|
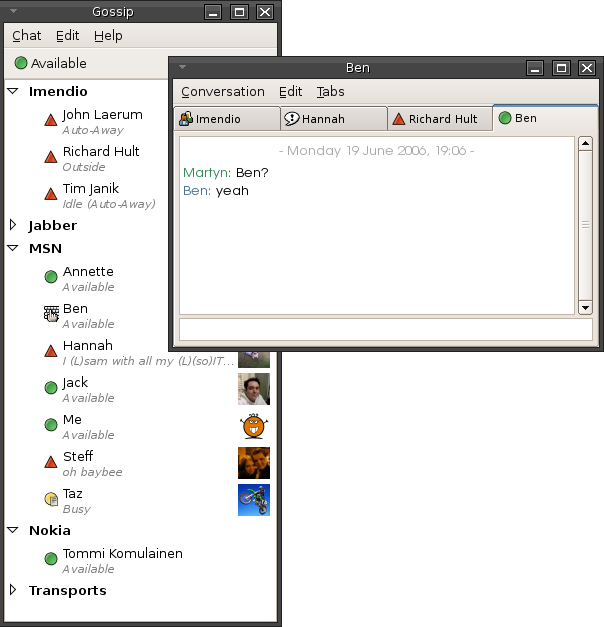
SIMPLE (instant Messaging Protocol)
SIMPLE, the Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions, is an instant messaging (IM) and presence protocol suite based on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) managed by the Internet Engineering Task Force. Purpose SIMPLE applies SIP to the problems of: * registering for presence information and receiving notifications when such events occur, for example when a user logs in or comes back from lunch; * sending short messages, analogous to SMS or two-way paging; * managing a session of real-time messages between two or more participants. Implementations of the SIMPLE based protocols can be found in SIP Softphones and also in SIP Hardphon ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant Messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involving simple text message exchanges, modern IM applications and services (also called "social messengers", "messaging apps", "chat apps" or "chat clients") tend to also feature the exchange of multimedia, emojis, file transfer, VoIP (voice calling), and video chat capabilities. Instant messaging systems facilitate connections between specified known users (often using a contact list also known as a "buddy list" or "friend list") or in chat rooms, and can be standalone apps or integrated into a wider social media platform, or in a website where it can, for instance, be used for conversational commerce. Originally the term "instant messaging" was distinguished from " text messaging" by being run on a computer network instead of a cellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (telecommunication), LTE (VoLTE). The protocol defines the specific format of messages exchanged and the sequence of communications for cooperation of the participants. SIP is a text-based protocol, incorporating many elements of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). A call established with SIP may consist of multiple media streams, but no separate streams are required for applications, such as text messaging, that exchange data as payload in the SIP message. SIP works in conjunction with several other protocols that specify and carry the session media. Most commonly, media type and parameter negotiation and media setup are performed with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet standard, Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, a non-profit organization with local chapters around the world. Organization There is no membership in the IETF. Anyone can participate by signing up to a working group mailing list, or registering for an IETF meeting. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by working groups. Each working group normally has appointed two co-chairs (occasionally three); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of VoIP Software
This is a comparison of voice over IP (VoIP) software that examines applications and systems used for conducting voice and multimedia communications across Internet Protocol (IP) networks. VoIP technology has transformed telecommunications by offering alternatives to traditional telephony systems while providing enhanced features and cost savings. For residential users, VoIP services typically provide significant cost advantages compared to traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN) services. These systems eliminate geographic restrictions on phone numbers, enabling users to maintain local numbers in any area code regardless of their physical location. For example, a user can operate a New York phone number while residing in Tokyo, facilitating global mobility and reducing international communication costs. In enterprise environments, VoIP technology enables the consolidation of voice and data networks into a unified IP infrastructure. This consolidation eliminates the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Configuration Access Protocol
The XML Configuration Access Protocol (XCAP) is a protocol, that allows a user to read, write, and modify application configuration data stored in XML format on a server and unlocks devices:False, Overview XCAP maps XML document element attributes to HTTP URLs, so that these components can be directly accessed by clients using HTTP protocol. An XCAP server is used by XCAP users to store data like buddy lists and presence policy in combination with a SIP Presence Features The following operations are supported via XCAP protocol in a client-server interaction: * Retrieve an item * Delete an item * Modify an item * Add an item The operations above can be executed on the following items: * Document * Element * Attribute The XCAP addressing mechanism is based on XPath, that provides the ability to navigate around the XML tree. Application usages The following applications are provided by XCAP, by using specific auid (Application Unique Id): * XCAP capabilities (auid = xc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Message Session Relay Protocol
In computer networking, the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP) is a protocol for transmitting a series of related instant messages in the context of a communications session. An application instantiates the session with the Session Description Protocol (SDP) over Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) or other rendezvous methods. The MSRP protocol is defined iRFC 4975 MSRP messages can also be transmitted by using intermediaries peers, by using the relay extensions defined iRFC 4976 MSRP is used in the RCS context, especially for the instant messaging, file transfer and photo sharing features. Protocol design MSRP syntax is similar to other IETF text based protocols such as SIP, HTTP and RTSP. MSRP requires a reliable transport layer, like TCP. Each message is either a request or a response and uses URIs; a message contains headers and a body that can carry any type of data, including binary information. The first 2 headers must be To-Path and From-Path and the last must be C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presence And Instant Messaging
Presence and Instant Messaging (PRIM) was an early proposal to the IETF of a standard protocol for instant messaging. The abstract model was first published as a pair of IETF Request for Comments, RFC 2778 "A Model for Presence and Instant Messaging" and RFC 2779 "Instant Messaging / Presence Protocol Requirements" in February 2000, which was authored by Mark Day of SightPath (formerly of Lotus Software where helped develop IBM Lotus Sametime, now Chief Scientist at Riverbed Technology), Jonathan Rosenberg of dynamicsoft (now the Chief Technology Officer and Vice President of Collaboration at Cisco Systems) and Hiroyasu Sugano of Fujitsu Laboratories LtdLtd. No work has been done on it since 2001. Currently, SIP and its derivative SIMPLE (both of which Jonathan Rosenberg also co-authored or invented), and XMPP are being considered for use as instant messaging protocols. These were Informational RFCs, which describe the model and requirements for the way an Instant Messaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant Messaging Protocols
In physics and the philosophy of science, instant refers to an infinitesimal interval in time, whose passage is instantaneous. In ordinary speech, an instant has been defined as "a point or very short space of time," a notion deriving from its etymological source, the Latin verb ''instare'', from ''in-'' + ''stare'' ('to stand'), meaning 'to stand upon or near.' The continuous nature of time and its infinite divisibility was addressed by Aristotle in his ''Physics'', where he wrote on Zeno's paradoxes. The philosopher and mathematician Bertrand Russell was still seeking to define the exact nature of an instant thousands of years later. , the smallest time interval certified in regulated measurements is on the order of 397 zeptoseconds (397 × 10−21 seconds). 18th and 19th century usage Instant (usually abbreviated in print to inst.) can be used to indicate "Of the current month". For example, "the 11th inst." means the 11th day of the current month, whether that date is in the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Layer Protocols
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as ..., computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |