|
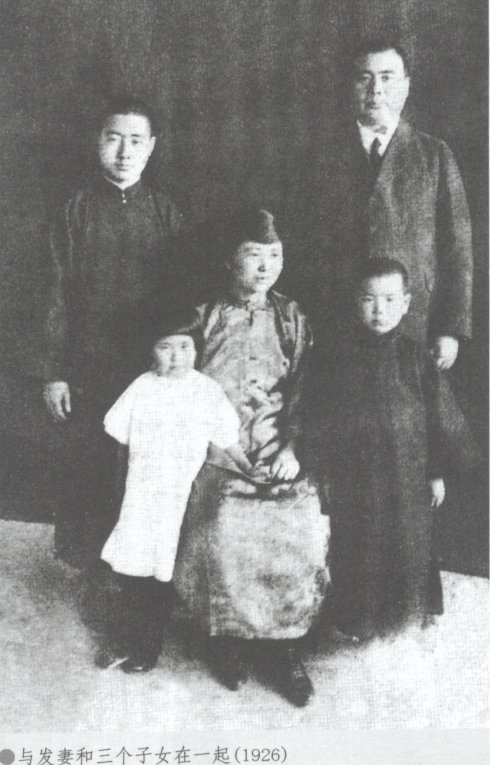
Robert Henry Mathews
Robert Henry Mathews (1877–1970) was an Australian missionary and Sinologist, best known for his 1931 '' A Chinese-English Dictionary: Compiled for the China Inland Mission by R. H. Mathews'', which was subsequently revised by Harvard University Press in 1943. He served with the China Inland Mission from 1906, before retiring to Australia in 1945. Early life Robert Henry Mathews was born in Flemington, now a suburb of Melbourne, Australia on 13 July 1877, to London-born William Mathews and Australian Mary Mathews, née Whitlaw. Mathews studied lithography at the Working Men's College of Melbourne, during which time he became interested in Christian missionary work. As an fervent Congregationalist, he was drawn to evangelism, especially the China Inland Mission (CIM). Although Mathews set up his own printing business after graduating, he abandoned it to join the CIM in 1906, receiving eighteen months' training in Adelaide where he ministered to the city's outcast poor. Mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Missionary' 2003, William Carey Library Pub, . In the Latin translation of the Bible, Jesus Christ says the word when he sends the disciples into areas and commands them to preach the gospel in his name. The term is most commonly used in reference to Christian missions, but it can also be used in reference to any creed or ideology. The word ''mission'' originated in 1598 when Jesuits, the members of the Society of Jesus sent members abroad, derived from the Latin ( nom. ), meaning 'act of sending' or , meaning 'to send'. By religion Buddhist missions The first Buddhist missionaries were called "Dharma Bhanaks", and some see a missionary charge in the symbolism behind the Buddhist wheel, which is said to travel all over the earth brin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhui Province
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River and the Huai River, bordering Jiangsu to the east, Zhejiang to the southeast, Jiangxi to the south, Hubei to the southwest, Henan to the northwest, and Shandong for a short section in the north. With a population of 63.65 million, Anhui is the 8th most populous province in China. It is the 22nd largest Chinese province based on area, and the 12th most densely-populated region of all 34 Chinese provincial regions. Anhui's population is mostly composed of Han Chinese. Languages spoken within the province include Jianghuai Mandarin, Wu, Hui, Gan and small portion of Zhongyuan Mandarin Chinese. The name "Anhui" derives from the names of two cities: Anqing and Huizhou (now Huangshan City). The abbreviation for Anhui is "" after the hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
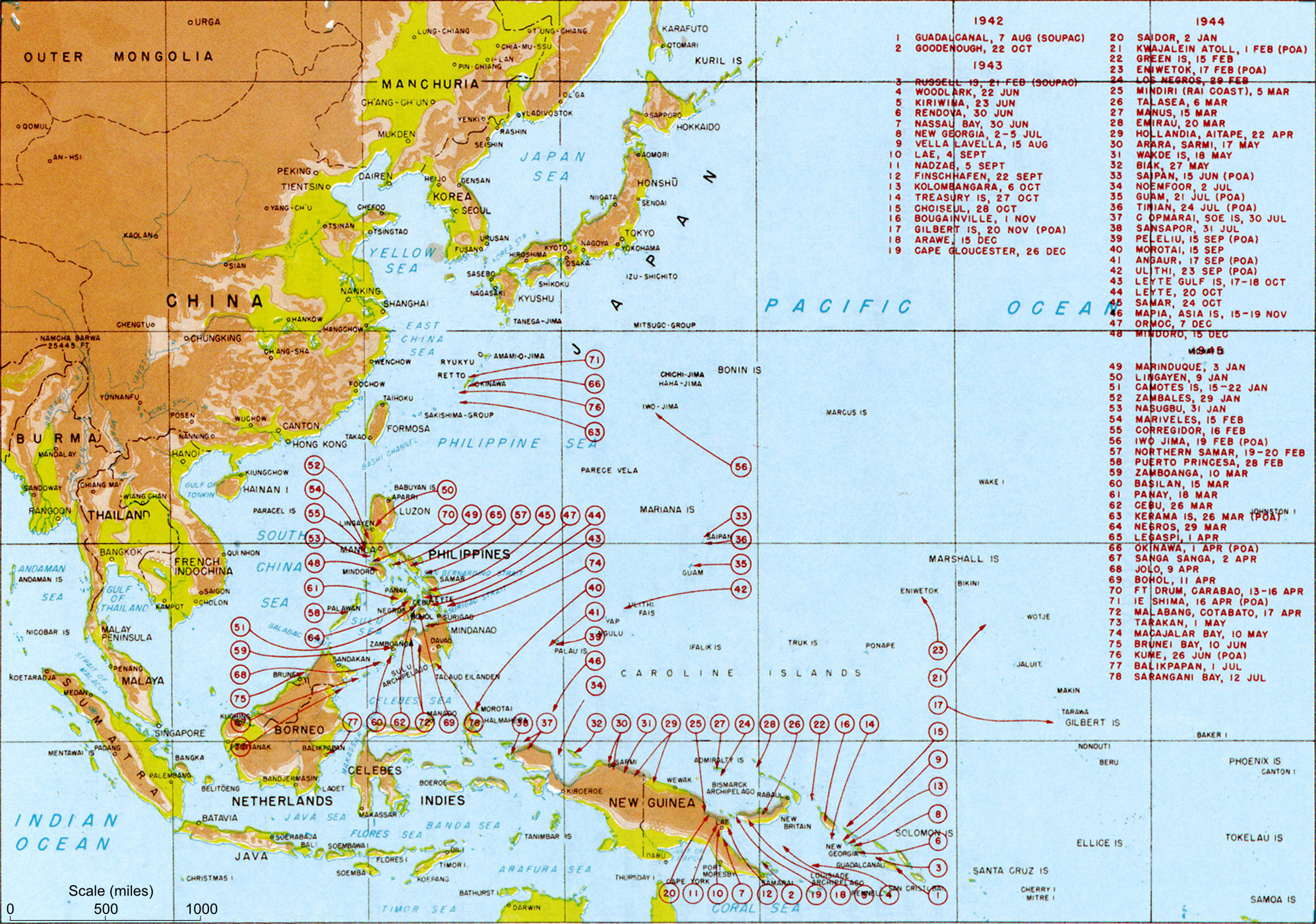
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunghua Civilian Assembly Centre
Lunghua Civil Assembly Centre was one of the internment camps eventually established by the Empire of Japan in Shanghai for European and American citizens, who had been resident under Japanese occupation since December 1941. Many had formerly lived in Shanghai within the Shanghai International Settlement before its occupation by the imperial Japanese army. J. G. Ballard was interned in the camp as an adolescent. His experiences there inspired the book (and subsequent movie) ''Empire of the Sun''. Description Lunghua Civil Assembly Centre was originally the Jiangsu Shanghai High School. It was located on Minghong Road about three miles (5 km) from Shanghai Longhua Airport. (Pre-WWII documents use the alternate spellings of ''Lunghua'' and ''Lunghwa''; the modern anglicized spelling of the town is ''Longhua''.) The school was damaged in the Second Sino-Japanese War and was empty until it was designated as a Civil Assembly Centre. It was then used from 1943 to intern 1,988 peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai International Settlement
The Shanghai International Settlement () originated from the merger in the year 1863 of the British and American enclaves in Shanghai, in which British subjects and American citizens would enjoy extraterritoriality and consular jurisdiction under the terms of treaties agreed by both parties. These treaties were abrogated in 1943. The British settlements were established following the victory of the British in the First Opium War (18391842). Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, the five treaty ports including Shanghai were opened to foreign merchants, overturning the monopoly then held by the southern port of Canton (Guangzhou) under the Canton System. The British also established a base on Hong Kong. American and French involvement followed closely on the heels of the British and their enclaves were established north and south, respectively, of the British area. Unlike the colonies of Hong Kong and Macau, where the United Kingdom and Portugal enjoyed full sovereign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Shanghai
The history of Shanghai spans over a thousand years and closely parallels the development of modern China. Originally a small agricultural village, Shanghai developed during the late Qing dynasty (1644–1912) as one of China's principal trading ports. Although nominally part of China, in practice foreign diplomats controlled the city under the policy of extraterritoriality. Since the economic reforms of the early 1990s the city has burgeoned to become one of Asia's major financial centers and the world's busiest container port. Early Era Around 6000 BCE, only the western part of the Shanghai region encompassing today's Qingpu, Songjiang and Jinshan districts were dry land formed by lacustrine silting from ancient Lake Tai. The modern Jiading, Minhang and Fengxian districts emerged around 1,000 BC while the downtown area remained underwater. The earliest Neolithic settlements known in this area date to the Majiabang culture (50003300 BCE). This was overlapped by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick W
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode * Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans Baden * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden Bohemia * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia Britain * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain Brandenburg/Prussia * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of Brandenburg * Frederick William, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing Decade
The Nanjing decade (also Nanking decade, , or the Golden decade, ) is an informal name for the decade from 1927 (or 1928) to 1937 in the Republic of China. It began when Nationalist Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek took Nanjing from Zhili clique warlord Sun Chuanfang halfway through the Northern Expedition in 1927. Chiang declared it to be the national capital despite the existence of a left-wing Nationalist government in Wuhan. The Wuhan faction gave in and the Northern Expedition continued until the Beiyang government in Beijing was overthrown in 1928. The decade ended with the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and the retreat of the Nationalist government to Wuhan. GDP growth averaged 3.9 per cent a year from 1929 to 1941 and per capita GDP about 1.8 per cent. Historians view the decade as a period of Chinese conservatism. Nanking was of symbolic and strategic importance. The Ming dynasty had made Nanjing a capital, the republic had been established there in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feng Yuxiang
Feng Yuxiang (; ; 6 November 1882 – 1 September 1948), courtesy name Huanzhang (焕章), was a warlord and a leader of the Republic of China from Chaohu, Anhui. He served as Vice Premier of the Republic of China from 1928 to 1930. He was also known as the "Christian General" for his zeal to convert his troops and the "Traitorous General" for his penchant to break with the establishment. In 1911 he was an officer in the ranks of Yuan Shikai's Beiyang Army but joined forces with revolutionaries against the Qing dynasty. He rose to high rank within Wu Peifu's Zhili warlord faction but launched the Beijing Coup in 1924 that knocked Zhili out of power and brought Sun Yat-sen to Beijing. He joined the Nationalist Party (KMT), supported the Northern Expedition and became blood brothers with Chiang Kai-shek, but resisted Chiang's consolidation of power in the Central Plains War and broke with him again in resisting Japanese incursions in 1933. He spent his later years suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.gif)
