|
Rye Panorama
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than other cereals, making it useful in those regions; its vigorous growth suppresses weeds and provides abundant forage for animals early in the year. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) which includes the cereals wheat and barley. It is likely that rye arrived in Europe as a secondary crop, meaning that it was a minor admixture in wheat as a result of Vavilovian mimicry, and was only later cultivated in its own right. Rye grain is used for bread, beer, rye whiskey, and animal fodder. In Scandinavia, rye was a staple food in the Middle Ages, and rye crispbread remains a popular food in the region. Europe produces around half of the world's rye; relatively little is traded between countries. A wheat-rye hybrid, triticale, combines the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Rye
Wild rye is a common name used for several grasses. Wild ryes belong to any of three genera: * ''Elymus (plant), Elymus'' (wheatgrasses) * ''Leymus'' * ''Psathyrostachys'' Poaceae {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaff
Chaff (; ) is dry, scale-like plant material such as the protective seed casings of cereal grains, the scale-like parts of flowers, or finely chopped straw. Chaff cannot be digested by humans, but it may be fed to livestock, ploughed into soil, or burned. Etymology "Chaff" comes from Middle English , from Old English , related to Old High German ', "husk". Grain chaff In grasses (including cereals such as rice, barley, oats, and wheat), the ripe seed is surrounded by thin, dry, scaly bracts (called glumes, lemmas, and paleas), forming a dry husk (or hull) around the grain. Once it is removed, it is often referred to as chaff. In wild cereals and in the primitive domesticated einkorn,Potts, D. T. (1996) ''Mesopotamia Civilization: The Material Foundations'' Cornell University Press. p. 62. . emmer and spelt wheats, the husks enclose each seed tightly. Before the grain can be used, the husks must be removed. The process of loosening the chaff from the grain so as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples. Carbon-14 was discovered on February 27, 1940, by Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California Radiation Laboratory in Berkeley, California. Its existence had been suggested by Franz Kurie in 1934. There are three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon on Earth: carbon-12 (C), which makes up 99% of all carbon on Earth; carbon-13 (C), which makes up 1%; and carbon-14 (C), which occurs in trace amounts, making up about 1-1.5 atoms per 10 atoms of carbon in the atmosphere. C and C are both stable; C is unstable, with half-life years. Carbon-14 has a specific activity of 62.4 mCi/mmol (2.31 GBq/mmol), or 164.9 GBq/g. Carbon-14 deca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
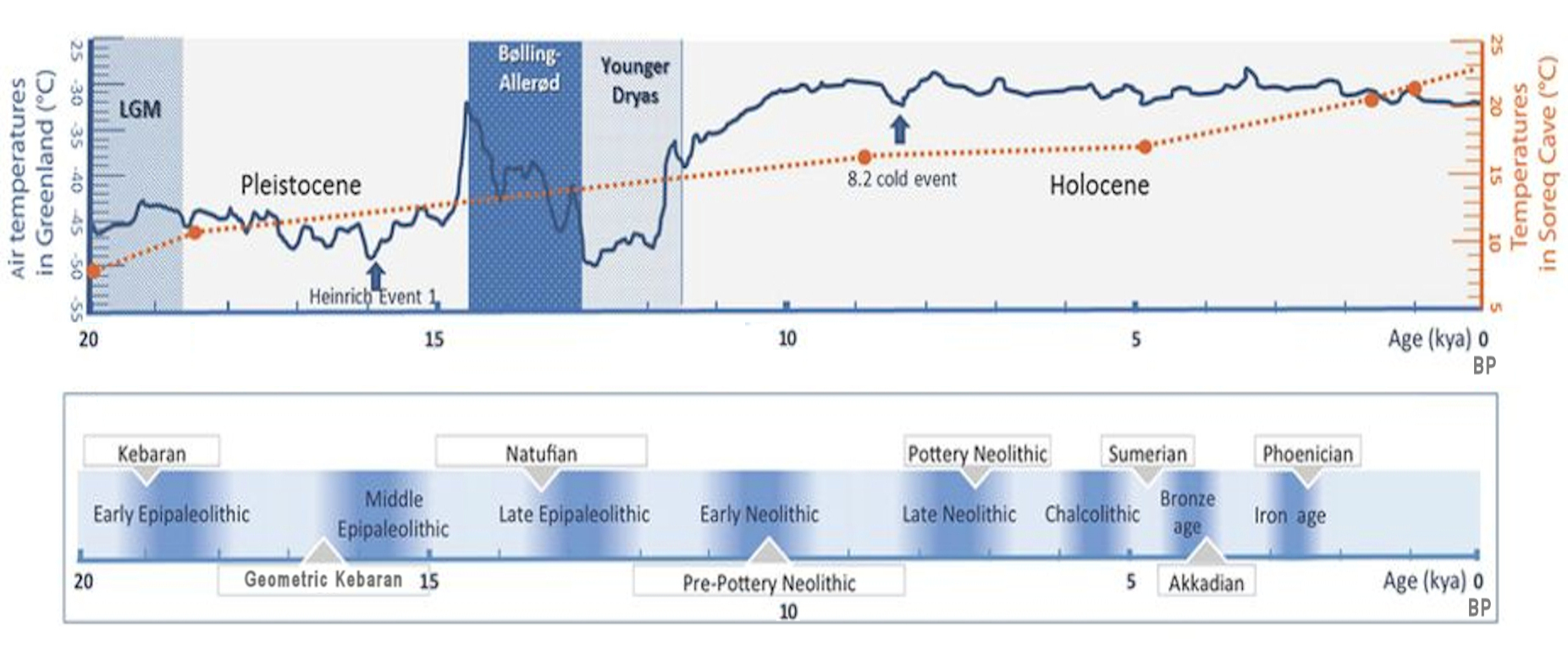
The Holocene
''The Holocene'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers research in the field of environmental studies, in particular environmental change over the last years, particularly the interface between the long Quaternary record and the natural and human-induced environmental processes operating at the Earth's surface today. It is published eight times a year by SAGE Publications. The editor-in-chief is John A. Matthews (University of Wales, Swansea). Scope Included within the scope of ''The Holocene'', according to the journal's website, are articles related to: * "Geological, biological and archaeological evidence of recent climate change; * "Interdisciplinary studies of environmental history and prehistory; * "The development of natural and cultural landscapes and ecosystems; and * "The prediction of future changes in the environment from the record of the past." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Abu Hureyra
Tell Abu Hureyra () is a prehistoric archaeological site in the Upper Euphrates valley in Syria. The tell was inhabited between 13,300 and 7,800 cal. BP in two main phases: Abu Hureyra 1, dated to the Epipalaeolithic, was a village of sedentary hunter-gatherers; Abu Hureyra 2, dated to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, was home to some of the world's first farmers. This almost continuous sequence of occupation through the Neolithic Revolution has made Abu Hureyra one of the most important sites in the study of the origins of agriculture. The site is significant because the inhabitants of Abu Hureyra started out as hunter-gatherers but gradually moved to farming, making them the earliest known farmers in the world. Cultivation started at the beginning of the Younger Dryas period at Abu Hureyra. Evidence uncovered at Abu Hureyra suggests that rye was the first cereal crop to be systematically cultivated. In light of this, it is now believed that the first systematic cultivation of cere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are sometimes confused or used as synonyms. More often, they are distinct, referring to approximately the same period of time in different geographic areas. Epipaleolithic always includes Epipalaeolithic Near East, this period in the Levant and, often, the rest of the Near East. It sometimes includes parts of Southeast Europe, where Mesolithic is much more commonly used. Mesolithic very rarely includes the Levant or the Near East; in Europe, Epipalaeolithic is used, though not very often, to refer to the early Mesolithic. The Epipalaeolithic has been defined as the "final Upper Palaeolithic industries occurring at the end of the final Last glacial period, glaciation which appear to merge technologically into the Mesolithic". The period is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Wild Relative
A crop wild relative (CWR) is a wild plant closely related to a domesticated plant. It may be a wild ancestor of the domesticated (cultivated) plant or another closely related taxon. Overview The wild relatives of crop plants constitute an increasingly important resource for improving agricultural production and for maintaining sustainable agro-ecosystems. Their natural selection in the wild accumulates a rich set of useful traits that can be introduced into crop plants by crossing. With the advent of anthropogenic climate change and greater ecosystem instability CWRs are likely to prove a critical resource in ensuring food security for the new millennium. It was Nikolai Vavilov, the Russian botanist who first realized the importance of crop wild relatives in the early 20th century. Genetic material from CWRs has been utilized by humans for thousands of years to improve the quality and yield of crops. Farmers have used traditional breeding methods for millennia, wild maize ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |