|
Sabo Bobaljević
Savino Bobali (, 1530–1585), nicknamed "the Deaf" (Sordo, Glušac), was a Ragusan nobleman, politician and founder of the literary "Academy of Concords". He wrote poetry in Italian and also in Croatian. Life Born into the local nobility of Ragusa, he became at 20 a member of the Great Council of the ''Republic of Ragusa'' and set about fulfilling the duties that fell to him as an aristocrat. With Amalteo and Nascimbeni he founded a literary academy, the "Academy of Concords". The members met in the Palace of Customs, to read their rhymes. This palace was also the meeting place for other important individuals of Dubrovnik, as Lucijan Ghetaldi, Natal Tudisi, Marin Kosta (also member of the'' Accademia dei Confusi'' of Viterbo), Marin Držić, Dinko Ranjina, Nikola Primi, Luka Sorkočević, the poet Julija Bona, Mihajlo Monaldi. Bobali contracted syphilis at a young age. Because of his condition he had to move to his castle in Ston near Dubrovnik, where he spent segregated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
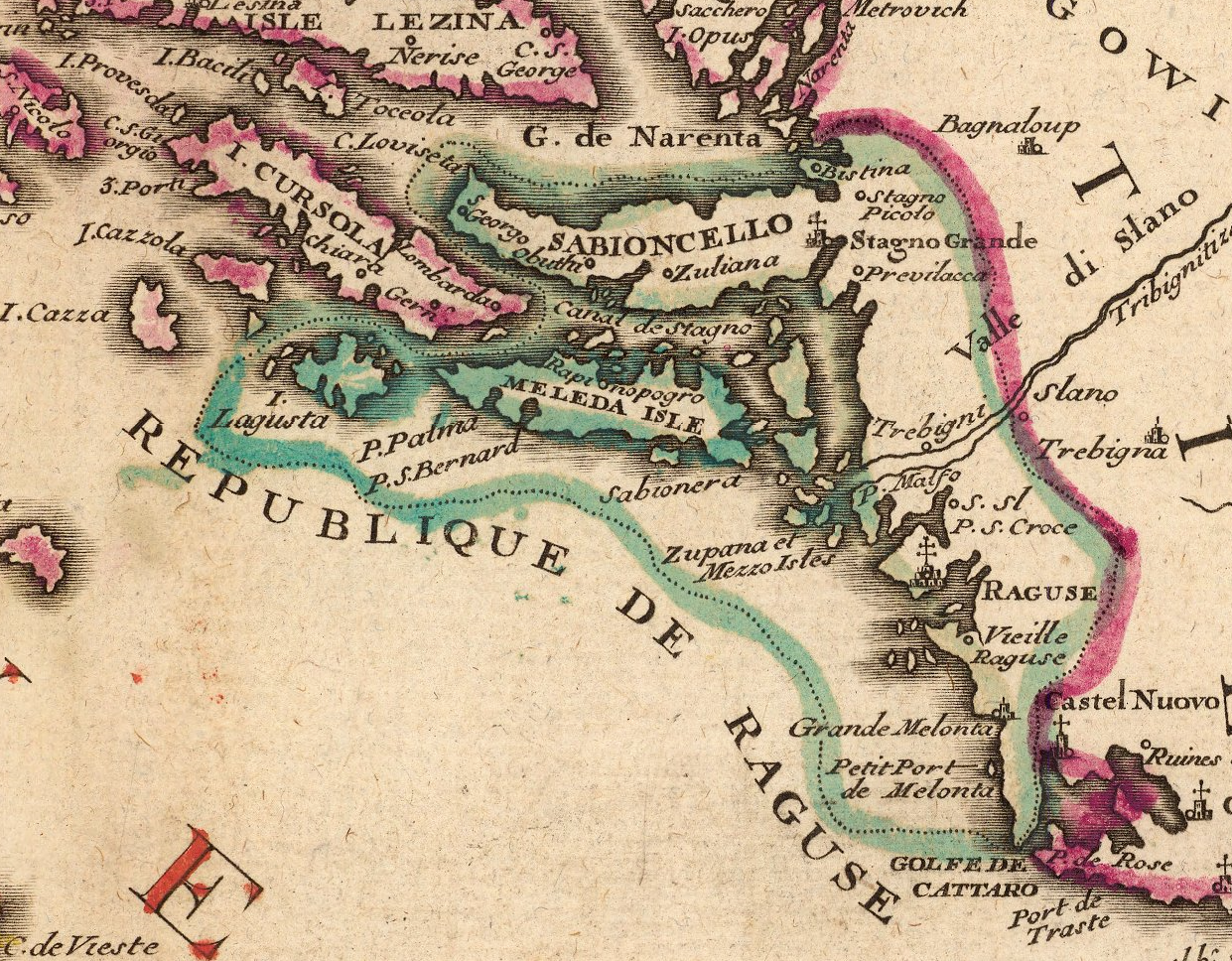
Republic Of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire and formally annexed by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldine Press
The Aldine Press was the printing office started by Aldus Manutius in 1494 in Venice, from which were issued the celebrated Aldine editions of the classics (Latin and Greek masterpieces, plus a few more modern works). The first book that was dated and printed under his name appeared in 1495. The Aldine Press is famous in the history of typography, among other things, for the introduction of italics. The press was the first to issue printed books in the small octavo size, similar to that of a modern paperback, and intended for portability and ease of reading. According to Curt F. Bühler, the press issued 132 books during twenty years of activity under Aldus Manutius. After Manutius' death in 1515, the press was continued by his wife Maria and her father Andrea Torresani (), until Manutius' son Paulus (1512–1574) took over. His grandson Aldus Manutius the Younger then ran the firm until his death in 1597. Today, the antique books printed by the Aldine Press in Venice are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragusan Nobility
The nobility of the Republic of Ragusa included patrician families, most of which originated from the City of Dubrovnik, and some coming from other, mostly neighbouring, countries. The Republic of Ragusa was ruled by a strict patriciate formally established in 1332, which was subsequently modified only once, following the 1667 Dubrovnik earthquake. Families * Basiljević * Benessa * Binciola * Bobali * Bocignolo * Bodazza * Bona * Bonda * Božidarević * Buća * Cerva * Giorgi * Ghetaldi * Gradić * Gučetić * Gundulić * Kaboga * Calich * Klašić * Crasso * Croce * Giuriceo * Gleda * Lukarić * Martinussio * Menčetić * Mlaschagna * Natali * Palmotić * Pavlić * Proculi * Prodanelli * Pucić * Radagli * Ranjina * Resti * Saraca * Sorgo * Tudisi * Vodopić * Volcasso * Zamagna * Zlatarić See also *Patrician (post-Roman Europe) Patricianship, the quality of belonging to a patriciate, began in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1585 Deaths
Events January–March * January 21 – Robert Nutter, Thomas Worthington, and 18 other Roman Catholic priests are "perpetually banished" from England by order of Queen Elizabeth, placed on the ship ''Mary Martin of Colchester'', and transported to France. * February 16 – Pachomius II is deposed by fellow bishops from his position as Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, head of the Eastern Orthodox Church, and replaced by the Metropolitan of Philippoupolis, Theoleptus II. * February 21 – King Johan III of Sweden, widowed since 1583, marries Gunilla Bielke in a ceremony at Västerås, which the King's siblings refuse to attend. The coronation of Queen consort Gunilla takes place the next day. Over the next seven years, she works on changing the Catholic government's attitude towards Protestants. * March 10 – The Spanish Army, commanded by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma, obtains the surrender of Brussels after a siege that began the yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1530 Births
Year 1530 (Roman numerals, MDXXX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 1530th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 530th year of the 2nd millennium, the 30th year of the 16th century, and the 1st year of the 1530s decade. Events January–March * January 5 – Strasbourg joins the ''Christliches Burgrecht'', the Protestant alliance of Swiss cities. * January 20 – Sent on a mission to penetrate the interior of Mexico and to conquer the Kingdom of Michoacán, the Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés leads a group of soldiers across the Lerma river through Cuitzeo and proceeds northwest. They arrive at Tonalá on March 24 and then take possession of the regions south of the Santiago River and north and west of Lake Chapala. * January 21 – Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, issues letters from his winter residence in Bologna, inviting members of the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet to convene at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Dubrovnik
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ... (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not mere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragusan Poets
Ragusan may refer to: * citizen of the Republic of Ragusa ** List of Ragusans Here follows a list of notable Ragusans and Rector (politics), Rectors of the Ragusan Republic, Republic of Ragusa (also known as the Republic of Dubrovnik), a Maritime republics, maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik on the eastern ... * person from any other place called Ragusa {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Literature
Italian literature is written in the Italian language, particularly within Italy. It may also refer to literature written by Italians or in other languages spoken in Italy, often languages that are closely related to modern Italian, including regional varieties and vernacular dialects. Italian literature began in the 12th century, when in different regions of the peninsula the Italian vernacular started to be used in a literary manner. The '' Ritmo laurenziano'' is the first extant document of Italian literature. In 1230, the Sicilian School became notable for being the first style in standard Italian. Renaissance humanism developed during the 14th and the beginning of the 15th centuries. Lorenzo de' Medici is regarded as the standard bearer of the influence of Florence on the Renaissance in the Italian states. The development of the drama in the 15th century was very great. In the 16th century, the fundamental characteristic of the era following the end of the Renaissanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Literature
Croatian literature refers to literary works attributed to the medieval and modern culture of the Croats, Croatia, and Croatian language, Croatian. Besides the modern language whose shape and orthography were standardized in the late 19th century, it also covers the oldest works produced within the modern borders of Croatia, written in Church Slavonic and Medieval Latin, as well as vernacular works written in Čakavian dialect, Čakavian and Kajkavian dialects. History Croatian medieval literature Croatian medieval prose is similar to other European medieval literature of the time. The oldest testaments to Croatian literacy are dated to the 11th and 12th centuries, and Croatian medieval literature lasted until the middle of the 16th century. Some elements of medieval forms can be found even in 18th-century Croatian literature, meaning their influence was stronger in Croatia than in the rest of Europe. Early Croatian literature was inscribed on stone tablets, hand-written on man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Literature
Renaissance literature refers to European literature which was influenced by the intellectual and cultural tendencies associated with the Renaissance. The literature of the Renaissance was written within the general movement of the Renaissance, which arose in 14th-century Italy and continued until the mid-17th century in England while being diffused into the rest of the western world. It is characterized by the adoption of a humanist philosophy and the recovery of the classical Antiquity. It benefited from the spread of printing in the latter part of the 15th century. Overview For the writers of the Renaissance, Greco-Roman inspiration was shown both in the themes of their writing and in the literary forms they used. The world was considered from an anthropocentric perspective. Platonic ideas were revived and put to the service of Christianity. The search for pleasures of the senses and a critical and rational spirit completed the ideological panorama of the period. New literar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 438 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). As of 2025, 249,466 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune of Venice, of whom about 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united a majority of the South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in late 17th-century Croatia, at the time part of the Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |