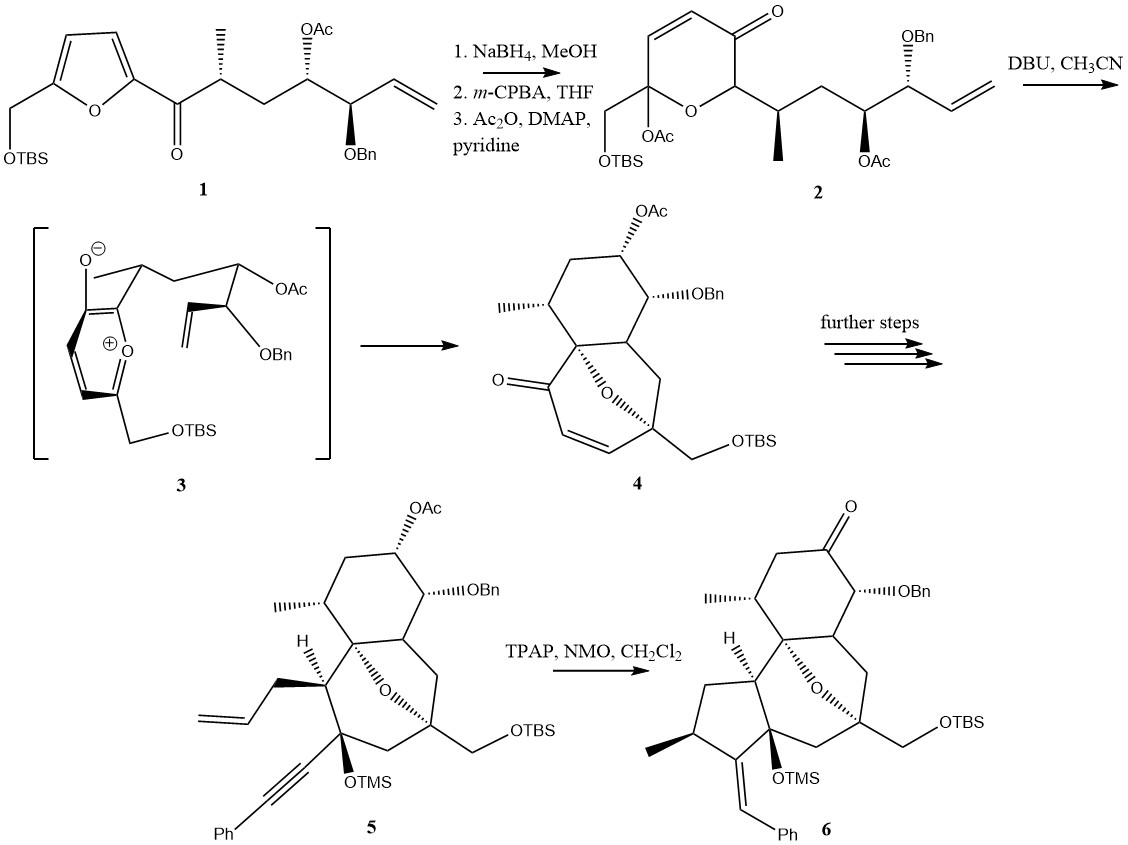
|
Resiniferatoxin
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is a naturally occurring chemical found in resin spurge (''Euphorbia resinifera''), a cactus-like plant commonly found in Morocco, and in '' Euphorbia poissonii'' found in northern Nigeria.''Euphorbia poissonii'' in BoDD – Botanical Dermatology Database It is a potent functional analog of , the active ingredient in . Biological activity ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphorbia Resinifera
''Euphorbia resinifera'', the resin spurge, is a species of spurge native to Morocco, where it occurs on the slopes of the Atlas Mountains. The dried latex of the plant was used in ancient medicine. It contains resiniferatoxin, an extremely potent capsaicin analog tested as an analgesic since 1997. Growth It is a shrub growing to tall, forming multi-stemmed cushion-shaped clumps up to wide. The stems are erect, succulent, superficially like a cactus, four-angled, with short but sharp pairs of spines on the angles, spaced about apart up the stem. Geographical distribution ''Euphorbia resinifera'' is a species of spurge native to Morocco, where it occurs on the slopes of the Atlas Mountains. It is similar to its relative '' Euphorbia echinus'', which occurs on the Moroccan coast and the Canary Islands. Due to its origin it is also called the African spurge. Chemical constituents ''Euphorbia resinifera'' contains a milky fluid or latex, which in its dried form is called E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphorbia Poissonii
''Euphorbia poissonii'', also known as ''Euphorbia poissoni'' and, incorrectly, as ''Euphorbia poisoni'', is a highly irritant and toxic succulent member of the large and varied spurge family of plants.''Euphorbia poissonii'' in BoDD – Botanical Dermatology Database It is native to northern , where local farmers extract its for use as a pesticide. Its powerfully irritant and pain-producing nature mandates use as a fencing plant. It is known to the Berom people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) ( or ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a chemical irritant for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burning in any tissue with which it comes into contact. Capsaicin and several related alkaloids are called capsaicinoids and are produced as secondary metabolites by chili peppers, probably as deterrents against certain mammals and fungi.What Made Chili Peppers So Spicy? Talk of the Nation, 15 August 2008. Pure capsaicin is a hydrophobic, colorless, highly pungent, crystalline to waxy s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoville Heat Units
The Scoville scale is a measurement of the pungency (spiciness or "heat") of chili peppers, as recorded in Scoville heat units (SHU), based on the concentration of capsaicinoids, among which capsaicin is the predominant component. The scale is named after its creator, American pharmacist Wilbur Scoville, whose 1912 method is known as the Scoville organoleptic test. The Scoville organoleptic test is a subjective assessment derived from the capsaicinoid sensitivity by people experienced with eating hot chilis. An alternative method, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), can be used to analytically quantify the capsaicinoid content as an indicator of pungency. As of 2011, the subjective organoleptic test has been largely superseded by analytical methods such as HPLC. Scoville organoleptic test In the Scoville organoleptic test, an exact weight of dried pepper is dissolved in alcohol to extract the heat components (capsaicinoids), then diluted in a solution of sugar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRPV1
The transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TrpV1), also known as the capsaicin receptor and the vanilloid receptor 1, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''TRPV1'' gene. It was the first isolated member of the transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor proteins that in turn are a sub-family of the transient receptor potential protein group. This protein is a member of the TRPV group of transient receptor potential family of ion channels. The function of TRPV1 is detection and regulation of body temperature. In addition, TRPV1 provides a sensation of scalding heat and pain (nociception). In primary afferent sensory neurons, it cooperates with TRPA1 (a chemical irritant receptor) to mediate the detection of noxious environmental stimuli. Function TRPV1 is an element of or mechanism used by the mammalian somatosensory system. It is a nonselective cation channel that may be activated by a wide variety of exogenous and endogenous physica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Wender
Paul A. Wender is an American chemist whose work is focused on organic chemistry, organometallic chemistry, synthesis, catalysis, chemical biology, imaging, drug delivery, and molecular therapeutics. He is currently the Francis W. Bergstrom Professor of Chemistry at Stanford University and is an Elected Fellow at the American Association for the Advancement of Science and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. Biography Born in 1947, Wender received his B.S. from Wilkes University in 1969, and his Ph.D. degree from Yale University in 1973. At Yale he worked with Frederick E. Ziegler, graduating with a thesis on the transformation of ketones into nitriles, and the total synthesis of eremophilone. He was a post-doctoral fellow at Columbia University in 1974. In 1974, he began his independent career as an assistant professor and later associate professor at Harvard University. In 1982, he became a professor at Stanford University. He is currently the Francis W. Bergstrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Tokyo
, abbreviated as or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. UTokyo has 10 faculties, 15 graduate schools and enrolls about 30,000 students, about 4,200 of whom are international students. In particular, the number of privately funded international students, who account for more than 80%, has increased 1.75 times in the 10 years since 2010, and the university is focusing on supporting international students. Its five campuses are in Hongō, Komaba, Kashiwa, Shirokane and Nakano. It is considered to be the most selective and prestigious university in Japan. As of 2021, University of Tokyo's alumni, faculty members and researchers include seventeen prime ministers, 18 Nobel Prize laureates, four Pritzker Prize laureates, five astronauts, and a Fields Medalist. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masayuki Inoue
Masayuki (written: , ,, , , , , , , , , , , , , , or ) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include: *, Japanese animator and director *, Japanese actor *, Japanese baseball player and manager *, Japanese politician *, Japanese samurai *, Japanese pianist and composer *, Japanese karateka *, Japanese ''daimyō'' *, Japanese handball player *, Japanese manga artist *, Japanese astronomer *, Japanese volleyball player *, Japanese voice actor *, Japanese speed skater *, Japanese physician *Masayuki Kawamura (golfer) (born 1967), Japanese golfer *, Japanese seismologist *, Japanese swimmer *, Japanese animator and anime director *, Japanese professional wrestler and mixed martial artist *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese sport wrestler *, Japanese gymnast *, Japanese volleyball player *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese anime director *, Japanese artist *, Japanese sumo wrestler *, Japanese actor *, Japanese film producer *, Japanese sculptor *, Japanese foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Burn
A chemical burn occurs when living tissue is exposed to a corrosive substance (such as a strong acid, base or oxidizer) or a cytotoxic agent (such as mustard gas, lewisite or arsine). Chemical burns follow standard burn classification and may cause extensive tissue damage. The main types of irritant and/or corrosive products are: acids, bases, oxidizers / reducing agents, solvents, and alkylants. Additionally, chemical burns can be caused by some types of cytotoxic chemical weapons, e.g., vesicants such as mustard gas and Lewisite, or urticants such as phosgene oxime. Chemical burns may: * need no source of heat * occur immediately on contact * not be immediately evident or noticeable * be extremely painful * diffuse into tissue and damage cellular structures under skin without immediately apparent damage to skin surface Presentation The exact symptoms of a chemical burn depend on the chemical involved. Symptoms include itching, bleaching or darkening of skin, burning sensat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes it from semisynthesis. Syntheses may sometimes conclude at a precursor with further known synthetic pathways to a target molecule, in which case it is known as a formal synthesis. Total synthesis target molecules can be natural products, medicinally-important active ingredients, known intermediates, or molecules of theoretical interest. Total synthesis targets can also be organometallic or inorganic, though these are rarely encountered. Total synthesis projects often require a wide diversity of reactions and reagents, and subsequently requires broad chemical knowledge and training to be successful. Often, the aim is to discover a new route of synthesis for a target molecule for which there already exist known routes. Sometimes, however, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapropylammonium Perruthenate
Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate (TPAP or TPAPR) is the chemical compound described by the formula N(C3H7)4RuO4. Sometimes known as the Ley–Griffith reagent, this ruthenium compound is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. This salt consists of the tetrapropylammonium cation and the perruthenate anion, . Uses Ruthenium tetroxide is a highly aggressive oxidant, but TPAP, which is its one-electron reduced derivative, is a mild oxidizing agent for the conversion of primary alcohols to aldehydes (the Ley oxidation). Secondary alcohols are similarly oxidized to ketones. It can also be used to oxidize primary alcohols all the way to the carboxylic acid with a higher catalyst loading, larger amount of the cooxidant, and addition of two equivalents of water. In this situation, the aldehyde reacts with water to form the geminal diol hydrate, which is then oxidized again. The oxidation generates water that can be removed by adding molecular sieves. TPAP is expensive, but it can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
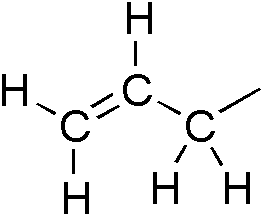
Allylic
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |