|
Saddleback (bird)
The saddlebacks or tīeke (Māori language, Māori) are two species of New Zealand birds of the family Callaeidae. Both are glossy black with a chestnut saddle. Their taxonomic family is also known as that of the (New Zealand) "wattlebirds" and includes the two species of kōkako, and the extinct huia. All members of the family Callaeidae have coloured fleshy Wattle (anatomy), wattles on either side of the beak; the saddlebacks' are a vivid red. Taxonomy The genus ''Philesturnus'' was introduced in 1832 by the French zoologist Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire to accommodate a single species, the South Island saddleback, which is therefore the type species of the genus. The name combines the honeyeater genus ''Philedon'' and the starling genus ''Sturnus''. The saddleback's common name derives from the demarcated brown plumage on its back, which resembles a saddle. The Māori name, , is onomatopoeic and comes from one of the species' calls: "ti-e-ke-ke-ke-ke". There are two spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island Saddleback
The North Island saddleback (''Philesturnus rufusater'') is a forest-dwelling passerine bird species endemic (ecology), endemic to the North Island of New Zealand. It was once considered conspecific with the South Island saddleback. The IUCN lists the species as Near Threatened, while it is listed as a "relict" species in the New Zealand Threat Classification System. Saddlebacks are known in Māori language, Māori as ''tīeke''. Taxonomy and systematics René Lesson first described the species in 1828 from a specimen collected in the Bay of Islands four years earlier, using the binomial name ''Icterus rufusater''. The Specific name (zoology), specific name ''rufusater'' refers to the saddleback's plumage – a combination of the Latin words ''rufus'' 'reddish-brown', and ''ater'' 'black'. Their placement in the genus ''New World oriole, Icterus'' has since been revised, and the two saddleback species are now in their own genus, ''Philesturnus''. The name of this genus, created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stitchbird
The stitchbird or hihi (''Notiomystis cincta'') is a honeyeater-like bird endemic to the North Island and adjacent offshore islands of New Zealand. Its evolutionary relationships have long puzzled ornithologists, but it is now classed as the only member of its own family, the Notiomystidae. It is rare, being extirpated everywhere except Little Barrier Island, but has been reintroduced to two other island sanctuaries and four locations on the North Island mainland.Adams (2019). Current population estimations for mature individuals in the wild are 2,500–3,400. In addition to hihi, the stitchbird is also known by a number of other Māori names, including: tihi, ihi, tihe, kotihe, tiora, tiheora, tioro, kotihe-wera (male only), hihi-paka (male only), hihi-matakiore (female only), mata-kiore (female only), tihe-kiore (female only). Taxonomy and systematics The stitchbird was originally described as a member of the primarily Australian and New Guinean honeyeater family Meliphag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Island / Rakiura
Stewart Island (, 'Aurora, glowing skies', officially Stewart Island / Rakiura, formerly New Leinster) is New Zealand's third-largest island, located south of the South Island, across Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a land area of . Its coastline is indented by Paterson Inlet (east), Port Pegasus (south), and Mason Bay (west). The island is generally hilly (rising to at Mount Anglem) and densely forested. Flightless Birds of New Zealand, birds, including penguins, thrive because there are few introduced predators. Almost all the island is owned by the New Zealand government, and over 80 percent of the island forms Rakiura National Park. Stewart Island's economy depends on fishing and summer tourism in New Zealand, tourism. Its permanent population was recorded at 408 people in the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census. Most residents live in the settlement of Oban, New Zealand, Oban on the eastern side of the island. Ferries connect Oban to Bluff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
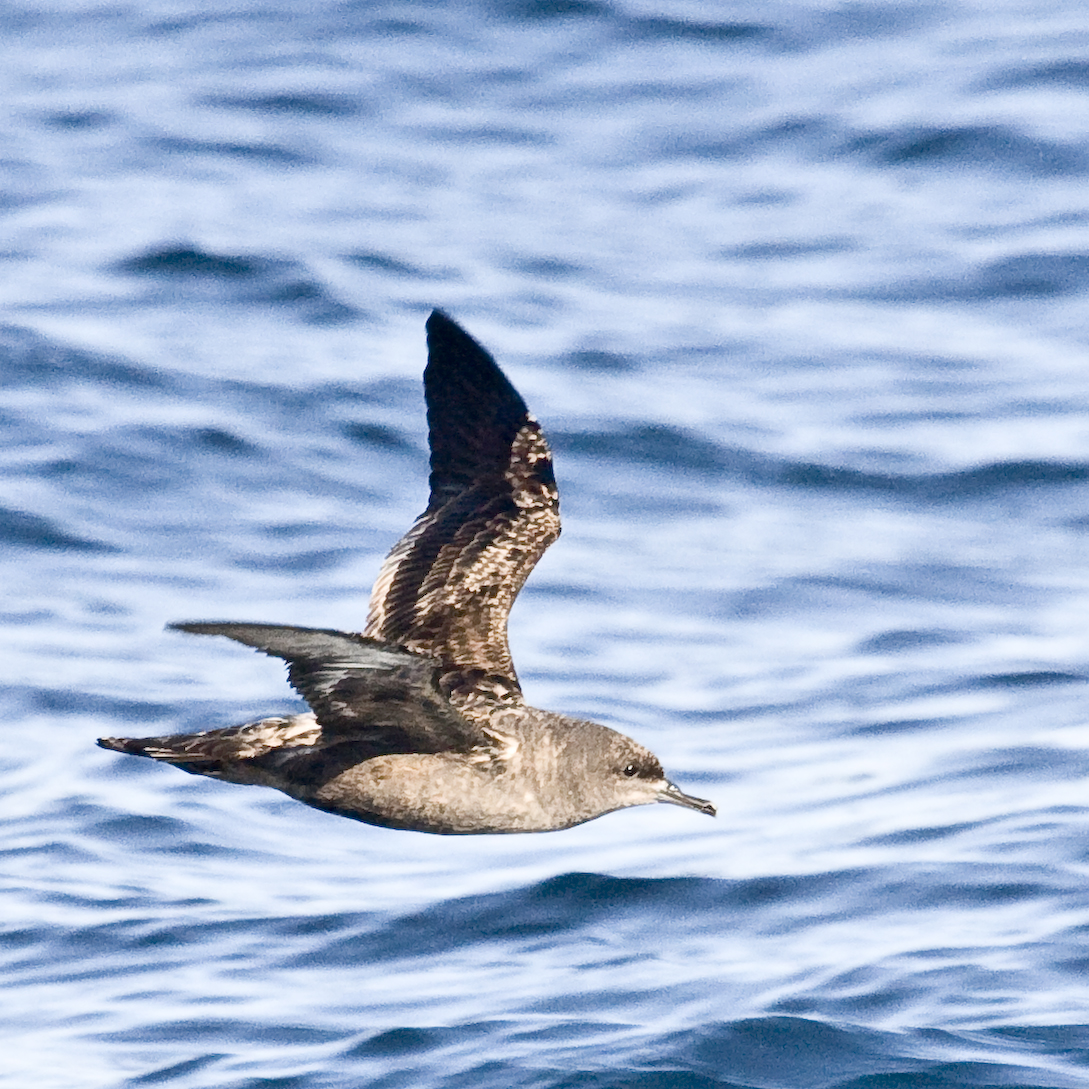
Taukihepa / Big South Cape Island
Taukihepa / Big South Cape Island is an offshore island of New Zealand to the west of the southern tip of Stewart Island / Rakiura. The island is the largest of the Tītī / Muttonbird Islands, and as such has no permanent inhabitants but is visited by muttonbirders in search of sooty shearwaters, known in New Zealand as "muttonbirds". Māori named the island "Taukihepa" and Europeans, who arrived later, called it "Big South Cape". The island was given dual names in 1998 as part of a Treaty of Waitangi settlement with Ngāi Tahu. The island is the largest of a group of islands off the southwestern coast of Stewart Island / Rakiura, from which it is separated by a wide channel. Surrounding smaller islands include Poutama Island to the south, Putauhina Island and the Putauhina Nuggets to the northwest, and Solomon Island to the north. The island rises to a height of at its centre, and numerous small streams run to the coast. Named features on the island include two inlets – M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hen And Chicken Islands
The Hen and Chicken Islands, usually known as the Hen and Chickens, lie to the east of the North Auckland Peninsula off the coast of northern New Zealand. They lie east of Bream Head and south-east of Whangārei with a total area of . History Approximately 18,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum when sea levels were over lower than present day levels, the islands were hilly features surrounded by a vast coastal plain. Sea levels began to rise 7,000 years ago, after which the islands separated from the rest of New Zealand. These islands were given their European name by Captain James Cook, who first sighted them on 25 November 1769. It has been suggested that the name was inspired by an old name for the star cluster usually known as the Pleiades. Originally owned by the Māori Ngā Puhi iwi, they were sold to the New Zealand Government in 1883. The islands were made a scenic reserve in 1908 owing to the rarity of their flora and fauna, and became a wildlife r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
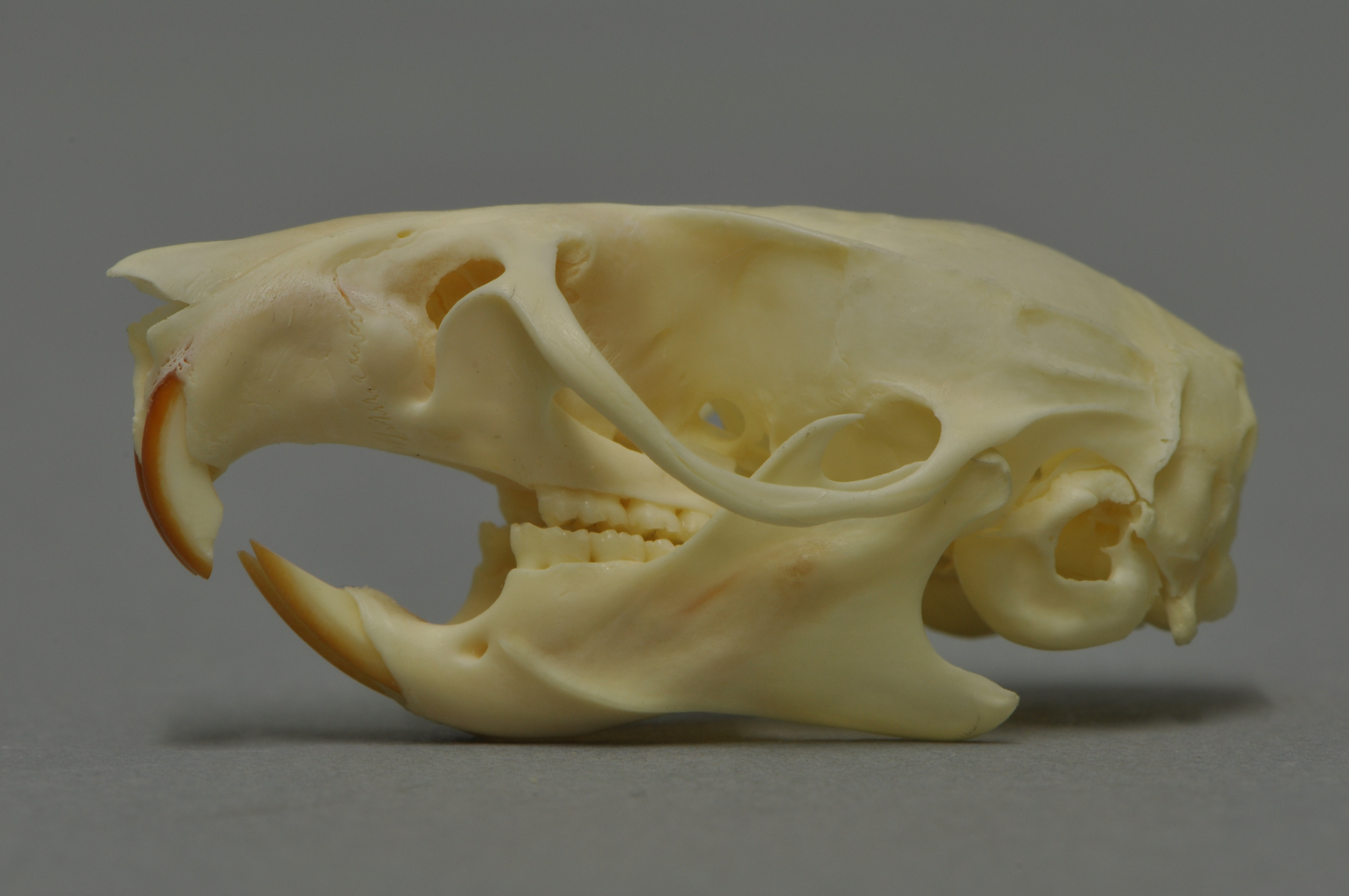
Ship Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus '' Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Rat
The brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus''), also known as the common rat, street rat, sewer rat, wharf rat, Hanover rat, Norway rat and Norwegian rat, is a widespread species of common rat. One of the largest Muroidea, muroids, it is a brown or grey rodent with a body length of up to long, and a tail slightly shorter than that. It weighs between . Thought to have originated in northern China and neighbouring areas, this rodent has now spread to all continents except Antarctica, and is the dominant rat in Europe and much of North America, having become Naturalisation (biology), naturalised across the world. With rare exceptions, the brown rat lives wherever humans live, particularly in urban areas. They are omnivorous, reproduce rapidly, and can serve as a vector for several human diseases. Selective breeding of the brown rat has produced the fancy rat (rats kept as pets), as well as the laboratory rat (rats used as model organisms in biological research). Both fancy rats and laborato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustelid
The Mustelidae (; from Latin , weasel) are a diverse family of carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids (), they form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora with about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies. Variety Mustelids vary greatly in size and behaviour. The smaller variants of the least weasel can be under in length, while the giant otter of Amazonian South America can measure up to and sea otters can exceed in weight. Wolverines can crush bones as thick as the femur of a moose to get at the marrow, and have been seen attempting to drive bears away from their kills. The sea otter uses rocks to break open shellfish to eat. Martens are largely arboreal, while European badgers dig extensive tunnel networks, called setts. Only one mustelid has been domesticated; the ferret. Tayra are also kept as pets (although they require a Dangerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māui (Māori Mythology)
In Māori mythology, as in other Polynesian traditions, Māui is a culture hero, demigod and a trickster, famous for his exploits and cleverness. He possessed superhuman strength, and was capable of shapeshifting into animals such as birds and worms. He was born premature and cast into the ocean by his mother, where the waves formed him into a living baby. He was discovered by his grandfather and later went to live with his siblings. One day he followed his mother to the underworld where he met his father, Makeatutara, who baptised Māui incorrectly. As a punishment from the gods for this mishap, Māui and all of humanity were doomed to die. Māui is credited with catching a giant fish using a fishhook taken from his grandmother's jaw-bone; the giant fish would become the North Island of New Zealand, known as . In some traditions, his canoe () became the South Island, known as . His last trick, which led to his death, involved the goddess Hine-nui-te-pō. While attempting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Legend
Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Cook Islands * Cook Islands Māori, the language of the Cook Islanders Ships * SS ''Maori'' (1893), a steamship of the Shaw Savill Line, shipwrecked 1909 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, sunk in 1915 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, launched 1936 and sunk 1942 * TEV ''Maori III'', a Union Steam Ship Company inter-island ferry, 1952–74 Sports teams * New Zealand Māori cricket team * New Zealand Māori rugby league team * New Zealand Māori rugby union team Other * ''Maori'', a 1988 novel by Alan Dean Foster * Mayotte, ''Maori'' in the Bushi language * Mount Maori Mount Maori is a mountain in the South Island of New Zealand. Description Mount Maori is located 10 kilometres southwest of Mount Aspiring / Titit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphytes
An epiphyte is a plant or plant-like organism that grows on the surface of another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phorophytes. Epiphytes take part in nutrient cycles and add to both the diversity and biomass of the ecosystem in which they occur, like any other organism. In some cases, a rainforest tree's epiphytes may total "several tonnes" (several long tons). They are an important source of food for many species. Typically, the older parts of a plant will have more epiphytes growing on them. Epiphytes differ from parasites in that they grow on other plants for physical support and do not necessarily affect the host negatively. An organism that grows on another organism that is not a plant may be called an epibiont. Epiphytes are usually found in the temperate zone (e.g., many mosses, liverworts, lichens, and algae) or in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threat Displays
Deimatic behaviour or startle display means any pattern of bluffing behaviour in an animal that lacks strong defences, such as suddenly displaying conspicuous eyespots, to scare off or momentarily distract a predator, thus giving the prey animal an opportunity to escape. The term deimatic or dymantic originates from the Greek δειματόω (deimatóo), meaning "to frighten". Deimatic display occurs in widely separated groups of animals, including moths, butterflies, mantises and phasmids among the insects. In the cephalopods, different species of octopuses, squids, cuttlefish and the paper nautilus are deimatic. Displays are classified as deimatic or aposematic by the responses of the animals that see them. Where predators are initially startled but learn to eat the displaying prey, the display is classed as deimatic, and the prey is bluffing; where they continue to avoid the prey after tasting it, the display is taken as aposematic, meaning the prey is genuinely distastefu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |