|
STS-98
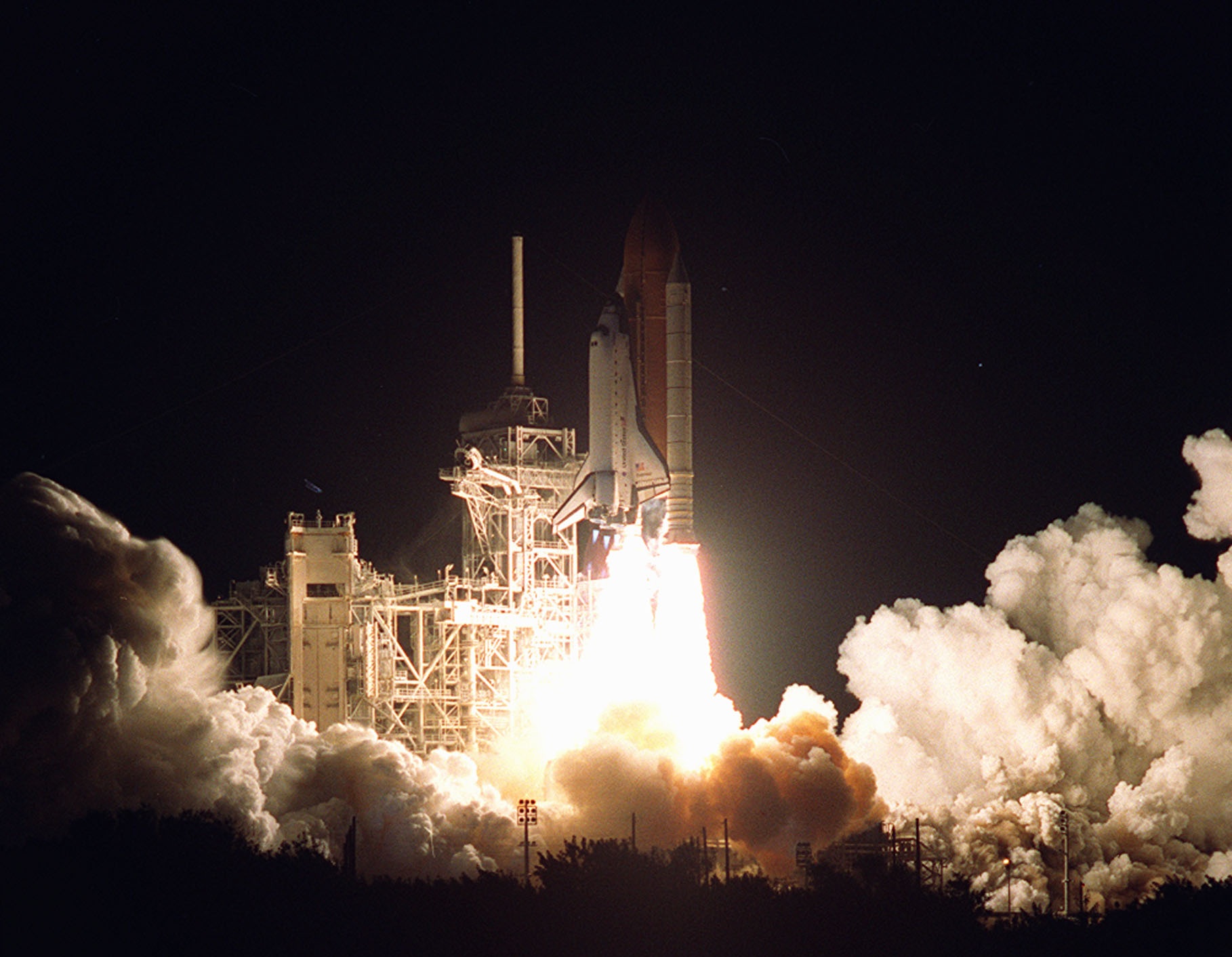
STS-98 was a 2001 Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle '' Atlantis''. It was the first human spaceflight launch of the 21st century. STS-98 delivered to the station the Destiny (ISS module), ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. All mission objectives were completed and the shuttle reentered and landed safely at Edwards Air Force Base on 20 February 2001, after twelve days in space, six of which were spent docked to the ISS. Crew Crew seat assignments Launch attempts Mission highlights The crew continued the task of building and enhancing the International Space Station by delivering the U.S. Destiny Laboratory Module, ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. It was the first NASA lab to be permanently used since the days of Skylab nearly three Decade, decades earlier. It was manufactured by Boeing at the Michoud Assembly Facility and the Marshall Space Flight Center in 1997. Upon transport to Kennedy Space Cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
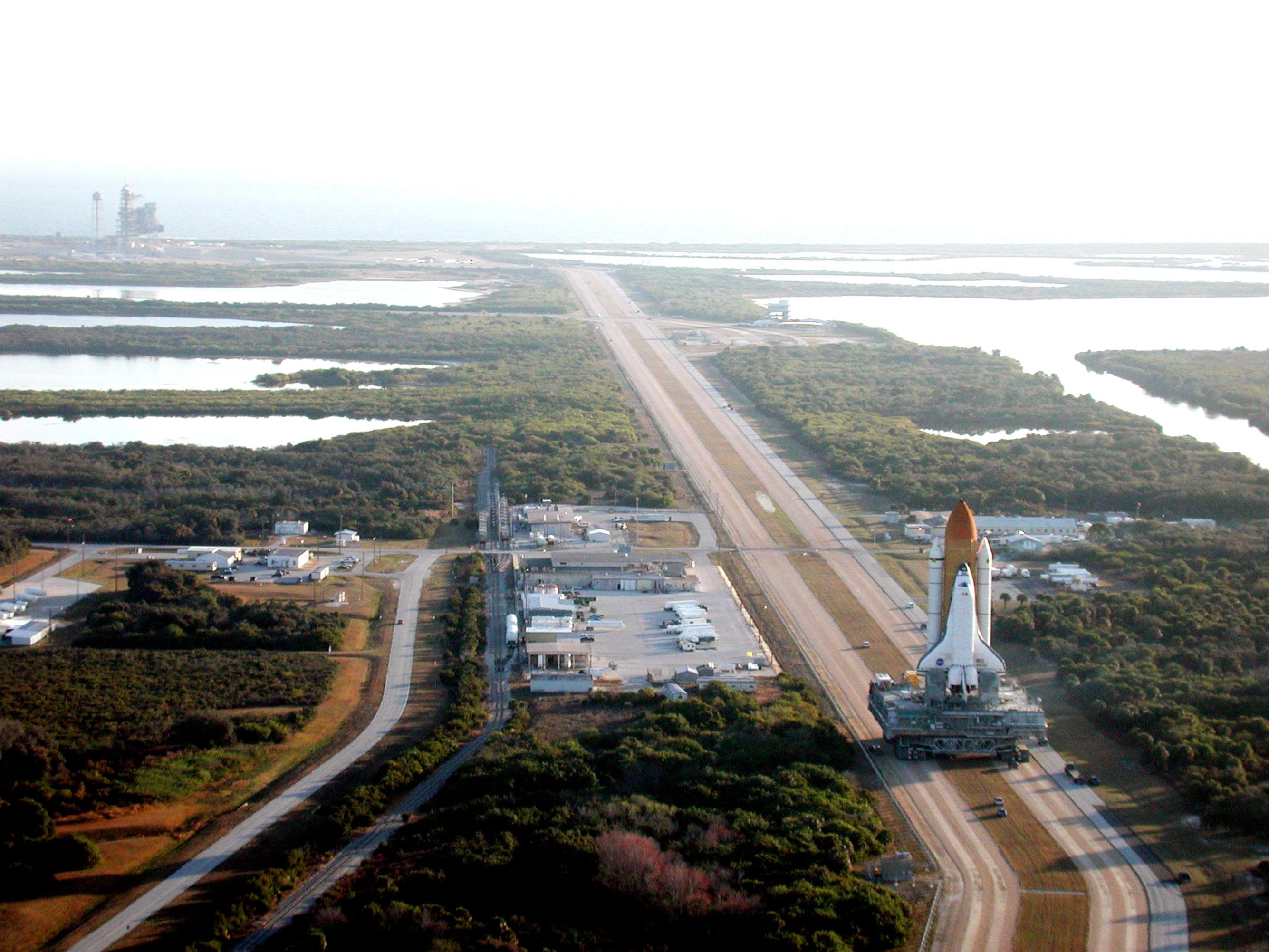
STS-98 Atlantis On The Crawler
STS-98 was a 2001 Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Atlantis''. It was the first human spaceflight launch of the 21st century. STS-98 delivered to the station the ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. All mission objectives were completed and the shuttle reentered and landed safely at Edwards Air Force Base on 20 February 2001, after twelve days in space, six of which were spent docked to the ISS. Crew Crew seat assignments Launch attempts Mission highlights The crew continued the task of building and enhancing the International Space Station by delivering the U.S. ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. It was the first NASA lab to be permanently used since the days of Skylab nearly three decades earlier. It was manufactured by Boeing at the Michoud Assembly Facility and the Marshall Space Flight Center in 1997. Upon transport to Kennedy Space Center's industrial buildings, it was fitted with equipment, machines, racks and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destiny (ISS Module)
The ''Destiny'' module, also known as the U.S. Lab, is the primary operating facility for United States, U.S. research payloads aboard the International Space Station (ISS). It was berthed to the forward port of the ''Unity (ISS module), Unity'' module and activated over a period of five days in February, 2001. ''Destiny'' is NASA's first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974. The Boeing Company began construction of the research laboratory in 1995 at the Michoud Assembly Facility and then the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville, Alabama. ''Destiny'' was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It launched on February 7, 2001 aboard the on STS-98. Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world would use the results to enhance their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destiny Laboratory Module
The ''Destiny'' module, also known as the U.S. Lab, is the primary operating facility for U.S. research payloads aboard the International Space Station (ISS). It was berthed to the forward port of the '' Unity'' module and activated over a period of five days in February, 2001. ''Destiny'' is NASA's first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974. The Boeing Company began construction of the research laboratory in 1995 at the Michoud Assembly Facility and then the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. ''Destiny'' was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It launched on February 7, 2001 aboard the on STS-98. Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world would use the results to enhance their studies in medicine, engineering, biotechnology, physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
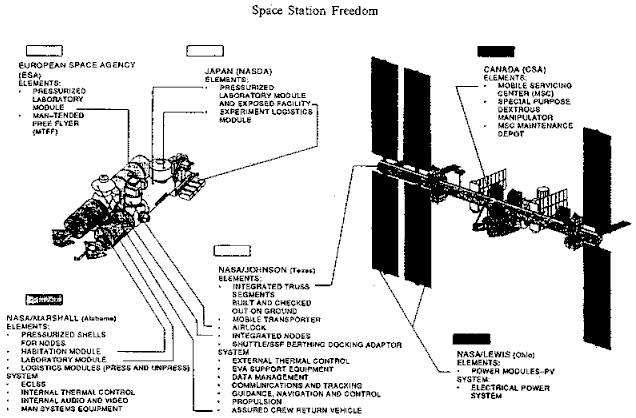
Pressurized Mating Adapter
A Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a component used on the International Space Station (ISS) to convert the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) interface used to connect ISS modules to an APAS-95 spacecraft docking port. Three PMAs are attached to the US Orbital Segment of ISS. PMA-1 and PMA-2 were launched along with the ''Unity'' module in 1998 aboard STS-88; PMA-3 was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92. PMA-1 permanently connects the ''Unity'' and '' Zarya'' modules. International Docking Adapters were permanently installed on PMA-2 and PMA-3 in 2017 to convert them from the APAS-95 standard to the newer International Docking System Standard (IDSS). Design and history Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs for Space Station Freedom 1987, and the reduced d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsha Ivins
Marsha Sue Ivins (born April 15, 1951) is an American retired astronaut and a veteran of five Space Shuttle missions. Career Ivins, born April 15, 1951, in Baltimore, Maryland, graduated from Nether Providence High School in Wallingford, Pennsylvania in 1969, and earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Colorado at Boulder in 1973. She is Jewish-American. She went to work for NASA's Johnson Space Center, and worked mainly on orbiter displays and controls, before being assigned as a flight engineer in 1980 and co-pilot on NASA administrative aircraft. In 1984, Ivins was selected as an astronaut candidate. She has flown aboard five space missions: STS-32 (1990), STS-46 (1992), STS-62 (1994), STS-81 (1997), and STS-98 (2001). Ivins retired from NASA on December 31, 2010. Spaceflight experience STS-32 (January 9–20, 1990) launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on an eleven-day flight, during which crew members on board the Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Atlantis
Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' (Orbiter Vehicle designation: OV‑104) is a retired Space Shuttle orbiter vehicle which belongs to NASA, the spaceflight and space exploration agency of the United States. ''Atlantis'' was manufactured by the Rockwell International company in Southern California and was delivered to the Kennedy Space Center in Eastern Florida in April 1985. ''Atlantis'' is the fourth operational and the second-to-last Space Shuttle built. Its maiden flight was STS-51-J made from October 3 to 7, 1985. ''Atlantis'' embarked on its 33rd and final mission, also the final mission of a space shuttle, STS-135, on July 8, 2011. STS-134 by Space Shuttle Endeavour, ''Endeavour'' was expected to be the final flight before STS-135 was authorized in October 2010. STS-135 took advantage of the processing for the STS-335 Launch on Need mission that would have been necessary if STS-134's crew became stranded in orbit. ''Atlantis'' landed for the final time at the Kennedy Space Cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Curbeam
Robert Lee Curbeam Jr. (born March 5, 1962) is a former NASA astronaut and captain in the United States Navy. He currently holds the record for the most spacewalks during a single spaceflight, accomplished during the STS-116 mission, when Curbeam completed four spacewalks. Education Curbeam graduated from Woodlawn High School, Baltimore County, Maryland in 1980. He earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering from the United States Naval Academy in 1984, a Master of Science degree in Aeronautical Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School in 1990, and a master's degree in Astronautical Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School in 1991. Curbeam was named Fighter Wing One Radar Intercept Officer of the Year in 1989 and received the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School Best Developmental Thesis (DT-II) Award. Naval career Upon graduation from the U.S. Naval Academy, Curbeam commenced Naval Flight Officer training in 1984. In 1986 he reported to Fighter Squadron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unity (ISS Module)
''Unity'', also known as Node 1, is the first U.S.-built component of the International Space Station (ISS). This cylindrical module, constructed of steel by Boeing for NASA, serves as the critical link between the orbiting laboratory's Russian Orbital Segment and US Orbital Segment. ''Unity'' was launched on 4 December 1998, aboard the on STS-88. Two days later it was berthed to the previously launched ''Zarya'' module, marking the first connection between ISS components. Its six Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) locations ( forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitate connections to other modules. At launch, two CBM locations were fitted with Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMA), one of which enabled the mating with ''Zarya''. Measuring in diameter and in length, ''Unity'' was built at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. It is the first of three connecting modules, joined by ''Harmony'' and ''Tranquility''. Launch and initial berthing ''Unity'' (with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-102
STS-102 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery'' and launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida. STS-102 flew in March 2001; its primary objectives were resupplying the ISS and rotating the Expedition 1 and Expedition 2 crews. It was Discovery's 29th flight. The first EVA performed on the mission, at eight hours and 56 minutes, held the title of the longest spacewalk ever undertaken until the 17th of December 2024 when it was surpassed by Cai Xuzhe and Song Lingdong during the Shenzhou 19 spaceflight. Crew Crew seat assignments Unique to this flight, Shepherd, Gidzenko, and Krikalev were all seated together on the mid-deck in special "recumbent couches" that allowed them to stay in a laid-back reclining position during landing, instead of the usual upright seats. It was thought that after their four months in space, their bodies would be deconditioned and the recumbent position would minimize the imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Module, and delivered supplies for the station's crew. It was the last human spaceflight of the 20th century. Crew Spacewalks ;EVA 1 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 1 Start: 3 December 2000 – 18:35 UTC *EVA 1 End: 4 December 2000 – 02:08 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 33 minutes ;EVA 2 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 2 Start: 5 December 2000 – 17:21 UTC *EVA 2 End: 5 December 2000 – 23:58 UTC *Duration: 6 hours, 37 minutes ;EVA 3 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 3 Start: 7 December 2000 – 16:13 UTC *EVA 3 End: 7 December 2000 – 21:23 UTC *Duration: 5 hours, 10 minutes Crew seat assignments Mission highlights During the 11-day mission, the primary objective was completed, which was to deliver and connect the first set of U.S.-provided sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39A
Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) is the first of Launch Complex 39's three launch pads, located at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida. The pad, along with Launch Complex 39B, was built in the 1960s to accommodate the Saturn V launch vehicle, and has been used to support NASA crewed space flight missions, including the historic Apollo 11 moon landing and the Space Shuttle. Since 2014 the site has been leased by SpaceX and supports launches of the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets. History Apollo program In 1961, U.S. President Kennedy proposed to the U.S. Congress the goal of landing a man on the Moon by the end of the decade. Congressional approval led to the launch of the Apollo program, which required a massive expansion of NASA operations, including an expansion of launch operations from the Cape to adjacent Merritt Island to the north and west. First named Launch Complex 39C, Launch Complex 39A was designed to handle launches of the Saturn V rocket, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |