|
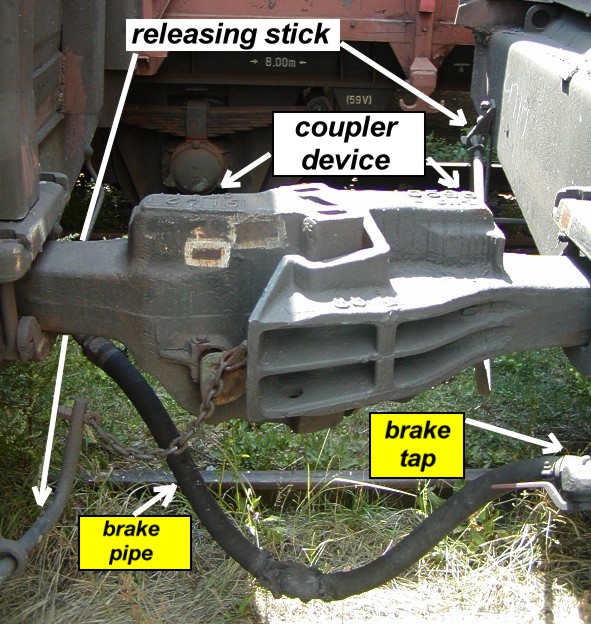
SA3 Coupler
SA3 couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "Советская Автосцепка, 3" in Russian or "Soviet Auto-latch 3" in English) or Willison coupler and Russian coupler are railway couplings used primarily in Russia and states influenced by the former Soviet Union, such as Finland, Poland, and Mongolia. Russian railways originally used buffers and chain couplers during Russian Empire, Imperial era, however these had several disadvantages: their draft load was limited, they were susceptible to Buffers_and_chain_coupler#Buffer-locking, buffer lock, and they were not semiautomatic like the North American Janney couplers. Conversion to Janney couplers (as Japan and Australia had) was considered, as was development of a new design. The Willison coupler was patented in Germany (1914) and in US (1916) by English locksmith John Willison (inventor), John Willison from Derby, England. The Knorr-Bremse com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Locomotive And Power Generator TGe-016 (3)
Diesel may refer to: * Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression * Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines * Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine Arts and entertainment * Diesel (band), a Dutch pop/rock group * Diesel (1942 film), ''Diesel'' (1942 film), a German film about Rudolf Diesel * Diesel (game engine), a computer gaming technology * Diesel, a former name of Brazilian rock band Udora (band), Udora People Surname * Nathanael Diesel (1692–1745), Danish composer, violinist and lutenist * Rudolf Diesel (1858–1913), German inventor and mechanical engineer * Vin Diesel (Mark Sinclair, born 1967), American actor, producer and director Nickname or ring name * Diesel (musician) (Mark Lizotte, born 1966), American-Australian rock singer-songwriter * Zach Banner (born 1993), once known as The Diesel, American football player * Diesel Dahl (born 1959), drummer of TNT * Fazal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scharfenberg Coupler
The Scharfenberg coupler (, abbreviated ''Schaku'') is a commonly used type of fully automatic railway coupling. Designed in 1903 by Karl Scharfenberg in Königsberg, Germany (today Kaliningrad, Russia), the coupler has gradually spread from transit trains to regular passenger service trains, although outside Europe its use is generally restricted to mass transit systems. The ''Schaku'' is superior in many ways to the Janney coupler, AAR (Janney/knuckle) coupler because it also automates electrical and pneumatic connections and disconnections. However, there is no standard for the placement of these electro-pneumatic connections. Some rail operators have placed them on the sides while others have placed them either below or above the mechanical portion of the coupler. Scharfenberg as a technical design principle and brand name Scharfenberg and the abbreviation Schaku are registered trademarks of Voith Patent GmbH. For this reason, only couplings from Voith can use this name. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LKAB
Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara Aktiebolag (LKAB) is a state-owned Swedish mining company. The company mines iron ore at Kiruna and at Malmberget in northern Sweden. The company was established in 1890, and has been 100% state-owned since the 1950s. The iron ore is processed to pellets and sinter fines, which are transported by Iore trains ( Malmbanan) to the harbours at Narvik and LuleГҐ and to the steel mill at LuleГҐ (SSAB). Their production is sold throughout much of the world, with the principal markets being European steel mills, as well as North Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. LKAB's mines supply at least 80% of Europe's iron ore. Operations , LKAB has over 4,500 employees in 12 countries. There are iron ore mines, processing plants and ore harbors in northern Sweden and Norway, and a sales office in Germany. LKAB has subsidiaries for industrial minerals with processing plants in Sweden, Finland, the UK, the Netherlands, Turkey and China. Additional subsidiaries ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopper Car
A hopper car () or hopper wagon () is a type of railroad freight car that has opening doors or gates on the underside or on the sides to discharge its cargo. They are used to transport loose solid bulk commodities such as coal, ore, grain, and track ballast. Plastic pellets and some finely ground material, similar to flour, are transported in hopper cars that have pneumatic unloading. The bottom gates on the pneumatic hoppers connect to a hose attached to industrial facilities' storage tanks. Air is injected to fluidize the railcar contents for unloading. The hopper car was developed in parallel with the development of automated handling of such commodities, including automated loading and unloading facilities. Hopper cars are distinguished from gondola cars, which do not have opening doors on their underside or sides. Gondola cars are simpler and more compact because sloping ends are not required, but a rotary car dumper is required to unload them. Some "dual-purpose" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malmbanan
The Iron Ore Line () is a long railway line between Riksgränsen and Boden in Norrbotten County, Sweden, owned by Trafikverket (the Swedish Transport Administration). The line also contains two branches, from Kiruna to Svappavaara and from Gällivare to Koskullskulle. The term is often colloquially used to also include the Ofoten Line, from Riksgränsen to Narvik in Norway, and the northernmost part of the Main Line Through Upper Norrland from Boden to Luleå. The railway from Narvik to Luleå is long. The line is dominated by the ore freight trains operated by LKAB's subsidiary Malmtrafik from their mines to the Port of Narvik and the Port of Luleå. In addition, Vy Tåg operates passenger trains and CargoNet operates container freight trains. The Iron Ore Line is single track, electrified at and has a permitted axle load of . The Swedish part of the line is the northernmost railway in Sweden and the Norwegian part outside Narvik is the northernmost railway in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vojany
Vojany () is a village and municipality in Michalovce District in the Kosice Region of eastern Slovakia. History In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1323. Geography The village lies at an altitude of 102 metres and covers an area of 10.923 kmВІ. The municipality has a population of about 830 people. Culture The village has a public library, and a football pitch. It also has a doctors surgery. Transport The village has a railway station. Economy * Vojany Power Station Vojany Power Station was a thermal power station at Vojany, Slovakia. It consists of 12 units, with 110 MW generation capacity each. Planning of the first plant began in 1959, the project was approved in 1960, and construction began in 1961. ... References Villages and municipalities in Michalovce District {{Michalovce-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kryvyi Rih
Kryvyi Rih ( ; , ), also known as Krivoy Rog ( ), is a city in central Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Kryvyi Rih Raion and its subordinate Kryvyi Rih urban hromada in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. The city is part of the Kryvyi Rih Metropolitan Region. Its population is estimated at making it the seventh-most populous city in Ukraine and the second largest by area. Kryvyi Rih is claimed to be the longest city in Europe. Located at the confluence of the Saksahan and Inhulets rivers, Kryvyi Rih was founded as a military staging post in 1775. Urban-industrial growth followed Belgian, French and British investment in the exploitation of the area's rich iron-ore deposits, generally called Kryvbas, in the 1880s. Kryvyi Rih gained city status after the October Revolution in 1919. Stalin-era industrialisation built Kryvorizhstal in 1934, the largest integrated metallurgical works in the Soviet Union. After a brutal German occupation in World War II, Kryvyi Rih experienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the north; Poland and Slovakia to the west; Hungary, Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and List of cities in Ukraine, largest city, followed by Kharkiv, Odesa, and Dnipro. Ukraine's official language is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. Humans have inhabited Ukraine since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, it was the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion and later became a key centre of East Slavs, East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful realm in Europe in the 10th and 11th centuries, but gradually disintegrated into rival regional powers before being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzhhorod
Uzhhorod (, ; , ; , ) is a List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality on the Uzh, Uzh River in western Ukraine, at the border with Slovakia and near the border with Hungary. The city is approximately equidistant from the Baltic, Adriatic Sea, the Adriatic and the Black Sea (650–690 km) making it the most inland city in this part of Europe. It is the Capital (political), administrative center of Zakarpattia Oblast (oblast, region), as well as the administrative center of Uzhhorod Raion (raion, district) within the oblast. Name The city's earliest known name is ''Ungvár'', from Hungarian language, Hungarian ''Ung'' (Uzh, River Uzh) and ''vár'' "castle, fortress", originally referring to a castle outside the city (probably Nevytske Castle). The name ''Uzhhorod'' was coined in early 19th century Slavophilia, Slavophile circles as a literal translation of the name ''Ungvár''. The city officially adopted this name some time after 1920, unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KoЕЎice
KoЕЎice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river HornГЎd at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, KoЕЎice is the second-largest city in Slovakia, after the capital Bratislava. Being the economic and cultural centre of eastern Slovakia, KoЕЎice is the seat of the KoЕЎice Region and KoЕЎice Self-governing Region, it belongs to the :sk:KoЕЎicko-preЕЎovskГЎ aglomerГЎcia, KoЕЎice-PreЕЎov agglomeration, and is home to the Constitutional Court of Slovakia, Slovak Constitutional Court, three universities, various dioceses, and many museums, galleries, and theatres. In 2013, KoЕЎice was the European Capital of Culture, together with Marseille, France. KoЕЎice is an important industrial centre of Slovakia, and the U. S. Steel KoЕЎice, s.r.o., U.S. Steel KoЕЎice steel mill is the largest employer in the city. The town has extensive railway connections and an KoЕЎice Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzhhorod–Košice Broad-gauge Track
The Uzhhorod–Košice broad-gauge line is a single-track 1,520-mm-gauge railway mostly in eastern Slovakia, which is used especially for transporting iron ore from Ukraine to the steel works near Košice. In the 1960s, after construction of the steel works in Košice, imports of iron ore to Slovakia rose steeply, and the checkpoint in Čierna nad Tisou could not handle this volume, particularly in winter, as Czechoslovakia and the Soviet Union had different gauges and all freight had to be transshipped. It was thus decided to build a Russian gauge line in Czechoslovakia to ease the bottleneck. Construction started on 4 November 1965, and the line opened on 1 May 1966. It was electrified in 1978. Trains are hauled by two electric twin-unit locomotives, similar to the late versions of PKP's ET40 but with SA3 couplers instead of buffers and chain couplings, except of westbound between Trebišov and Ruskov where the gradient is over 15 ‰ and two sets of locos are needed. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |