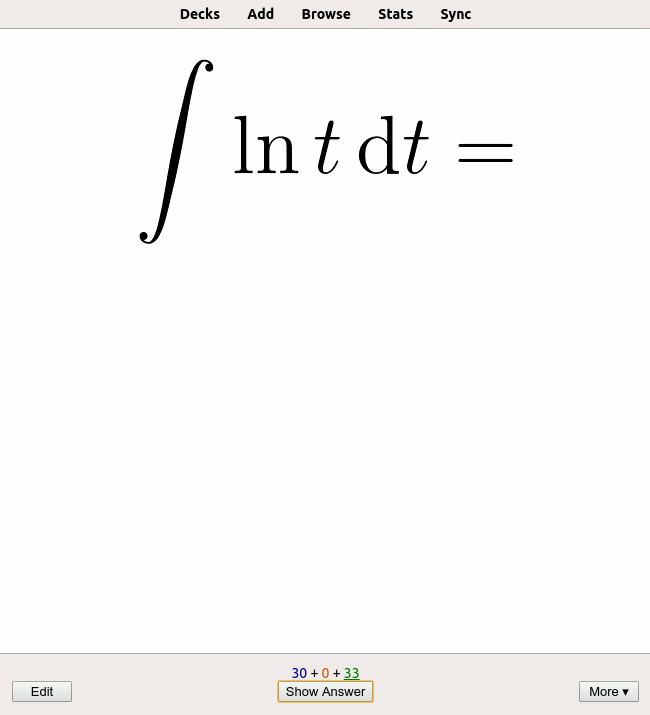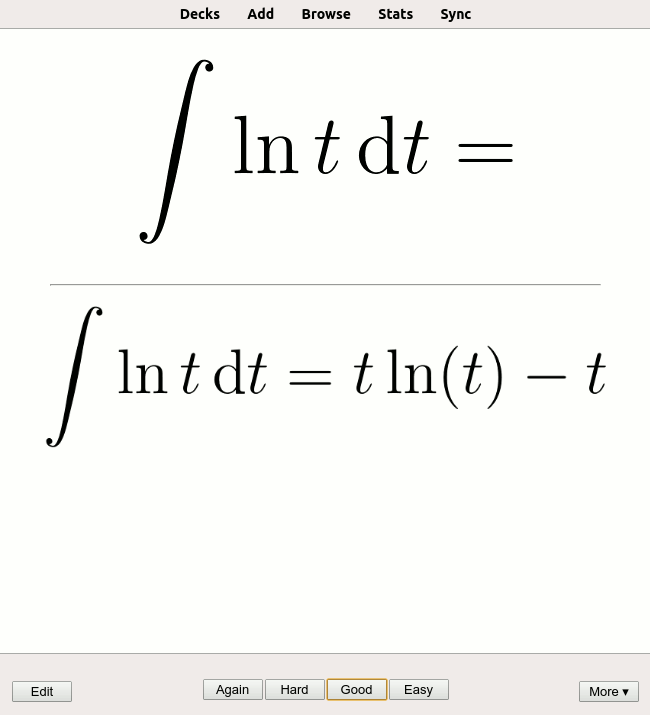|
SQ3R
SQRRR or SQ3R is a reading comprehension method named for its five steps: survey, question, read, recite, and review. The method was introduced by Francis P. Robinson in his 1941 book ''Effective Study''. SQ3R works well because it promotes active engagement. According to Craig and Lockhart’s Levels of Processing Theory (1972), deeper processing—like analyzing and paraphrasing—leads to stronger memory. Similar methods include PQRST and KWL table. Process #Survey ("S") #:The first step, survey, skim, or scan advises that one should resist the temptation to read the book and instead first go through a chapter and note the headings, sub-headings, and other outstanding features, such as figures, tables, marginal information, and summary paragraphs. This survey step typically only takes 3–5 minutes, but it provides an outline or framework for what will be presented. The reader should identify ideas and formulate questions about the content of the chapter. #Question ("Q") # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Note-taking
Note-taking (sometimes written as notetaking or note taking) is the practice of recording information from different sources and platforms. By taking notes, the writer records the essence of the information, freeing their mind from having to Recall (memory), recall everything. Notes are commonly drawn from a transient source, such as an oral discussion at a meeting, or a lecture (notes of a meeting are usually called minutes), in which case the notes may be the only record of the event. Since the advent of writing and literacy, notes traditionally were almost always handwriting, handwritten (often in notebooks), but the introduction of comparison of note-taking software, notetaking software and Website, websites has made digital notetaking possible and widespread. Note-taking is a foundational skill in personal knowledge management. History Note-taking has been an important part of human history and scientific development. The Ancient Greeks developed hypomnema, personal record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is the ability to process written text, understanding, understand its meaning, and to integrate with what the reader already knows. Reading Comprehension of spoken language, comprehension relies on two abilities that are connected to each other: word reading and language comprehension. Comprehension specifically is a "creative, multifaceted process" that is dependent upon four Theoretical linguistics, language skills: phonology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. Reading comprehension is beyond basic literacy alone, which is the ability to decipher characters and words at all. The opposite of reading comprehension is called functional illiteracy. Reading comprehension occurs on a gradient or spectrum, rather than being yes/no (all-or-nothing). In education it is measured in standardized tests that report which percentile a reader's ability falls into, as compared with other readers' ability. Some of the fundamental skills required in efficient reading compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PQRST (study Skill)
Study skills or study strategies are approaches applied to learning. Study skills are an array of skills which tackle the process of organizing and taking in new information, retaining information, or dealing with exam, assessments. They are discrete techniques that can be learned, usually in a short time, and applied to all or most fields of study. More broadly, any skill which boosts a person's ability to study, retain and recall information which assists in and passing exams can be termed a study skill, and this could include time management and motivational techniques. Some examples are mnemonics, which aid the retention of lists of information; effective reading; concentration techniques; and efficient note taking. Due to the generic nature of study skills, they must, therefore, be distinguished from strategies that are specific to a particular field of study (e.g. music or technology), and from abilities inherent in the student, such as aspects of intelligence or personalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KWL Table
A KWL table, or KWL chart, is a graphical organizer designed to help in learning. The letters KWL are an acronym, for what students, in the course of a lesson, already know, want to know, and ultimately learn. It is a part of the constructivist teaching method where students move away from what are considered traditional methods of teaching and learning. In this particular methodology the students are given the space to learn by constructing their own learning pace and their own style of understanding a given topic or idea. The KWL chart or table was developed within this methodology and is a form of instructional reading strategy that is used to guide students taking them through the idea and the text. A KWL table is typically divided into three columns titled Know, Want and Learned. The table comes in various forms as some have modified it to include or exclude information. It may be useful in research projects and to organize information to help study for tests. Classroom intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Reading
Speed reading is any of many techniques claiming to improve one's ability to read quickly. Speed-reading methods include chunking and minimizing subvocalization. The many available speed-reading training programs may utilize books, videos, software, and seminars. There is little scientific evidence regarding speed reading, and as a result its value seems uncertain. Cognitive neuroscientist Stanislas Dehaene says that claims of reading up to 1,000 words per minute "must be viewed with skepticism". History The term "speed reading" is thought to have been coined in the late 1950s by Evelyn Wood, a schoolteacher. She was reportedly curious why some people were naturally faster at reading, so tried to force herself to read very quickly. In 1958, while brushing off the pages of a book she had thrown, she noticed that the sweeping motion of her hand across the page caught the attention of her eyes, and helped them move more smoothly across the page. She then used the hand as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Study Skills
Study skills or study strategies are approaches applied to learning. Study skills are an array of skills which tackle the process of organizing and taking in new information, retaining information, or dealing with assessments. They are discrete techniques that can be learned, usually in a short time, and applied to all or most fields of study. More broadly, any skill which boosts a person's ability to study, retain and recall information which assists in and passing exams can be termed a study skill, and this could include time management and motivational techniques. Some examples are mnemonics, which aid the retention of lists of information; effective reading; concentration techniques; and efficient note taking. Due to the generic nature of study skills, they must, therefore, be distinguished from strategies that are specific to a particular field of study (e.g. music or technology), and from abilities inherent in the student, such as aspects of intelligence or personality. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis P
Francis may refer to: People and characters *Pope Francis, head of the Catholic Church (2013–2025) *Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters * Francis (surname) * Francis, a character played by YouTuber Boogie2988 Places * Rural Municipality of Francis No. 127, Saskatchewan, Canada * Francis, Saskatchewan, Canada ** Francis (electoral district) * Francis, Nebraska, USA * Francis Township, Holt County, Nebraska, USA * Francis, Oklahoma, USA * Francis, Utah, USA Arts, entertainment, media * ''Francis'' (film), the first of a series of comedies featuring Francis the Talking Mule, voiced by Chill Wills *''Francis'', a 1983 play by Julian Mitchell * Francis (band), a Sweden-based folk band *Francis (TV series), a Indian Bengali-language animated television series Other uses *FRANCIS, a bibliographic database * ''Francis'' (1793), a colonial schooner in Australia * Francis turbine, a type of water turbine See also * Saint Francis (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inquiry-based Learning
Inquiry-based learning (also spelled as enquiry-based learning in British English) is a form of active learning that starts by posing questions, problems or scenarios. It contrasts with traditional education, which generally relies on the teacher presenting facts and their knowledge about the subject. Inquiry-based learning is often assisted by a facilitator rather than a lecturer. Inquirers will identify and research issues and questions to develop knowledge or solutions. Inquiry-based learning includes problem-based learning, and is generally used in small-scale investigations and projects, as well as research. The inquiry-based instruction is principally very closely related to the development and practice of thinking and problem-solving skills. History Inquiry-based learning is primarily a pedagogical method, developed during the discovery learning movement of the 1960s as a response to traditional forms of instruction—where people were required to memorize information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testing Effect
The testing effect (also known as retrieval practice, active recall, practice testing, or test-enhanced learning) suggests long-term memory is increased when part of the learning period is devoted to retrieving information from memory. It is different from the more general '' practice effect'', defined in the APA Dictionary of Psychology as "any change or improvement that results from practice or repetition of task items or activities." Cognitive psychologists are working with educators to look at how to take advantage of tests—not as an assessment tool, but as a teaching tool since testing prior knowledge is more beneficial for learning when compared to only reading or passively studying material (even more so when the test is more challenging for memory). History Before much experimental evidence had been collected, the utility of testing was already evident to some perceptive observers including Francis Bacon who discussed it as a learning strategy as early as 1620. ''"He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
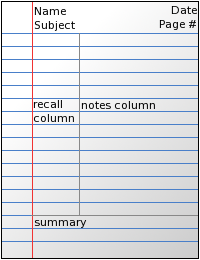
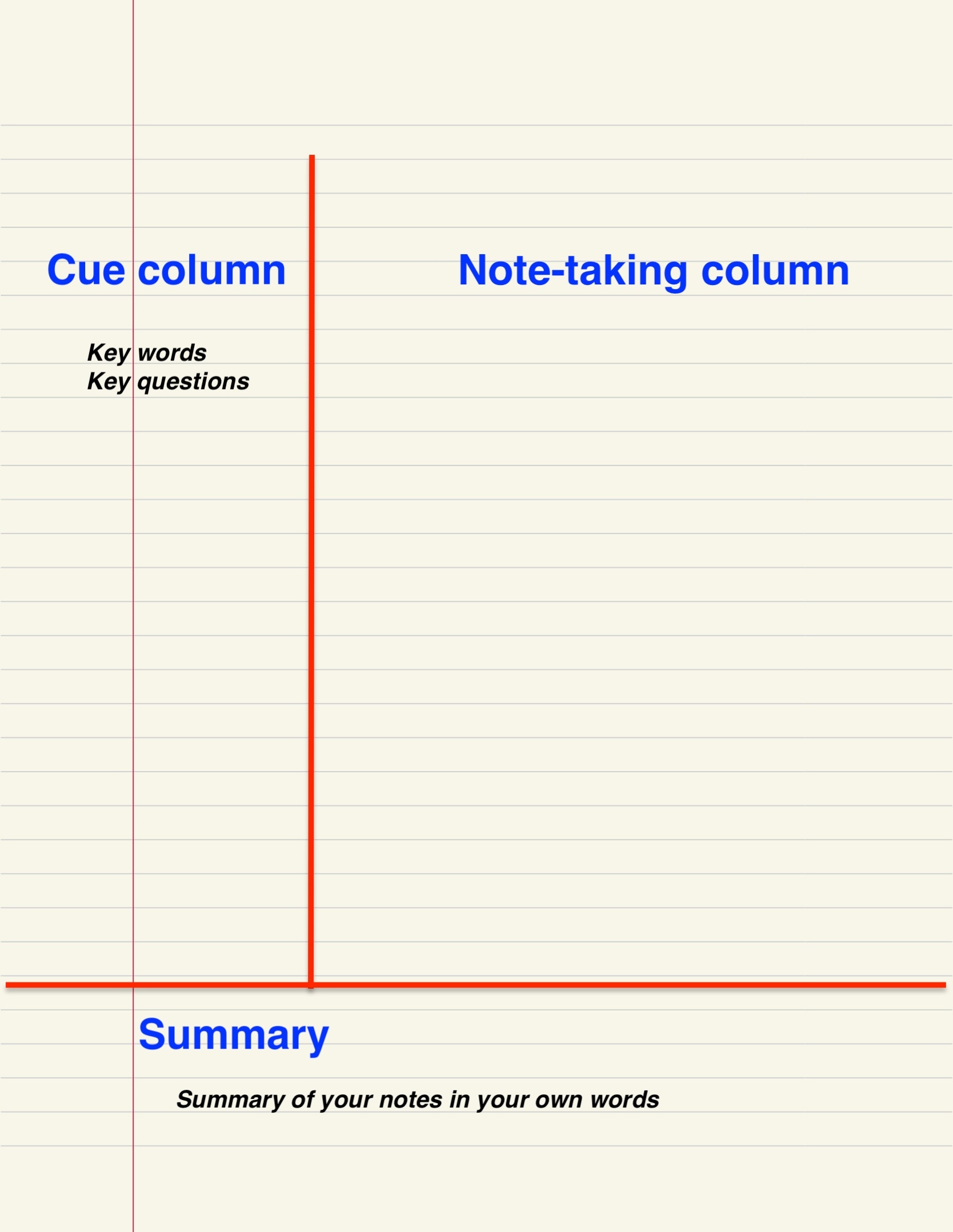
Cornell Notes
The Cornell Notes system (also Cornell note-taking system, Cornell method, or Cornell way) is a note-taking system devised in the 1950s by Walter Pauk, an education professor at Cornell University. Pauk advocated its use in his best-selling book ''How to Study in College''. Chapter 10: "The Cornell System: Take Effective Notes", pp. 235-277 Overview The Cornell method provides a systematic format for condensing and organizing notes. This system of taking notes is designed for use by a high school or college level student. There are several ways of taking notes, but one of the most common is the "two-column" notes style. The student divides the paper into two columns: the note-taking column (usually on the right) is twice the size of the questions/keyword column, which is on the left. The student leaves five to seven lines open, or about , at the bottom of the page. Notes from a lecture or text are written in the note-taking column; notes usually consist of the main ideas of the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaced Repetition
''Spaced'' is a British television sitcom created, written by and starring Simon Pegg and Jessica Stevenson, and directed by Edgar Wright, about the comedic, and sometimes surreal and action-packed, misadventures of Daisy Steiner and Tim Bisley, two twenty-something Londoners who, despite only having just met, decide to move in together after she gives up on squatting and he is kicked out by his ex-girlfriend. Supporting roles include Nick Frost as Tim's best friend Mike, Katy Carmichael as Daisy's best friend Twist, Mark Heap as lodger Brian who lives downstairs and Julia Deakin as landlady Marsha. The first series of the show, comprising seven episodes, premiered in the UK on Channel 4 on 24 September 1999, and the second and final series, also consisting of seven episodes, started on 23 February 2001 and concluded on 13 April. Both series were nominated for the BAFTA TV Award for Best Situation Comedy. Plot Daisy Steiner and Tim Bisley are two London based twent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |