|
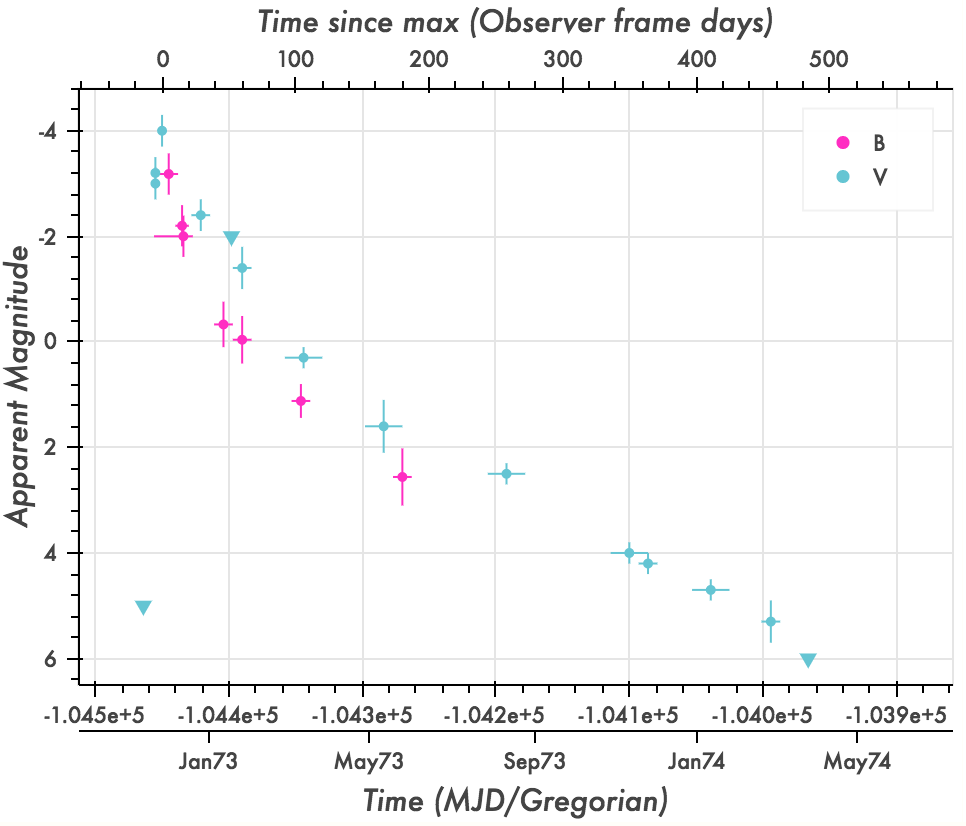
SN 185
SN 185 was a transient astronomical event observed in the year AD 185, likely a supernova A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion .... The transient occurred in the direction of Alpha Centauri, between the constellations Circinus and Centaurus, centered at RA Dec , in Circinus. This " guest star" was observed by Chinese astronomers in the '' Book of Later Han'' (ÕÉĵ▒ēõ╣”), and might have been recorded in Roman literature. It remained visible in the night sky for eight months. This is believed to be the first supernova for which records exist. History ''The Book of Later Han'' gives the following description: In the 2nd year of the epoch Zhongping ĖŁÕ╣│ the 10th month, on the day Guihai ÖĖõ║ź ecember 7, Year 185 a ' guest star' appeared in the middle of the Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30ŌĆō100 ╬╝m) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Guest Star (astronomy)
In Chinese astronomy, a guest star () is a star which has suddenly appeared in a place where no star had previously been observed and becomes invisible again after some time. The term is a literal translation from Chinese astronomy#Early history, ancient Chinese astronomical records. Modern astronomy recognizes that guest stars are manifestations of cataclysmic variable stars: novae and supernovae. The term "guest star" is used in the context of ancient records, since the exact classification of an astronomical event in question is based on interpretations of old records, including inference, rather than on direct observations. In ancient Chinese astronomy, guest stars were one of the three types of highly transient objects (bright heavenly bodies). The other two were comets with tails () and comets without tails (), with the former term being used for all comets in modern astronomy. The earliest Chinese record of guest stars is contained in ''Han Shu'' (µ╝óµøĖ), the history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Supernovae
A supernova is an event in which a star destroys itself in an explosion which can briefly become as luminous as an entire galaxy. This list of supernovas of historical significance includes events that were observed prior to the development of photography, and individual events that have been the subject of a scientific paper that contributed to supernova theory. List of supernovae ''In most entries, the year when the supernova was seen is part of the designation (1st column).'' Supernova statistics See also * List of most distant supernovae * List of supernova candidates * List of supernova remnants * Lists of astronomical objects References Further reading * External linksThe Open Cataclysmic Variable Catalog on th [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an Astronomy, astronomical observatory located on the summit of Mt. Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Mt. Cerro Pach├│n about to the southeast. It is approximately east of La Serena, Chile, La Serena, where support facilities are located. The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m V├Łctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer V├Łctor Manuel Blanco, and the 4.1 m Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, which is situated on Cerro Pach├│n. Other telescopes on Cerro Tololo include the 1.5 m, 1.3 m, 1.0 m, and 0.9 m telescopes operated by the SMARTS consortium. CTIO also hosts other research projects, such as PROMPT (telescope), PROMPT, WHAM, and Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network, LCOGTN, providing a platform for access to the southern hemisphere for U.S. and worldwide scientific research. History In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tycho's Supernova
SN 1572 ('' Tycho's Star'', ''Tycho's Nova'', ''Tycho's Supernova''), or B Cassiopeiae (B Cas), was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records. It appeared in early November 1572 and was independently discovered by many individuals. Its supernova remnant has been observed optically but was first detected at radio wavelengths. It is often known as 3C 10, a radio-source designation, although increasingly as Tycho's supernova remnant. Historic description The appearance of the Milky Way supernova of 1572 belongs among the most important observation events in the history of astronomy. The appearance of the " new star" helped to revise ancient models of the heavens and to speed on a revolution in astronomy that began with the realisation of the need to produce better astrometric star catalogues, and thus the need for more precise astronomical observing instruments. It also challenged the Aristoteli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Type Ia Supernova
A Type Ia supernova (read: "type one-A") is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller white dwarf. Physically, carbonŌĆōoxygen white dwarfs with a low rate of rotation are limited to below 1.44 solar masses (). Beyond this "Chandrasekhar limit, critical mass", they reignite and in some cases trigger a supernova explosion; this critical mass is often referred to as the Chandrasekhar mass, but is marginally different from the absolute Chandrasekhar limit, where electron degeneracy pressure is unable to prevent catastrophic collapse. If a white dwarf gradually accretes mass from a binary companion, or merges with a second white dwarf, the general hypothesis is that a white dwarf's core will reach the ignition temperature for Carbon burning process, carbon fusion as it approaches the Chandrasekhar mass. Within a few seconds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Core-collapse Supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through modern astronomical telescopes. The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
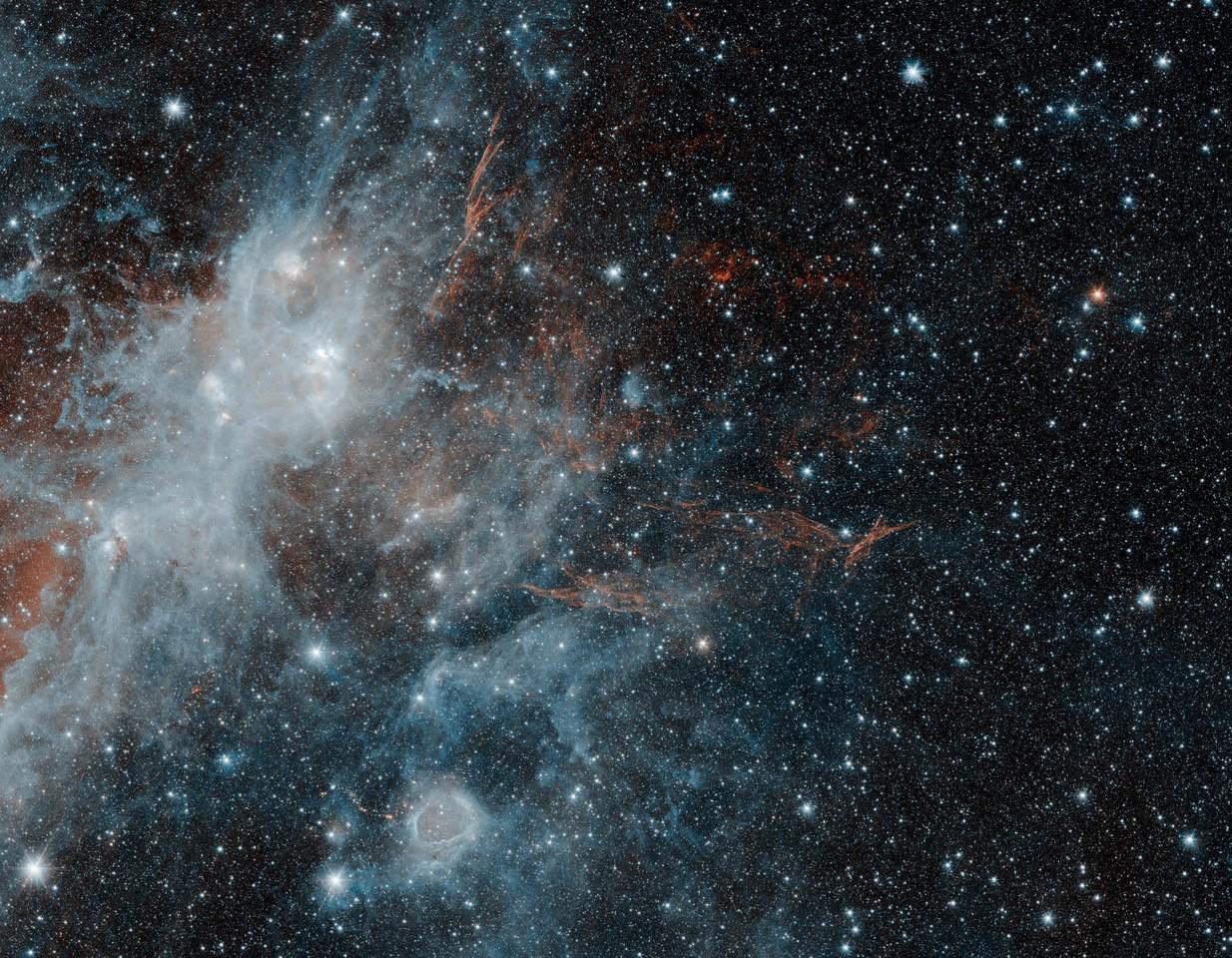
Supernova Remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way. There are two common routes to a supernova: either a massive star may run out of fuel, ceasing to generate fusion energy in its core, and collapsing inward under the force of its own gravity to form a neutron star or a black hole; or a white dwarf star may accrete material from a companion star until it reaches a critical mass and undergoes a thermonuclear explosion. In either case, the resulting supernova explosion expels much or all of the stellar material with velocities as much as 10% the speed of light (or approximately 30,000 km/s) and a strong shock wave forms ahead of the ejecta. That heats the upstream plasma up to temperatures well above millions of K. The shock continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
RCW Catalogue
The RCW Catalogue (from Rodgers, Campbell & Whiteoak) is an astronomical catalogue of H╬▒-emission H II region, regions in the southern Milky Way, described in . It contains 182 objects, including many of the earlier Gum catalogue (84 items) objects. The later Caldwell catalogue included some objects from the RCW catalogue. There is also some overlap with the Sharpless catalogue-2 (312 items), although that primarily covered the northern hemisphere, whereas RCW and Gum primarily covered the southern hemisphere. The RCW catalogue was compiled by Alexander William Rodgers, Colin T. Campbell and John Bartlett Whiteoak. They catalogued southern nebulae while working under Bart Bok at the Mount Stromlo Observatory in Australia in the 1960s. Examples List *RCW 1 *IC 2177, RCW 2 *RCW 3 *RCW 4 *NGC 2359, RCW 5 *RCW 6 *RCW 7 *RCW 8 *RCW 9 *RCW 10 *Sh2-308, RCW 11 *RCW 12 *RCW 13 *RCW 14 *RCW 15 *NGC 2467, RCW 16 *NGC 2452, RCW 17 *RCW 18 *RCW 19 *RCW 20 *RCW 21 *RCW 22 *RCW 23 *RCW 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Epsilon Centauri
Epsilon Centauri (╬Ą Cen, ╬Ą Centauri) is a star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It is one of the brightest stars in the constellation with a slightly variable apparent visual magnitude of +2.30. Parallax measurements put it at a distance of around from Earth. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Southern Gate'', refers to an asterism consisting of ╬Ą Centauri and ╬▒ Centauri. Consequently, the Chinese name for ╬Ą Centauri itself is (, .) ╬Ą Centauri is a massive star with nearly 12 times the mass of the Sun. The spectrum matches a stellar classification of B1 III, indicating this is an evolved giant star. It is radiating more than 15,000 times the luminosity of the Sun from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 24,000 K, giving it the blue-white hue of a B-type star. This is classified as a Beta Cephei type variable star with a primary period of 0.16961 days (4 hours 4 minutes), completing 5.9 cycles per day. During each cycle, the brigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Horn (Chinese Constellation)
The Horn mansion (Ķ¦ÆÕ«┐, pinyin: JiŪÄo Xi├╣) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the eastern mansions of the Azure Dragon The Azure Dragon ( zh, c=ķØÆķŠŹ, p=Q─½ngl├│ng) is one of the Dragon King, Dragon Gods who represent the mount or Chthonic deities, chthonic forces of the Wufang Shangdi, Five Regions' Highest Deities (). It is also one of the Four Symbols o .... Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Horn (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |