse is connected to this line. In 1997, the Ministry of Culture designated the Gare d'Austerlitz a historical monument; it became the fifth large railway station in Paris to receive such a label, as currently only Montparnasse has not been attributed it. Since the opening of the LGV Atlantiqueending at Gare MontparnasseAusterlitz has lost most of its long-distance southwestern services. It is used by some 30 million passengers annually, about half the number passing through Montparnasse. The Elipsos Train Hotels (Trenhotel) operated jointly by Renfe and SNCF operated from here to Madrid and Barcelona from 2001 to 2013. They would leave in the early evenin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compagnie Du Chemin De Fer De Paris à Orléans
The ''Compagnie du chemin de fer de Paris à Orléans'' (, PO) was an early French railway company. It merged with the '' Chemins de fer du Midi'' to form the '' Chemins de fer de Paris à Orléans et du Midi'' (PO-Midi) in 1934. In 1938 the PO-Midi was nationalized with five other companies to become a part of the ''Société nationale des chemins de fer français'' (SNCF). History Beginnings as railway company The company was founded on 13 August 1838 under the name ''Compagnie du chemin de fer de Paris à Orléans'' (PO). It had the right to form a limited company and was equipped with a starting capital of 40 million francs. In addition, the company had one of the French government's awarded temporary concession of 70 years, to build and operate a railway between the cities of Paris and Orléans. It had its headquarters in Paris. The first president of the board was François Bartholony. The first operation of the line dated 20 September 1840, but it only reached to C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Métro Line 10
Paris Métro Line 10 is one of 16 Paris métro, metro lines in Paris, France. The line links in Boulogne-Billancourt in the west with , traveling under the neighborhoods situated on the Rive Gauche in the southern half of Paris and the commune of Boulogne-Billancourt. Its two termini are and . The line is entirely underground and stretches across 23 stations. It has the least traffic of any of the 14 main metro lines (excluding lines Paris Métro Line 3bis, 3bis and Paris Métro Line 7bis, 7bis). Initially, the MA 51 model trains, which had previously been used on Paris Métro Line 13, Line 13 until it joined Paris Métro Line 14, Line 14, circulated on the tracks of Line 10. These trains were first constructed with three cars on four Bogie, bogies per train, and two trains permanently connected to make six cars per train, having an equivalent capacity to five cars on the classic metro trains. Because of the ineffectiveness of the MA 51 model, it was eventually completely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Métro Line 4
Line 4 () is one of the sixteen lines of the Paris Métro rapid transit system and one of its three fully automated lines. Situated mostly within the boundaries of the City of Paris, it connects Porte de Clignancourt (Paris Métro), Porte de Clignancourt in the north and Bagneux–Lucie Aubrac (Paris Métro), Bagneux-Lucie Aubrac in the south, travelling across the heart of the city. Until its southern terminus was changed from Porte d'Orléans (Paris Métro), Porte d'Orléans to Mairie de Montrouge (Paris Métro), Mairie de Montrouge in 2013, the line was sometimes referred to as the Clignancourt – Orléans Line. At in length, it connects with all Paris Métro lines apart from the very short Paris Métro Line 3bis, 3bis and Paris Métro Line 7bis, 7bis branch lines, as well as with all 5 Réseau Express Régional, RER express lines. It also serves three of the Paris Railway stations, Gare du Nord, Gare de l'Est, and Gare Montparnasse. It is the second-busiest Métro line aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |