|
S1G Reactor
The S1G reactor is a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The S1G designation stands for: * S = Submarine platform * 1 = First generation core designed by the contractor * G = General Electric was the contracted designer History This nuclear reactor was constructed by General Electric as a prototype for the USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575) submarine. It was a liquid metal cooled reactor using pure sodium to cool the core instead of water, because the higher temperature of liquid sodium (compared to pressurized water) enabled the production of more superheated steam in the steam generators. This resulted in a more efficient thermal cycle, yielding more shaft horsepower for a given reactor size. The reactor design had problems because of limited operating temperature constraints. The major disadvantage of this concept was the ignition of sodium when exposed to air. The reactor core was beryllium- moderated. S1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Reactor
United States naval reactors are nuclear reactors used by the United States Navy aboard certain ships to generate the steam used to produce Power (physics), power for Marine nuclear propulsion, propulsion, electric power, catapulting airplanes in aircraft carriers, and a few minor uses. Such naval nuclear reactors have a complete power plant associated with them. All commissioned U.S. Navy submarines and supercarriers built since 1975 are nuclear powered, with the last conventional carrier, , being decommissioned in May 2009. The U.S. Navy also had nine nuclear-powered cruisers with such reactors, but they have since been decommissioned also. Reactors are designed by a number of contractors, then developed and tested at one of several United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy-owned and prime contractor-operated facilities: Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory in West Mifflin, Pennsylvania and its associated Naval Reactors Facility in Idaho, and Knolls Atomic Power Labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Generator (nuclear Power)
A steam generator (aka nuclear steam raising plant ('NSRP')) is a heat exchanger used to convert water into steam from heat produced in a nuclear reactor core. It is used in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), between the primary and secondary coolant loops. It is also used in liquid metal cooled reactors (LMRs), pressurized heavy-water reactors (PHWRs), and gas-cooled reactors (GCRs). In typical PWR designs, the primary coolant is high-purity water, kept under high pressure so it cannot boil. This primary coolant is pumped through the reactor core where it absorbs heat from the fuel rods. It then passes through the steam generator, where it transfers its heat (via conduction through metal) to lower-pressure water which is allowed to boil. Purpose Unlike PWRs, boiling water reactors (BWRs) do not use steam generators. The primary coolant is allowed to boil directly in the reactor core, and the steam is simply passed through a steam turbine. While theoretically simple, this has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D1G Reactor
The D1G reactor was a prototype naval reactor designed for the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The D1G designation stands for: * D = Destroyer platform * 1 = First generation core designed by the contractor * G = General Electric was the contracted designer This prototype nuclear reactor was constructed for the United States Department of Energy's Office of Naval Reactors as part of the Naval Nuclear Propulsion Program. The reactor was built by General Electric and operated by the Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory at the Kesselring Site Operation in West Milton, New York. It was used for testing components and as a training tool for the Nuclear Power Training Unit. The reactor operated from 1962 to 1996, when it was shut down in March of that year. It was later defuelled, with the pressure vessel eventually removed in 2002. The containment structure — which housed both the primary (nuclear reactor) and secondary (steam plant) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
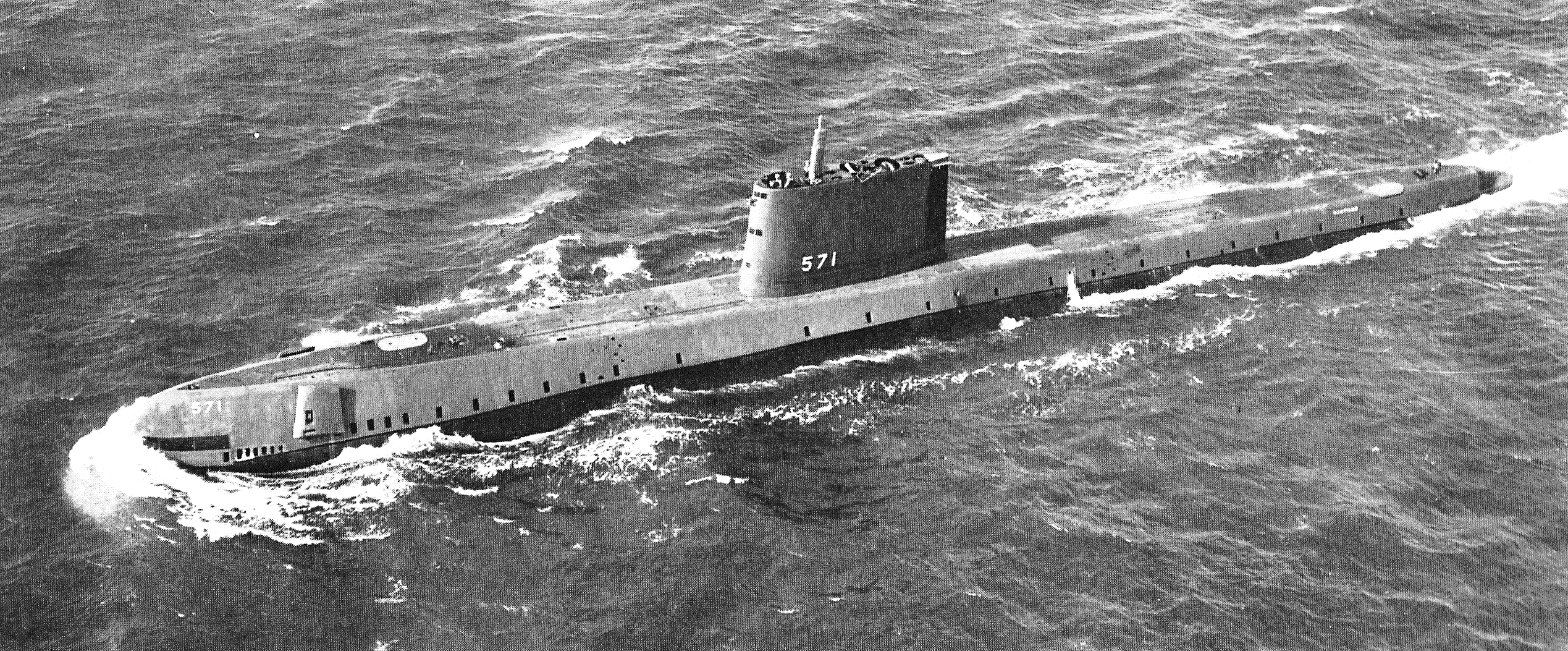
USS Nautilus (SSN-571)
USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571) was the world's first operational nuclear-powered submarine and on 3 August 1958 became the first submarine to complete a submerged transit of the North Pole. Her initial commanding officer was Eugene "Dennis" Wilkinson, a widely respected naval officer who set the stage for many of the protocols of today's Nuclear Navy of the US, and who had a storied career during military service and afterwards. Sharing a name with Captain Nemo's fictional submarine in Jules Verne's classic 1870 science fiction novel ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas'' and the that served with distinction in World War II, the new nuclear-powered ''Nautilus'' was authorized in 1951. Construction began in 1952, and the boat was launched in January 1954, sponsored by Mamie Eisenhower, First Lady of the United States, wife of 34th President Dwight D. Eisenhower; it was commissioned the following September into the United States Navy. ''Nautilus'' was delivered to the Navy in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressurized Water Reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada). In a PWR, water is used both as a neutron moderator and as coolant fluid for the reactor core. In the core, water is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms contained in the fuel. Using very high pressure (around 155 bar: 2250 psi) ensures that the water stays in a liquid state. The heated water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to the water of a secondary cycle kept at a lower pressure which allows it to vaporize. The resulting steam then drives steam turbines linked to an electric generator. A boiling water reactor (BWR) by contrast does not maintain such a high pressure in the primary cycle and the water thus vaporizes inside of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) before being sent to the turbine. Most PWR designs ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S2W Reactor
The S2W (Submarine platform Second generation core Westinghouse) reactor was a naval reactor built by Westinghouse used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. History The S2W reactor was a naval nuclear reactor developed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation for use in the United States Navy's nuclear-powered submarines. The reactor's designation, S2W, stands for "Submarine platform," "second-generation core design," and "Westinghouse," the contractor responsible for its development. It was a pressurized water reactor (PWR) initially installed aboard the USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575), the second nuclear-powered submarine launched by the U.S. Navy in 1955. The S2W reactor was originally designed as a sodium-cooled system, but operational difficulties with this cooling method led to its later conversion to a conventional pressurized water reactor. This design provided substantial improvements in submerged endurance and speed over con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S1W Reactor
The S1W reactor was the first prototype naval reactor used by the United States Navy to prove that the technology could be used for electricity generation and propulsion on submarines. The designation of "S1W" stands for * S = Submarine platform * 1 = First generation core designed by the contractor * W = Westinghouse was the contracted designer and is a later Navy designation. During the plant's early years the project name was "Submarine Thermal Reactor" (STR) The land-based nuclear reactor was built at the National Reactor Testing Station, later called Idaho National Engineering Laboratory near Arco, Idaho. The plant was the prototype for the power system of USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571), the world's first nuclear-powered submarine, which used the improved S2W reactor. The specific location within the vast Idaho National Laboratory where the S1W prototype was located was the Naval Reactors Facility. Design Under the leadership of Captain (later Admiral) Hyman G. Ric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus. Water (sometimes called "light water" in this context) is the most commonly used moderator (roughly 75% of the world's reactors). Solid graphite (20% of reactors) and heavy water (5% of reactors) are the main alternatives. Beryllium has also been used in some experimental types, and hydrocarbons have been suggested as another possibility. Moderation Neutrons are normally bound into an atomic nucleus and do not exist free for long in nature. The unbound neutron has a half-life of 10 minutes and 11 seconds. The release of neutrons from the nucleus requires exceeding the binding ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Gemstones high in beryllium include beryl (Aquamarine (gemstone), aquamarine, emerald, red beryl) and chrysoberyl. It is a Abundance of the chemical elements#Universe, relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the maximum operating temperature (or peak operating temperature). Outside this range of safe operating temperatures the device may fail. It is one component of reliability engineering. Similarly, biological systems have a viable temperature range, which might be referred to as an "operating temperature". Ranges Most semiconductor devices are manufactured in several temperature grades. Broadly accepted grades are: *Commercial: 0 °C to 70 °C () *Industrial: −40 °C to 85 °C () *Military: −55 °C to 125 °C () Nevertheless, each manufacturer defines its own temperature grades so designers must pay attention to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the imperial horsepower as in "hp" or "bhp" which is about , and the metric horsepower as in "cv" or "PS" which is approximately . The electric horsepower "hpE" is exactly , while the boiler horsepower is 9809.5 or 9811 watts, depending on the exact year. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other power-generating machinery such as piston engines, turbines, and electric motors. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |