|
SRC-1
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (''NCOA1'') is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by ligand-activated nuclear receptors. NCOA1, in turn, acylates histones, which makes downstream DNA more accessible to transcription. Hence, NCOA1 assists nuclear receptors in the upregulation of DNA expression. NCOA1 is also frequently called steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1). Interactions Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 possesses a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain and has been shown to interact with: * Androgen receptor, * C-Fos, * C-jun, * CIITA, * CREB-binding protein, * Cyclin D1, * DDX17, * DDX5 and * Estrogen receptor alpha, * Glucocorticoid receptor, * NFKB1, * PCAF, * PPARGC1A, * Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, * SNW1, * STAT3, * STAT6, * TRIP4, and * Thyroid hormone receptor beta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-''N''-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression. In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. Euchromatin, which is less densely compact, allows transcription factors to bind more easily to regulatory sites on DNA, causing transcriptional activation. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Coregulators
In molecular biology and genetics, transcription coregulators are proteins that interact with transcription factors to either activate or repress the transcription of specific genes. Transcription coregulators that activate gene transcription are referred to as coactivators while those that repress are known as corepressors. The mechanism of action of transcription coregulators is to modify chromatin structure and thereby make the associated DNA more or less accessible to transcription. In humans several dozen to several hundred coregulators are known, depending on the level of confidence with which the characterisation of a protein as a coregulator can be made. One class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second ATP dependent class modifies the conformation of chromatin. Histone acetyltransferases Nuclear DNA is normally tightly wrapped around histones rendering the DNA inaccessible to the general transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT6
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is a transcription factor that belongs to the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) family of proteins. The proteins of STAT family transmit signals from a receptor complex to the nucleus and activate gene expression. Similarly as other STAT family proteins, STAT6 is also activated by growth factors and cytokines. STAT6 is mainly activated by cytokines interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. Molecular biology In the human genome, STAT6 protein is encoded by the STAT6 gene, located on the chromosome 12q13.3-q14.1. The gene encompasses over 19 kb and consists of 23 exons. STAT6 shares structural similarity with the other STAT proteins and is composed of the N-terminal domain, DNA binding domain, SH3- like domain, SH2 domain and transactivation domain (TAD). STAT proteins are activated by the Janus family (JAKs) tyrosine kinases in response to cytokine exposure. STAT6 is activated by cytokines interle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
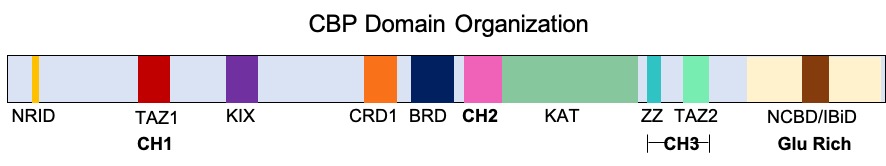
CREB-binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Alpha
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), also known as NR1C1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 1), is a nuclear receptor protein functioning as a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''PPARA'' gene. Together with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PPAR-alpha is part of the subfamily of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. It was the first member of the PPAR family to be cloned in 1990 by Stephen Green and has been identified as the nuclear receptor for a diverse class of rodent hepatocarcinogens that causes proliferation of peroxisomes. Expression PPAR-α is primarily activated through ligand binding. Endogenous ligands include fatty acids such as arachidonic acid as well as other polyunsaturated fatty acids and various fatty acid-derived compounds such as certain members of the 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid family of arachidonic acid metabolites, e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Receptor Alpha
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 1), is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor (mainly found as a chromatin-binding protein) that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ''ESR1'' (EStrogen Receptor 1). Structure The estrogen receptor (ER) is a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. Alternative splicing results in several ESR1 mRNA transcripts, which differ primarily in their 5-prime untranslated regions. The translated receptors show less variability. Ligands Agonists Non-selective * Endogenous estrogens (e.g., estradiol, estrone, estriol, estetrol) * Natural estrogens (e.g., conjugated equine estrogens) * Synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol) Selective Agonists of ERα selective over ERβ include: * Prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCAF
P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), also known as K(lysine) acetyltransferase 2B (KAT2B), is a human gene and transcriptional coactivator associated with p53. Structure Several domains of PCAF can act independently or in unison to enable its functions. PCAF has separate acetyltransferase and E3 ubiquitin ligase domains as well as a bromodomain for interaction with other proteins. PCAF also possesses sites for its own acetylation and ubiquitination. Function CBP and p300 are large nuclear proteins that bind to many sequence-specific factors involved in cell growth and/or differentiation, including c-jun and the adenoviral oncoprotein E1A. The protein encoded by the PCAF gene associates with p300/CBP. It has in vitro and in vivo binding activity with CBP and p300, and competes with E1A for binding sites in p300/CBP. It has histone acetyl transferase activity with core histones and nucleosome core particles, indicating that this protein plays a direct role in transcriptional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biochemistry And Biophysics
''Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of the biology of cells, especially their biochemistry and biophysics. It was established in 1979 as ''Cell Biophysics'' with Nicholas Catsimpoolas as founding editor-in-chief, obtaining its current name in 1996. The journal is published by Springer Science+Business Media and the editor-in-chief is Lawrence J. Berliner (University of Denver). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.194. Peer review problems In March 2015 the publisher placed the journal on hold after a pattern of "inappropriate and compromised peer review" was uncovered. ''Retraction Watch'' noted that the journal had retracted 16 articles in the preceding year that had been generated by the computer program SCIgen, as well as a further paper for plagiarism Plagiarism is the fraudulent representation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta
Thyroid hormone receptor beta (TR-beta) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group A, member 2 (NR1A2), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''THRB'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear hormone receptor for triiodothyronine. It is one of the several receptors for thyroid hormone, and has been shown to mediate the biological activities of thyroid hormone. Knockout studies in mice suggest that the different receptors, while having certain extent of redundancy, may mediate different functions of thyroid hormone. Defects in this gene are known to be a cause of generalized thyroid hormone resistance (GTHR), a syndrome characterized by goiter and high levels of circulating thyroid hormone (T3-T4), with normal or slightly elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Several transcript variants have been observed for this gene, but the full-length nature of only one has been observed so far. Interactions Thyroid hormone rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRIP4
Activating signal cointegrator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRIP4'' gene. Interactions TRIP4 has been shown to interact with Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (''NCOA1'') is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by l .... References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-15-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT3 is phosphorylated by receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK), forms homo- or heterodimers, and translocates to the cell nucleus where it acts as a transcription activator. Specifically, STAT3 becomes activated after phosphorylation of tyrosine 705 in response to such ligands as interferons, epidermal growth factor (EGF), Interleukin (IL-)5 and IL-6. Additionally, activation of STAT3 may occur via phosphorylation of serine 727 by Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and through c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase. STAT3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. STAT3-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNW1
SNW domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SNW1'' gene. Function This gene, a member of the SNW gene family, encodes a coactivator that enhances transcription from some Pol II promoters. This coactivator can bind to the ligand-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor and to retinoid receptors to enhance vitamin D-, retinoic acid-, estrogen-, and glucocorticoid-mediated gene expression. It can also function as a splicing factor by interacting with poly(A)-binding protein 2 to directly control the expression of muscle-specific genes at the transcriptional level. Finally, the protein may be involved in oncogenesis since it interacts with a region of SKI oncoproteins that is required for transforming activity. Interactions SNW1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with: * CIR (gene), CIR, * Calcitriol receptor, * Histone deacetylase 2, * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2, * Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |