|
Robert Grove (bishop)
Robert Grove (1634–1696) was an English Bishop of Chichester. Life Born in London in 1634 or 1635, he was the son of William Grove of Morden, Dorset. In 1645 he was sent to Winchester College, and was admitted a pensioner of St. John's College, Cambridge, on 18 October 1652. He was elected a scholar in 1653, graduated B.A. in 1657, and became a fellow on 23 March 1658. For several years he lived in college as tutor, proceeding M.A. in 1660, B.D. in 1667, and D.D. in 1681. Grove, on becoming chaplain to Humphrey Henchman, Bishop of London, was presented by him to the rectory of Wennington, Essex, on 21 February 1667, which he left before 27 January 1669. On 2 September 1669 he received from the crown the rectory of Langham, Essex and on 5 October following the rectory of Aldham, in the same county, from the bishop. These livings he resigned on obtaining from Henchman the wealthy rectory of St. Andrew Undershaft, London, on 18 February 1670. On 6 October 1679 he was made p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument To Robert Grove (Bishop Of Chichester)
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, historical, political, technical or architectural importance. Some of the first monuments were dolmens or menhirs, megalithic constructions built for religious or funerary purposes. Examples of monuments include statues, (war) memorials, historical buildings, archaeological sites, and cultural assets. If there is a public interest in its preservation, a monument can for example be listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Etymology It is believed that the origin of the word "monument" comes from the Greek ''mnemosynon'' and the Latin ''moneo'', ''monere'', which means 'to remind', 'to advise' or 'to warn', however, it is also believed that the word monument originates from an Albanian word 'mani men' which in Albanian language means 'remember ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberty Of Conscience
Freedom of thought (also called freedom of conscience) is the freedom of an individual to hold or consider a fact, viewpoint, or thought, independent of others' viewpoints. Overview Every person attempts to have a cognitive proficiency by developing knowledge, concepts, theories and assessing them in the given environment. This cognitive proficiency gives a sense of contentment and replaces the feeling of helplessness. Apart from bringing ease to the ego of a person, new knowledge and ideas also bring a hope for the future. Freedom of thought is the precursor and progenitor of—and thus is closely linked to—other liberties, including freedom of religion, freedom of speech, and freedom of expression. Though freedom of thought is axiomatic for many other freedoms, they are in no way required for it to operate and exist. The conception of a freedom or a right does not guarantee its inclusion, legality, or protection via a philosophical caveat. It is a very important concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishops Of Chichester
The Bishop of Chichester is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Chichester in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers the counties of East Sussex, East and West Sussex. The Episcopal see, see is based in the Chichester, City of Chichester where the bishop's seat is located at the Chichester Cathedral, Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity. On 3 May 2012 the appointment was announced of Martin Warner (bishop), Martin Warner, Bishop of Whitby, as the next Bishop of Chichester. His enthronement took place on 25 November 2012 in Chichester Cathedral. The bishop's residence is The Palace, Chichester. Since 2015, Warner has also fulfilled the diocesan-wide role of alternative episcopal oversight, following the decision by Mark Sowerby, then Bishop of Horsham, to recognise the orders of priests and bishops who are women. Between 1984 and 2013, the Bishop of Chichester, in addition to being the diocesan bishop, also had specific oversight of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1696 Deaths
Events January–March * January 21 – The Recoinage Act, passed by the Parliament of England to pull counterfeit silver coins out of circulation, becomes law.James E. Thorold Rogers, ''The First Nine Years of the Bank of England'' (Clarendon Press, 1887 p. 41 * January 27 – In England, the ship HMS ''Royal Sovereign'' (formerly ''HMS Sovereign of the Seas'', 1638) catches fire and burns at Chatham, after 57 years of service. * January 31 – In the Netherlands, undertakers revolt after funeral reforms in Amsterdam. * January – Colley Cibber's play ''Love's Last Shift'' is first performed in London. * February 8 (January 29 old style) – Peter the Great who had jointly reigned since 1682 with his mentally-ill older half-brother, Tsar Ivan V, becomes the sole Tsar of Russia when Ivan dies at the age of 29. * February 15 – A plot to ambush and assassinate King William III of England in order to restore King James and the House of Stuar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1634 Births
Events January–March * January 12– After suspecting that he will be dismissed, Albrecht von Wallenstein, supreme commander of the Holy Roman Empire's Army, demands that his colonels sign a declaration of personal loyalty. * January 14– France's ''Compagnie normande'' obtains a one-year monopoly on trade with the African kingdoms in Guinea. * January 19– Charles IV, Duke of Lorraine abdicates in favor of his brother Nicholas II, who is only able to hold the throne for 75 days. * January 24– Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, signs a classified order dismissing Albrecht von Wallenstein, the supreme commander of the Imperial Army. * February 18– Emperor Ferdinand II's dismissal of Commander Wallenstein for high treason, and the order for his capture, dead or alive, is made public. * February 25– Rebel Scots and Irish soldiers assassinate Bohemian military leader Albrecht von Wallenstein at Cheb. * March 1 – The Russians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Patrick
Simon Patrick (8 September 1626 – 31 May 1707) was an English theologian and bishop. Life He was born at Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, eldest son of Henry Patrick, a wealthy merchant, on 8 September 1626, and attended Boston Grammar School. He entered Queens' College, Cambridge, in 1644, and after taking orders in 1651 became successively chaplain to Sir Walter St. John and vicar of Battersea, Surrey. He was afterwards (1662) preferred to the rectory of St. Paul's, Covent Garden, London, where he continued to labor during the plague. He was appointed Dean of Peterborough in 1679, and Bishop of Chichester in 1689, in which year he was employed, along with others of the new bishops, to settle the affairs of the Church in Ireland. In 1691 he was translated to the see of Ely, which he held until his death on 31 May 1707. He was buried in Ely Cathedral. His memorial is by Edward Stanton. He had Dalham Hall built. Works His sermons and devotional writings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
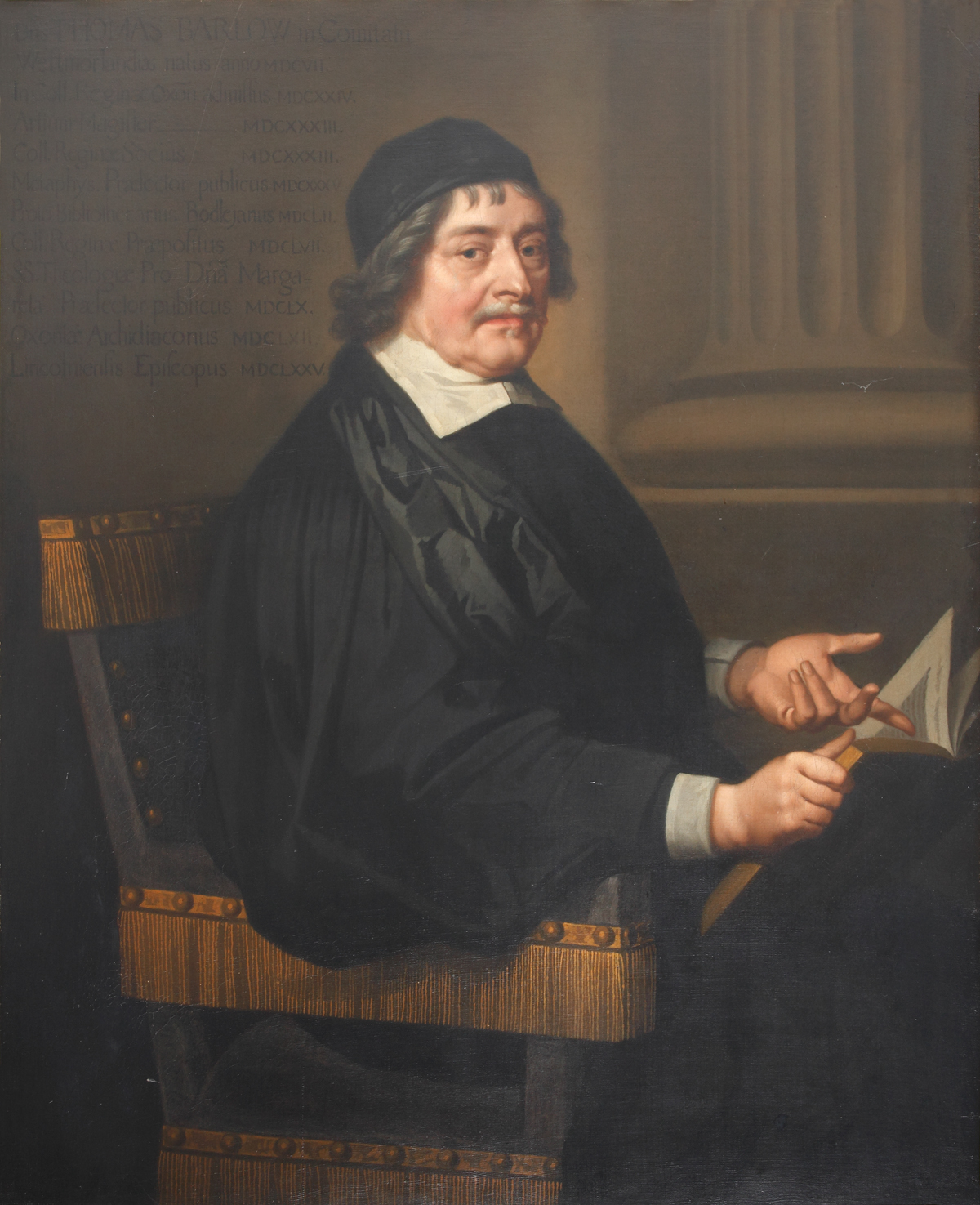
Thomas Barlow (bishop)
Thomas Barlow (1607, 1608 or 1609 – 8 October 1691) was an English academic and clergyman, who became Provost of The Queen's College, Oxford, and Bishop of Lincoln. He was seen in his own time and by Edmund Venables in the ''Dictionary of National Biography'' to have been a trimmer (conforming politically for advancement's sake), and have a reputation mixed with his academic and other writings on casuistry. His views were Calvinist and strongly anti-Catholic – he was among the last English bishops to dub the Pope Antichrist. Christopher Hill, ''A Turbulent, Seditious and Factious People: John Bunyan and his Church'' (1988), p. 167. He worked in the 1660s for "comprehension" of nonconformists, but supported a crackdown in the mid-1680s and declared loyalty to James II of England on his accession, though he had supported the Exclusion Bill, which would have denied it to him. :s:Barlow, Thomas (DNB00) Early life Barlow was the son of Richard Barlow of Long-gill in the parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Bellarmine
Robert Bellarmine, SJ ( it, Roberto Francesco Romolo Bellarmino; 4 October 1542 – 17 September 1621) was an Italian Jesuit and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. He was canonized a saint in 1930 and named Doctor of the Church, one of only 37. He was one of the most important figures in the Counter-Reformation. Bellarmine was a professor of theology and later rector of the Roman College, and in 1602 became Archbishop of Capua. He supported the reform decrees of the Council of Trent. He is also widely remembered for his role in the Giordano Bruno affair, the Galileo affair, and the trial of Friar Fulgenzio Manfredi. Early life Bellarmine was born in Montepulciano, the son of noble, albeit impoverished, parents, Vincenzo Bellarmino and his wife Cinzia Cervini, who was the sister of Pope Marcellus II. As a boy he knew Virgil by heart and composed a number of poems in Italian and Latin. One of his hymns, on Mary Magdalene, is included in the Roman Breviary. He entered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Lowth
Simon Lowth (1636–1720) was an English nonjuring schism, nonjuring clergyman, nominated by James II as Dean of Rochester, and later a controversialist on the position of bishops. Life He studied at Clare College, Cambridge, Clare Hall, Cambridge, where he matriculated 1653. He graduated B.A.in 1657 and M.A. in 1660. He was appointed rector of St. Michael, Harbledown, in 1670, and vicar of St. Cosmus and Damian on the Blean, two parishes near Canterbury, in 1679. James II nominated him on 12 November 1688 as Dean of Rochester, in succession to John Castilion. He was instituted by Bishop Thomas Sprat, but his installation was put off when it was discovered that he had taken no higher degree than M.A., and the statutes required that he should be at least B.D. Although he took the degree of D.D, 18 January 1689, he was not installed, and William III shortly afterwards appointed Henry Ullock in his place. Lowth declined the oath of allegiance to William, and was in consequence suspend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Jenkyn
William Jenkyn (1613–1685) was an English clergyman, imprisoned during the Interregnum for his part in the 'Presbyterian plot' of Christopher Love, ejected minister in 1662, and imprisoned at the end of his life for nonconformity. Life Jenkyn was the eldest son of William Jenkyn (d. 1618), vicar of All Saints', Sudbury, Suffolk, born at Sudbury and baptised at All Saints' Church in December 1613. His father, son of a gentleman of landed property at Folkestone, Kent, had been disinherited for his Puritanism. His mother was daughter of Richard Rogers of Wethersfield, Essex. On his father's death his grandfather sent for him to Folkestone; when he was nine years old his mother, who had remarried, claimed him, gave him a good education, and sent him to St John's College, Cambridge, where he matriculated on 3 July 1628. He graduated B.A. 1632, migrated to Emmanuel College in 1634, and graduated M.A. 1635. Some time afterwards he began to preach. Having held a lectureship at St. Nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdeacon Of Middlesex
The Archdeacon of Middlesex is a senior cleric in the Church of England, co-responsible for the Archdeaconry of "Middlesex", which mirrors the "Kensington" episcopal area of the Diocese of London — the other person responsible being the Bishop of Kensington. History The ancient archdeaconry has been a division of London diocese since archdeaconries were first created in England in the 12th century. Historically it covered most of London other than the City of London and the East End. It was for ten years in the Marian-period (Roman Catholic) Diocese of Westminster from 1540, then re-absorbed back into the London diocese in 1550 as the church parted, for the final time, from Rome. It was split on 23 July 1912 to create the Archdeaconry of Hampstead and since further split to create the Archdeaconries of Northolt (in 1970) and of Charing Cross (in ). List of archdeacons High Medieval *bef. 1102–aft. 1106: RobertThe first Robert is not recorded as "Archdeacon of Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)