|
Saihō-ji (Sendai)
Saihō-ji (西方寺) is a Buddhist temple built in 1706 belonging to the Jōdo-shū sect in Aoba-ku, Sendai, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture. It is rarely called by its formal name by locals, and is more often called Jogi Nyorai or Jogi-san. History The temple's main treasure is a scroll depicting Amida Buddha, which is kept in the main temple. This scroll is called Jogi Nyorai. The temple is said to have been the location of a Taira clan fugitive, who is said to have been hiding out here after the Battle of Dan-no-ura, when Taira no Sadayoshi, a senior vassal of Taira no Shigemori, enshrined the Amida Nyorai scroll and prayed for the repose of the souls of Emperor Antoku and the Taira clan. Eight hundred years ago, the belongings of the young Emperor Antoku, who died with the Taira clan in Dannoura Bay in 1185, were buried under trees on the temple grounds. Over the decades, the trees merged and grew together to form a single tree, which today is one of the important landmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōdo-shū
Jōdo-shū (浄土宗, "The Pure Land School"), is a Japanese branch of Pure Land Buddhism derived from the teachings of the Kamakura era monk Hōnen (1133–1212). The school is traditionally considered as having been established in 1175 and is the most widely practiced branch of Buddhism in Japan, along with Jōdo Shinshū. There are various branches of Jōdo-shū, which the largest and most influential ones being Chinzei-ha and Seizan-ha. Jōdo-shū Buddhism focuses exclusively on devotion to Amitābha Buddha (Amida Nyorai), and its practice is focused on the Nembutsu (recitation of Amitābha’s name). As in other forms of Pure Land Buddhism, adherents believe that the faithful recitation of the phrase " Namu Amida Butsu" (Homage to Amida Buddha) results in birth in the pure land of Sukhavati. The Jōdo-shū as an independent sect is not to be confused with the term "Jōdo Tradition" (Jōdo-kei, 浄土系) which is used as a classification for "Japanese Pure Land Buddhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aoba-ku, Sendai
is one of five Wards of Japan, wards of Sendai, the largest city in the Tōhoku region of Japan. Aoba-ku encompasses 302.278 km² and had a population of 296,551, with 147,622 households as of March 1, 2012. Infrastructure The Miyagi Prefecture government office and the main city government offices are located there, along with Sendai Station (Miyagi), JR Sendai Station, a train station that is surrounded by many types of stores. A short walk from the station is the Ichibancho shopping district, a popular destination. The outdoor shopping mall is home to countless shops and restaurants, such as McDonald's and kimono stores. Eight stations of the Sendai Subway Nanboku Line (Sendai), Nanboku Line are also located in this ward. Economy Iris Ohyama has its headquarters in Aoba-ku. Air China has an office on the 1st floor of the Sendai Honcho Park Building in Aoba-ku. Asiana Airlines operates a sales office in the Taiyoseimei Sendai Station (Miyagi), Sendai-eki Kita Buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sendai
is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Miyagi Prefecture and the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,098,335 in 539,698 households, making it the List of cities in Japan, twelfth most populated city in Japan. The modern city was founded in 1600 by the ''daimyō'' Date Masamune. It is nicknamed the ; there are Japanese zelkova trees lining many of the main thoroughfares such as and . In the summer, the Sendai Tanabata Festival, the largest Tanabata festival in Japan, is held. In winter, the trees are decorated with thousands of lights for the , lasting through most of December. The city is also home to Tohoku University, one of the former Imperial Universities. On 11 March 2011, coastal areas of the city suffered catastrophic damage from a 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, magnitude 9.0 offshore earthquake,] which triggered a destructive tsunami. History Edo period Although the Sendai area was inhabited as early as 20,000 years ago, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miyagi Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Miyagi Prefecture has a population of 2,265,724 (1 August 2023) and has a geographic area of . Miyagi Prefecture borders Iwate Prefecture to the north, Akita Prefecture to the northwest, Yamagata Prefecture to the west, and Fukushima Prefecture to the south. Sendai is the capital and largest city of Miyagi Prefecture, and the largest city in the Tōhoku region, with other major cities including Ishinomaki, Ōsaki, Miyagi, Ōsaki, and Tome, Miyagi, Tome. Miyagi Prefecture is located on Japan's eastern Pacific coast and bounded to the west by the Ōu Mountains, the longest mountain range in Japan, with 24% of its total land area being designated as List of national parks of Japan, Natural Parks. Miyagi Prefecture is home to Matsushima, Matsushima Islands, a group of islands ranked as one of the Three Views of Japan, near the town of Matsushima, Miyagi, Matsushima. History Miyagi Prefectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amida Buddha
Amida can mean : Places and jurisdictions * Amida (Mesopotamia), now Diyarbakır, an ancient city in Asian Turkey; it is (nominal) seat of: ** The Chaldean Catholic Archeparchy of Amida ** The Latin titular Metropolitan see of Amida of the Romans ** The Armenian Catholic titular see Amida of the Armenians ** The Syrian Catholic (Antiochian Rite) titular Metropolitan see Amida of the Syriacs * Mount Amida, mountain in Saeki-ku, Hiroshima, Japan Other * Amitābha Buddha, in Japanese * Amida (beetle), ''Amida'' (beetle), a beetle genus * ''Amida'', a ladder climbing puzzle video game * Amida, is Swiss watchmaker founded in 1925 in Grenchen. See also * Amitabha (other) * Amidah, the central prayer of Jewish worship * Amidakuji, a way of drawing lots * Aëtius of Amida, 6th century medical writer {{dab, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
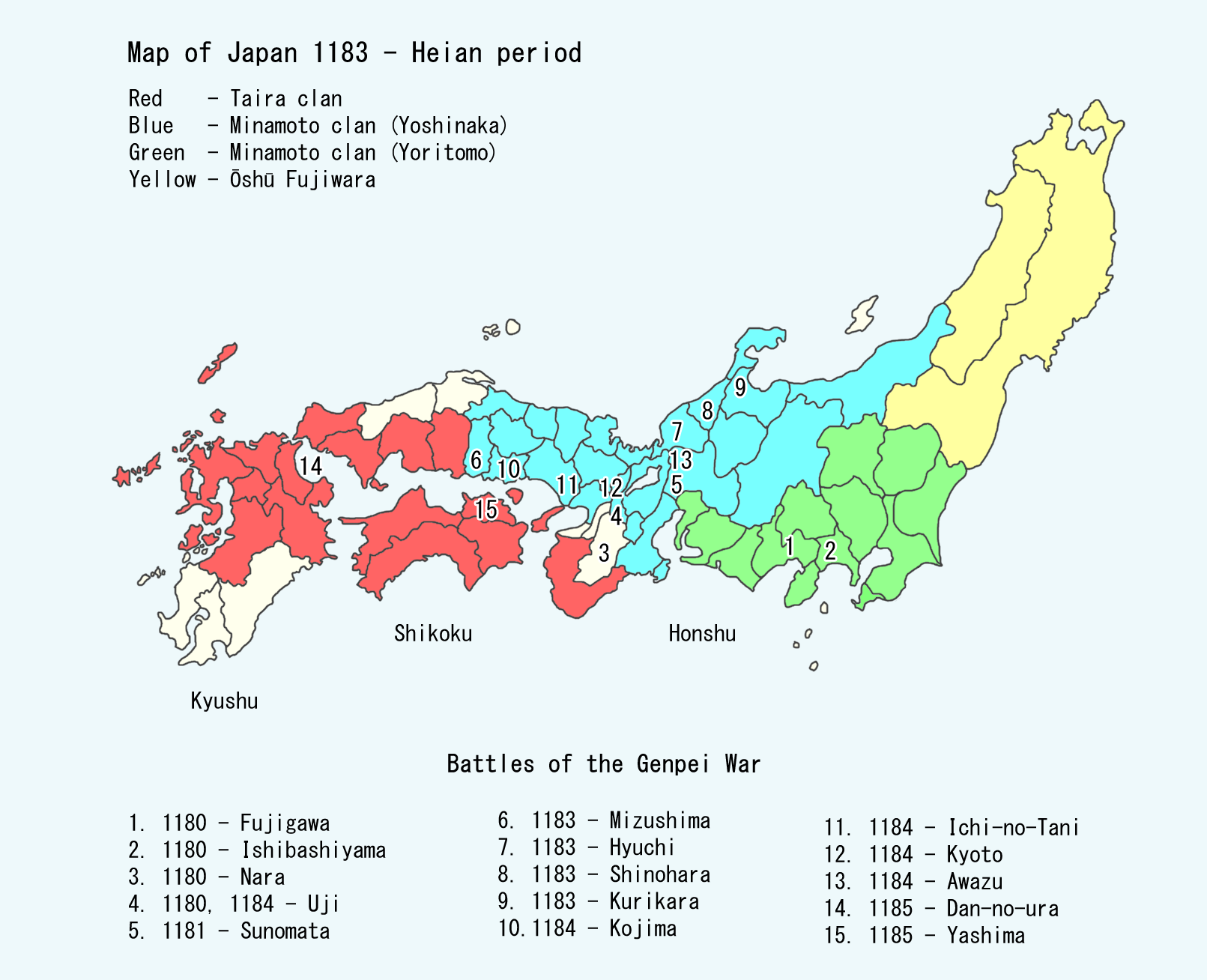
Taira Clan
The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the Emperor of Japan, emperors they descended from: Emperor Kanmu, Kanmu Heishi, Emperor Ninmyō, Ninmyō Heishi, Emperor Montoku, Montoku Heishi, and Emperor Kōkō, Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Emperor Antoku, Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō, Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dan-no-ura
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira No Sadayoshi
{{family name hatnote, Taira, lang=Japanese Taira no Sadayoshi (平 貞能) was a governor of Higo and Chikugo provinces in Kyūshū, and a samurai commander for the Taira clan during the Genpei War of the 1180s. Following the war, his life was spared as a result of an intercession by Utsunomiya Tomotsuna. He thus spent his retirement as a Buddhist monk, going by the appellation Higo-Nyūdo. His father was Taira no Iesada. When Kikuchi Takanao sided with Minamoto no Yoritomo and began levying troops in Kyūshū in 1180, at the beginning of the Genpei War, Sadayoshi marched against him and defeated him. Sadayoshi then traveled to Kyoto, and met up with Taira no Munemori along with the Emperor Antoku on the Saikaidō road from the capital. He tried in vain to convince Munemori to return to the city, but ultimately left him to take care of the remains of Taira no Shigemori, which were brought to the sacred Mount Kōya. Sadayoshi then reunited with Munemori and served under him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira No Shigemori
was the eldest regent of the Taira clan patriarch, Taira no Kiyomori. He supported his father in the Heiji Rebellion. He died two years before his father. His son, Taira no Koremori, became a monk in 1184 during Genpei War period, and drowned himself. Oda Nobunaga claimed to have descended from him through his grandson, Taira no Chikazane. Life Shigemori was caught between his father Kiyomori and Emperor Go-Shirakawa, Cloistered Emperor Go-Shirakawa, and suffered mentally. His words are well known in Japan. He was Kiyomori's favourite son, but as he had died ("some said of grief at his father's stubborn and misguided treatment of his opponents") his brother, Taira no Munemori was left in charge of the affairs of state. Sansom, G. (1958). A History of Japan to 1334. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, p.287. Portrayal in ''The Tale of the Heike'' Taira no Shigemori appeared in ''The Tale of the Heike,'' one of the traditional classics in medieval Japan. Death On Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amida Nyorai
Amida can mean : Places and jurisdictions * Amida (Mesopotamia), now Diyarbakır, an ancient city in Asian Turkey; it is (nominal) seat of: ** The Chaldean Catholic Archeparchy of Amida ** The Latin titular Metropolitan see of Amida of the Romans ** The Armenian Catholic titular see Amida of the Armenians ** The Syrian Catholic (Antiochian Rite) titular Metropolitan see Amida of the Syriacs * Mount Amida, mountain in Saeki-ku, Hiroshima, Japan Other * Amitābha Buddha, in Japanese * ''Amida'' (beetle), a beetle genus * ''Amida'', a ladder climbing puzzle video game * Amida, is Swiss watchmaker founded in 1925 in Grenchen. See also * Amitabha (other) * Amidah, the central prayer of Jewish worship * Amidakuji, a way of drawing lots * Aëtius of Amida Aëtius of Amida (; ; Latin: ''Aëtius Amidenus''; fl. mid-5th century to mid-6th century) was a Byzantine Greek physician and medical writer, particularly distinguished by the extent of his erudition. His birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Antoku
was the 81st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1180 through 1185. His death marked the end of the Heian period and the beginning of the Kamakura period. During this time, the Imperial family was involved in a bitter struggle between warring clans. Minamoto no Yoritomo with his cousin Minamoto no Yoshinaka, led a force from the Minamoto clan against the Taira, who controlled the emperor. During the climactic sea Battle of Dan-no-ura in April 1185, Antoku's grandmother Taira no Tokiko took him and plunged with him into the water in the Shimonoseki Straits, drowning the child emperor rather than allowing him to be captured by the opposing forces. This clash of clans led to numerous legends and tales. The story of Emperor Antoku and his mother's family became the subject of the Kamakura period epic poem ''The Tale of the Heike'' (Heike is an alternative reading of the Japanese characters for "House of the Taira"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |