|
S-V
The S-V (pronounced "S-five") was the third stage of the Saturn I rocket. It was built by Convair. It was designed to use two RL-10A-1 engines fueled by liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) in tanks utilizing a common bulkhead to separate the propellants. History Convair Astronautics was awarded a contract to deliver the S-V stage for the Saturn I. The stage was intended to boost lift capacity for U.S. military launches in the 1960s. The S-V would ultimately fly as the third stage on early launches of the Saturn I. Convair delivered two S-V stages in February 1961 with one being flown on SA-1 attached to an also inert S-IV, the second was used for dynamic testing of the complete Saturn I before being later flown. In May 1961 NASA eliminated the requirement for all Saturn I launches to be flown with S-V's by flying in a two-stage only version. Despite this, the stage would fly four times in total. With the introduction of the Saturn IB and the needs of the military fulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". The rocket's first stage was built as a cluster of propellant tanks engineered from older rocket tank designs, leading critics to jokingly refer to it as "Cluster's Last Stand". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency in 1958 by the newly formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion, launching the Pegasus satellites, and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift derivative Saturn IB, which used a larger, higher total impulse second stage and an improved guidance and control system. It also led the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur (rocket Stage)
The Centaur is a family of rocket propelled upper stages produced by U.S. launch service provider United Launch Alliance, with one main active version and one version under development. The diameter Common Centaur/Centaur III flies as the upper stage of the Atlas V launch vehicle, and the diameter Centaur V is being developed as the upper stage of ULA's new Vulcan rocket. Centaur was the first rocket stage to use liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, a high-energy combination that is ideal for upper stages but has significant handling difficulties. Characteristics Common Centaur is built around stainless steel pressure stabilized balloon propellant tanks with thick walls. It can lift payloads of up to . The thin walls minimize the mass of the tanks, maximizing the stage's overall performance. A common bulkhead separates the LOX and LH2 tanks, further reducing the tank mass. It is made of two stainless steel skins separated by a fiberglass hone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
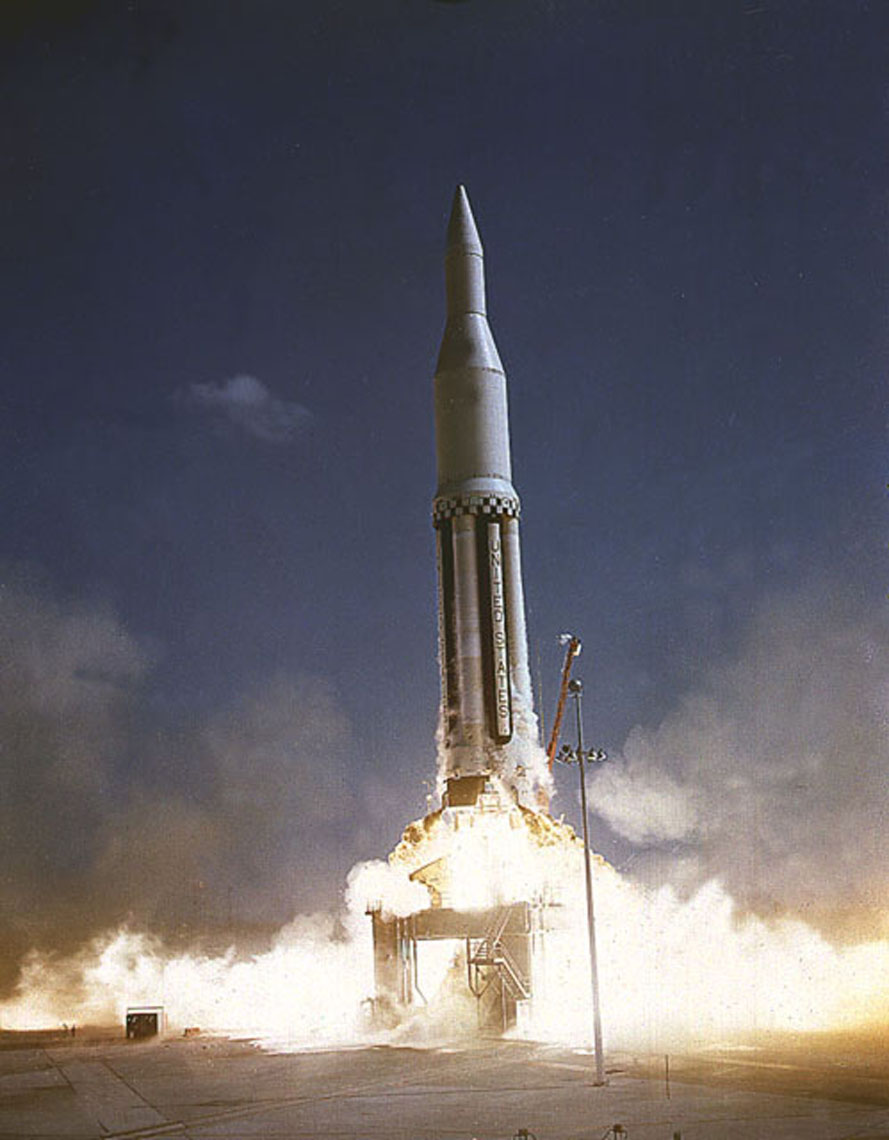
Saturn I SA-3
Saturn-Apollo 3 (SA-3) was the third flight of the Saturn I launch vehicle, the second flight of Project Highwater, and part of the American Apollo program. The rocket was launched on November 16, 1962, from Cape Canaveral, Florida. History The Saturn I launch vehicle components were delivered to Cape Canaveral by the barge ''Promise'' on September 19, 1962, but erection of the first-stage booster onto its launch pedestal was delayed until September 21 due to a tropical depression that moved over the Florida peninsula. The dummy second and third stages (S-IV and S-V) and payload were assembled on the booster on September 24. Ballast water was loaded into the dummy stages on October 31, and the RP-1 fuel was loaded on November 14. For this launch, Cape Canaveral director Kurt Debus asked Marshall Space Flight Center director Wernher von Braun, who was overseeing the Saturn project, that no outside visitors be allowed on NASA grounds due to the ongoing tensions of the Cuban Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I SA-2
Saturn-Apollo 2 (SA-2) was the second flight of the Saturn I launch vehicle, the first flight of Project Highwater, and was part of the American Apollo program. The rocket was launched on April 25, 1962, from Cape Canaveral, Florida. History Launch preparation for the mission began at Cape Canaveral on February 27, 1962, with the arrival of the second Saturn I launch vehicle. The only significant change made to the vehicle from the previous SA-1 flight was the addition of extra baffles in the propellant tanks to mitigate fuel sloshing. While no serious delays were encountered, there were several minor problems reported. A leak was detected between the liquid oxygen dome and injector for the #4 H-1 rocket engine; while attempts were made to fix the problem, it was eventually decided to launch without replacing the engine. Minor problems were found in the guidance subsystem and service structure operations, damaged strain gauges were found in a liquid oxygen stud and truss m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas LV-3B
The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas family of rockets. With the Atlas having been originally designed as a weapon system, testing and design changes were made to the missile to make it a safe and reliable launch vehicle. After the changes were made and approved to, the US launched the LV-3B nine times, four of which had crewed Mercury spacecraft. Design The Atlas LV-3B was a human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by American aircraft manufacturing company Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas family of rockets. The Atlas D missile was the natural choi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I SA-4
Saturn-Apollo 4 (SA-4) was the fourth launch of a Saturn I launch vehicle and the last of the initial test phase of the first stage. It was part of the Apollo Program. Objectives SA-4 was the last flight to test only the S-I first stage of the Saturn I rocket. As with the first three launches this would be a suborbital flight and would test the structural integrity of the rocket. The major addition to this flight was that, in order to test the rocket's ability to deal with an engine failure during the flight, one of the engines would be programmed to shut down about 100 seconds after launch. If all went well the rocket would reroute the fuel for this engine to the other engines and have the rocket burn longer to compensate for the loss of acceleration. This was used successfully on the later Apollo 6 and Apollo 13 Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo space program and the third meant to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
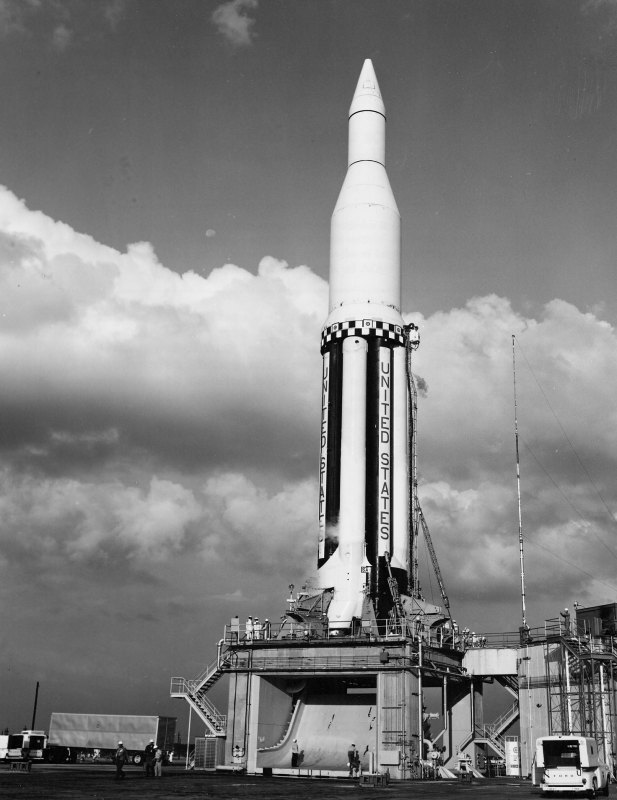
Saturn I SA-1
Saturn-Apollo 1 (SA-1) was the first flight of the Saturn I space launch vehicle, the first in the Saturn family, and first mission of the American Apollo program. The rocket was launched on October 27, 1961, from Cape Canaveral, Florida. Objectives The Saturn I booster was a huge increase in size and power over anything previously launched. It was three times taller, required six times more fuel and produced ten times more thrust than the Juno I rocket that had launched the first American satellite, ''Explorer 1'', into orbit in 1958. At the time, NASA had decided to not use all-up testing, when an entire system is tested at once. The agency planned to test each rocket stage in separate launches, so for SA-1 the only live stage was the S-I first stage. This first flight was designed to test the structure of the launch vehicle during a suborbital flight using the nose cone from a Jupiter rocket. Preparation As this was the first Saturn flight, the systems were still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulcan Centaur
Vulcan Centaur is a two-stage-to-orbit, heavy-lift launch vehicle that is under development by the United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2014 with an initial flight expected in early 2023. It is principally designed to meet launch demands for the U.S. government's National Security Space Launch (NSSL) program for use by the United States Space Force and U.S. intelligence agencies for national security satellite launches. The maiden flight is slated to launch Astrobotic Technology's ''Peregrine'' lunar lander for NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program and Kuiper Systems' Kuipersat-1 and Kuipersat-2, no earlier than 2023, after multiple delays from the initially planned first flight in 2019. Description Vulcan is ULA's first new launch vehicle design; it adapts and evolves technologies that were developed for the Atlas V and Delta IV rockets of the USAF's EELV program. The first-stage propellant tanks have the same diameter as the Delta IV Common Booster Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing. Atlas V is also a major NASA launch vehicle. It is America's longest-serving active rocket. In August 2021, ULA announced that Atlas V would be retired, and all 29 remaining launches had been sold. , 19 launches remain. Each Atlas V launch vehicle consists of two main stages. The first stage is powered by a Russian RD-180 engine manufactured by Energomash and burning kerosene and liquid oxygen. The Centaur upper stage is powered by one or two American RL10 engine(s) manufactured by Aerojet Rocketdyne and burns liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. The Star 48 upper stage was used on the '' New Horizons'' mission as a third stage. Strap-on solid rocket boosters (SRBs) are used in most configurations. AJ-60A SRBs were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Highwater
Project Highwater was an experiment carried out as part of two of the test flights of NASA's Saturn I launch vehicle (using battleship upper stages), successfully launched into a sub-orbital trajectory from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Highwater experiment sought to determine the effect of a large volume of water suddenly released into the ionosphere. The project answered questions about the effect of the diffusion of propellants in the event that a rocket was destroyed at high altitude. The first flight, SA-2, took place on April 25, 1962. After the flight test of the rocket was complete and first stage shutdown occurred, explosive charges on the dummy upper stages destroyed the rocket and released of ballast water weighing into the upper atmosphere at an altitude of , eventually reaching an apex of . The second flight, SA-3, launched on November 16, 1962, and involved the same payload. The ballast water was explosively released at the flight's peak altitude of . For both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with multistage rocket, three stages, and powered with liquid-propellant rocket, liquid fuel. It was flown from 1967 to 1973. It was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station. the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to carry humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). Saturn V holds records for the heaviest payload launched and largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit: , which included the third stage and unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module to the Moon. The largest production model of the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee, was an American aircraft manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, it was purchased by General Dynamics, and operated as their Convair Division for most of its corporate history. Convair is best known for its military aircraft; it produced aircraft such as the Convair B-36 Peacemaker and Convair B-58 Hustler strategic bombers, and the Convair F-102 Delta Dagger and Convair F-106 Delta Dart interceptors. It also manufactured the first Atlas rockets, including the rockets that were used for the crewed orbital flights of Project Mercury. The company's subsequent Atlas-Centaur design continued this success and derivatives of the design remain in use as of 2020. The company also entered the jet airliner business with its Convair 880 and Convair 990 designs. These were smaller than contemporary aircraft like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |