|
Sailing Ballast
Ballast is weight placed low in ships to lower their centre of gravity, which increases stability (more technically, to provide a righting moment to resist any heeling moment on the hull). Insufficiently ballasted boats tend to tip or heel excessively in high winds. Too much heel may result in the vessel filling with water and/or capsizing. If a sailing vessel needs to voyage without cargo, then ballast of little or no value will be loaded to keep the vessel upright. Some or all of this ballast will then be discarded when the cargo is loaded. If a cargo vessel (such as a tanker, bulk carrier or container ship) wishes to travel empty or partially empty to collect cargo, it must travel "in ballast". This keeps the vessel in trim and keeps the propeller and rudder submerged. Typically, being "in ballast" will mean flooding ballast tanks with sea water. Serious problems may arise when ballast water is discharged, as water-borne organisms can create havoc when deposited in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballast
Ballast is dense material used as a weight to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within a boat, ship, submarine, or other floating structure that holds water is called a ballast tank. Water should be moved in and out from the ballast tank to balance the ship. In a vessel that travels on the water, the ballast will be kept below the water level, to counteract the effects of weight above the water level. The ballast may be redistributed in the vessel or disposed of altogether to change its effects on the movement of the vessel. History The basic concept behind the ballast tank can be seen in many forms of aquatic life, such as the blowfish or members of the argonaut group of octopus. The concept has been invented and reinvented many times by humans to serve a variety of purposes. In the fifteenth and sixteenth century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactured material in the world. When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that can be poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called hydration, which hardens it after several hours to form a solid matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material with various uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means that ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a confidential, nonpartisan basis. CRS is sometimes known as Congress' think tank due to its broad mandate of providing research and analysis on all matters relevant to national policymaking. CRS has roughly 600 employees, who have a wide variety of expertise and disciplines, including lawyers, economists, historians, political scientists, reference librarians, and scientists. In the 2023 fiscal year, it was appropriated a budget of roughly $133.6 million by Congress. Modeled after the Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau, CRS was founded during the height of the Progressive Era as part of a broader effort to professionalize the government by providing independent research and information to public officials. Its work was initially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Miguel de Cervantes, Zoroaster, Lao Zi, Confucius, Aristotle, L. Frank Baum, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the formulae of Classical mechanics, Newtonian physics and cooking recipes. Other works are actively dedicated by their authors to the public domain (see waiver) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Issues With Shipping
Environment most often refers to: __NOTOC__ * Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or a group of organisms Other physical and cultural environments *Ecology, the branch of ethology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings *Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or other properties. *Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the settings for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic surroundings to the personal places *Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact * Market environment, business term Arts, entertainment and publishing * ''Environment'' (magazine), a peer-reviewed, popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tugboat Boss Discharging Ballast Water Before Departure
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, such as in crowded harbors or narrow canals, or cannot move at all, such as barges, disabled ships, log rafts, or oil platforms. Some are ocean-going, and some are icebreakers or salvage tugs. Early models were powered by steam engines, which were later superseded by diesel engines. Many have deluge gun water jets, which help in firefighting, especially in harbours. Types Seagoing Seagoing tugs (deep-sea tugs or ocean tugboats) fall into four basic categories: #The standard seagoing tug with model bow that tows almost exclusively by way of a wire cable. In some rare cases, such as some USN fleet tugs, a synthetic rope hawser may be used for the tow in the belief that the line can be pulled aboard a disabled ship by the crew owing to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the '' weather gage''. Since it captures rainfall, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wetter than the leeward side it blocks. The drier leeward area is said to be in a rain shadow. Origin The term "windward" has roots in both Low German and Old English. The word "lee", which means a place without wind, comes from the Old Norse "hle" for "cover" and has been used in marine navigation in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daggerboard
A daggerboard is a retractable centreboard used by various sailing craft. While other types of centreboard may pivot to retract, a daggerboard slides in a casing. The shape of the daggerboard converts the forward motion into a windward lift, countering the leeward push of the sail. The theoretical centre of lateral resistance is on the trailing edge of the daggerboard. General A daggerboard is a removable vertical keel that is inserted through a "trunk" in the center of a vessel's hull, usually amidships. Daggerboards are usually found in small sailing craft such as day sailers, which are easily handled by a single person. Daggerboards are not usually ballasted but are locked in place by a clip or pin. Unlike a centreboard, which can be set at different angles to the hull of the boat, daggerboards are generally limited to a single perpendicular position relative to the hull. If a daggerboard is located off center, it is called a leeboard or a bilgeboard. The characteristic whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
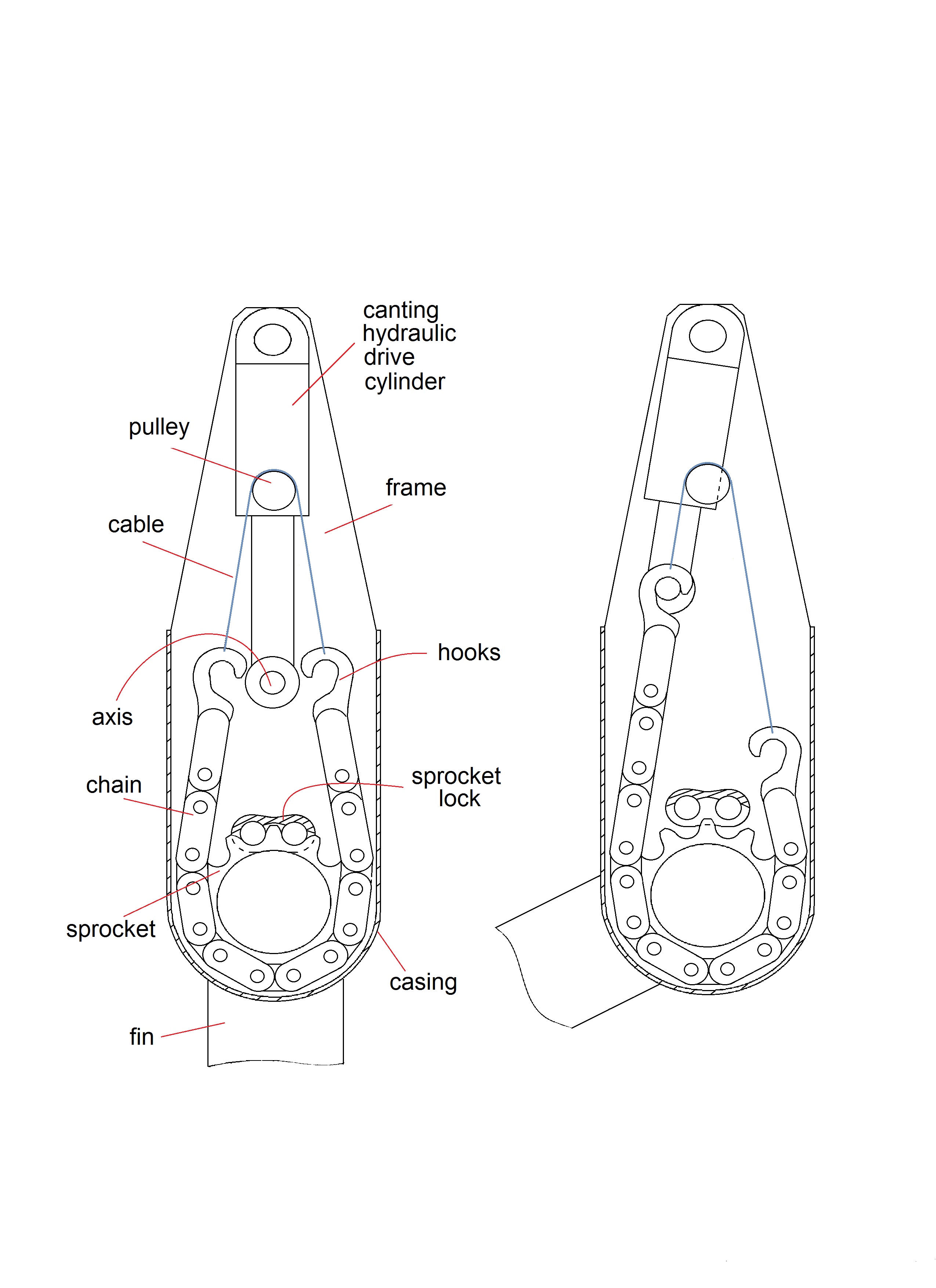
Canting Keel
A canting keel is a form of sailing ballast, suspended from a rigid canting strut beneath the boat, which can be swung to windward of a boat under sail, in order to counteract the heeling force of the sail. The canting keel must be able to pivot to either port or starboard, depending on the current tack. Purpose and history The traditional yacht keel performs four functions: * the development of lateral water force to resist lateral aerodynamic force from sails and superstructure, * the physical housing of ballast load as low as possible, * roll-damping to resist energy inputs from waves and disturbed water, and * a contribution to directional stability. The traditional fin keel, pointing straight down from the boat, provides no righting moment when the boat is level. The heeling force of the wind on the sails is therefore not counteracted until the boat has heeled over by a certain amount, moving the fixed keel to windward of the centerline. The purpose of the canting keel is to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foil (fluid Mechanics)
A foil is a solid object with a shape such that when placed in a moving fluid at a suitable angle of attack the lift (force generated perpendicular to the fluid flow) is substantially larger than the drag (force generated parallel to the fluid flow). If the fluid is a gas, the foil is called an airfoil or aerofoil, and if the fluid is water the foil is called a hydrofoil. Physics of foils A foil generates lift primarily because of its shape and angle of attack. When oriented at a suitable angle, the foil deflects the oncoming fluid, resulting in a force on the foil in the direction opposite to the deflection. This force can be resolved into two components: lift and drag. This "turning" of the fluid in the vicinity of the foil creates curved streamlines which results in lower pressure on one side and higher pressure on the other. This pressure difference is accompanied by a velocity difference, via Bernoulli's principle, so for foils generating lift the resulting flowfield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centerboard
A centreboard or centerboard (US) is a retractable hull appendage which pivots out of a slot in the hull of a sailboat, known as a ''centreboard trunk'' (UK) or ''centerboard case'' (US). The retractability allows the centreboard to be raised to operate in shallow waters, to move the centre of lateral resistance (offsetting changes to the sailplan that move the centre of effort aft), to reduce drag when the full area of the centreboard is not needed, or when removing the boat from the water, as when trailering. A centreboard which consists of solely a pivoting metal plate is called a centerplate; the term "centreboard" may refer to either a wooden or a metal pivoting retractable foil. A daggerboard is similar but slides vertically rather than pivoting. The analog in a scow is a bilgeboard: these are fitted in pairs and used one at a time. General History Lt. John Schank (c. 1740 – 6 February 1823) was an officer of the British Royal Navy and is credited with the invention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |