|
RATAN-600
The RATAN-600 (russian: РАТАН-600 – радиоастрономический телескоп Академии наук – 600, an acronym for the "Academy of Sciences Radio Telescope – 600") is a radio telescope in Zelenchukskaya, Karachay–Cherkess Republic, Russia. It comprises a 576 m diameter circle of rectangular radio reflectors and a set of secondary reflectors and receivers, based at an altitude of 970 m. Each of the 895 2×7.4 m reflectors can be angled to reflect incoming radio waves towards a central conical secondary mirror, or to one of five parabolic cylinders. Each secondary reflector is combined with an instrumentation cabin containing various receivers and instruments. The overall effect is that of a partially steerable antenna with a maximum resolving power of a nearly 600 m diameter dish, when using the central conical receiver, making it the world's largest-diameter individual radio telescope. Operating modes The telescope c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Astrophysical Observatory Of The Russian Academy Of Science
The Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Science (SAO RAS; russian: Специальная Астрофизическая Обсерватория) is an astronomical observatory, set up in 1966 in the USSR, and now operated by the Russian Academy of Sciences. Based in the Bolshoi Zelenchuk Valley of the Greater Caucasus near the village of Nizhny Arkhyz, the observatory houses the BTA-6 and RATAN-600, an optical and radio telescope, respectively. The two instruments are about apart. BTA-6 optical telescope The BTA-6 (Bolshoi Teleskop Altazimutalny; , or Large Altazimuth Telescope), with first light in 1975, was for several years the world's largest single primary mirror optical reflecting telescope. The BTA-6's primary mirror has a diameter of 6 metres (236 inches) and is housed in a 48 m (157.5 ft) diameter dome at an altitude of 2,070 m (6,791 ft). It held the record from its completion until 1993, when it was surpassed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
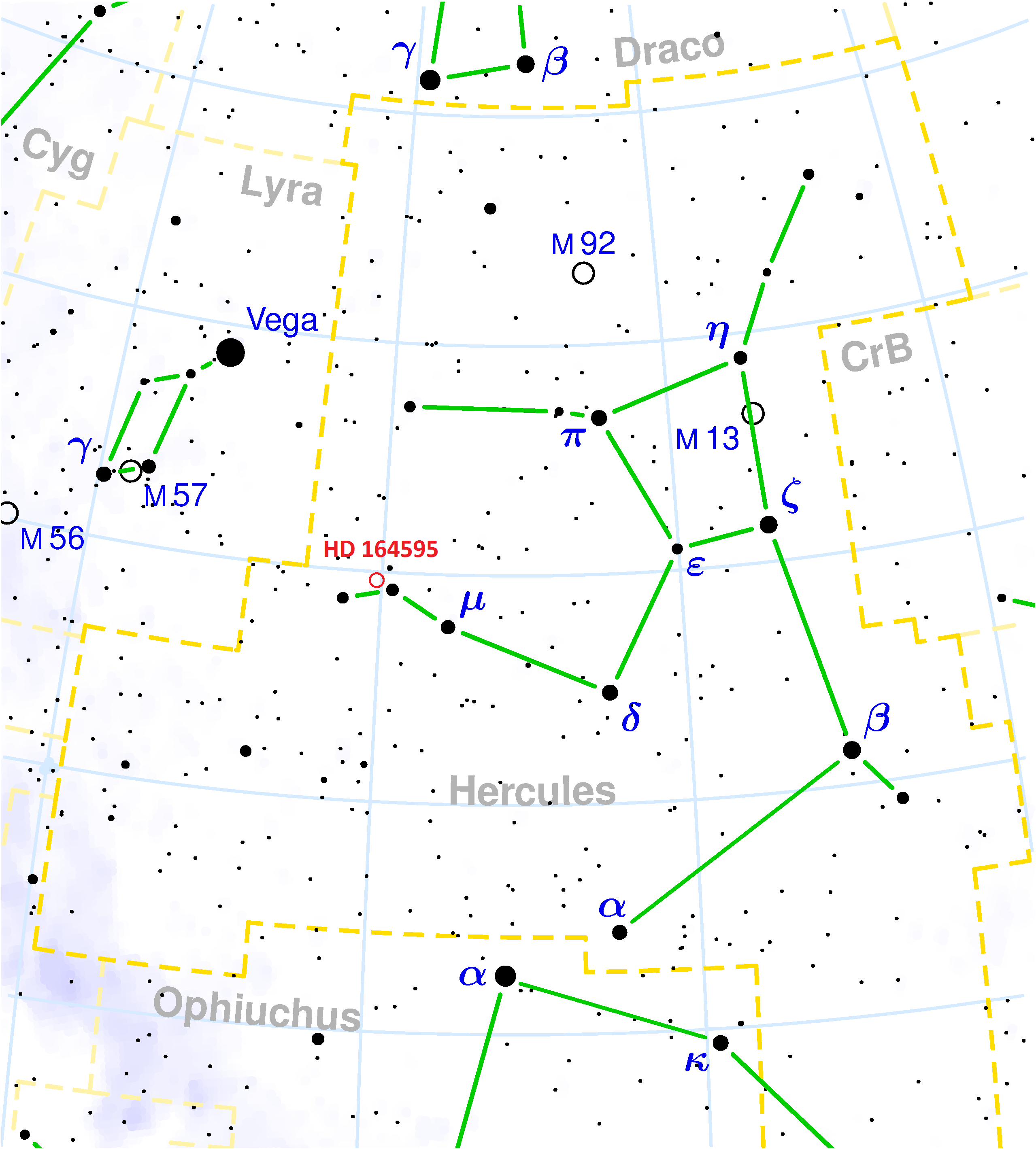
HD164595
HD 164595 is a G-type star located in the constellation of Hercules, from Earth that is notably similar to the Sun. With an apparent magnitude of 7.075, the star can be found with binoculars or a small telescope in the constellation Hercules. The star has the same stellar classification as the Sun: G2V. It has a similar temperature, at compared with for the Sun. It has a lower logarithm of metallicity ratio, at −0.06 compared with 0.00, and a slightly younger age, at 4.5 versus 4.6 billion years. Planetary system HD 164595 has one known planet, , which orbits HD 164595 every 40 days. It was detected with the radial velocity technique with the SOPHIE echelle spectrograph. The planet has a minimal mass equivalent of 16 Earths. Signal observation and SETI In 2016, HD 164595 briefly attracted media attention after it was reported that a possible SETI signal had been detected from the direction of the star in the previous year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTA-6
The BTA-6 (russian: Большой Телескоп Альт-азимутальный, translit=Bolshoi Teleskop Alt-azimutalnyi, translation=Large Altazimuth Telescope) is a aperture optical telescope at the Special Astrophysical Observatory located in the Zelenchuksky District of Karachay-Cherkessia on the north side of the Caucasus Mountains in southern Russia. The BTA-6 achieved first light in late 1975, making it the largest telescope in the world until 1990, when it was surpassed by the partially constructed Keck 1. It pioneered the technique, now standard in large astronomical telescopes, of using an altazimuth mount with a computer-controlled derotator. For a variety of reasons, BTA-6 has never been able to operate near its theoretical limits. Early problems with poorly fabricated mirror glass were addressed in 1978, improving but not eliminating the most serious issue. But due to its location downwind of numerous large mountain peaks, astronomical seeing is rarely go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in tracking an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karachay-Cherkessia
The Karachay-Cherkess Republic (russian: Карача́ево-Черке́сская Респу́блика, ''Karachayevo-Cherkesskaya Respublika''; krc, Къарачай-Черкес Республика, ''Qaraçay-Çerkes Respublika''; Circassian: Къэрэшей-Шэрджэс Республика, ''Ķêrêšei-Šêrdžês Respublikê'', nog, Карашай-Шеркеш Республика, ''Karaşay-Şerkeş Respublika'', abq, Къарча-Черкес Республика, ''Qarça-Çerkes Respublika'') or Karachay-Cherkessia (russian: Карача́ево-Черке́сия, ''Karachayevo-Cherkesiya'') is a federal subject (a republic) of Russia. It is geographically located in the North Caucasus region of Southern Russia and is administratively part of the North Caucasian Federal District. Karachay-Cherkessia has a population of 477,859 ( 2010 Census). Cherkessk is the largest city and the capital of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. Karachay-Cherkessia is one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescopes
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in tracking and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope
The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST; ), nicknamed Tianyan (, lit. "Sky's/Heaven's Eye"), is a radio telescope located in the Dawodang depression (), a natural basin in Pingtang County, Guizhou, southwest China. FAST has a diameter dish constructed in a natural depression in the landscape. It is the world's largest filled-aperture radio telescope and the second-largest single-dish aperture, after the sparsely-filled RATAN-600 in Russia. It has a novel design, using an active surface made of 4,500 metal panels which form a moving parabola shape in real time. The cabin containing the feed antenna, suspended on cables above the dish, can move automatically by using winches to steer the instrument to receive signals from different directions. It observes at wavelengths of 10 cm to 4.3 m. Construction of FAST began in 2011. It observed first light in September 2016. After three years of testing and commissioning, it was declared fully operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraus-type
The Kraus-type radio telescope design was created by Dr. John D. Kraus (1910–2004). Kraus-type telescopes are transit instruments, where the flat primary mirror reflects radio waves towards the spherical secondary mirror, which focuses it towards a mobile focal carriage. The primary tilts north–south to select any object near the meridian, while the focal carriage moves east–west along railroad ties to track objects near transit. Examples The Nançay radio telescope in France and the former Big Ear in Ohio are Kraus-type telescopes, and the southern section of the RATAN-600 The RATAN-600 (russian: РАТАН-600 – радиоастрономический телескоп Академии наук – 600, an acronym for the " Academy of Sciences Radio Telescope – 600") is a radio telescope in Zelenchukskaya, ... ring in Russia can operate as a Kraus-type telescope. Radio telescopes {{Astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1987 CPA 5893
File:1987 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The MS Herald of Free Enterprise capsizes after leaving the Port of Zeebrugge in Belgium, killing 193; Northwest Airlines Flight 255 crashes after takeoff from Detroit Metropolitan Airport, killing everyone except a little girl; The King's Cross fire kills 31 people after a fire under an escalator Flashover, flashes-over; The MV Doña Paz sinks after colliding with an oil tanker, drowning almost 4,400 passengers and crew; Typhoon Nina (1987), Typhoon Nina strikes the Philippines; LOT Polish Airlines Flight 5055 crashes outside of Warsaw, taking the lives of all aboard; The USS Stark is USS Stark incident, struck by Iraq, Iraqi Exocet missiles in the Persian Gulf; President of the United States, U.S. President Ronald Reagan gives a famous Tear down this wall!, speech, demanding that Soviet Union, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev tears down the Berlin Wall., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Zeebrugge disaster rect 200 0 400 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Karachay-Cherkessia
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy. Radio astronomy is conducted using large radio antennas referred to as radio telescopes, that are either used singularly, or with multiple linked telescopes utilizing the techniques of radio interferometry and aperture synthesis. The use of interferometry allows radio astronomy to achieve high angular resolution, as the resolving power of an interferometer is set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



