|
Rustam Zaman
Rustam Zaman was the title of a Bijapuri general who commanded Adil Shah's 10,000-strong army in the Battle of Kolhapur against Shivaji's forces. Rustam had participated in many wars against the Marathas and their leader Shivaji. One of those battles were Siege of Panhala (1660), Battle of Pavan Khind, Battle of Kolhapur and many more.He also was the son of Ranadulla Khan (who also held the title ''Rustam-i-Zaman''), an experienced and senior general of Bijapur and the chief mentor and guardian of Shahaji. He participated in the war against the Marathas under Afzal Khan. He was routed but he was allowed to go back to Bijapur by Nur Khan Beg and Tanaji Malusare, military commanders of Shivaji. He led the 10,000-strong Bijapuri army against the 3500 light cavalry of Marathas at Kolhapur. Due to the superior use of flanks by Shivaji, the Marathas won the battle and Rustam Zaman and Fazal Khan fled to Bijapur. It is said that in this battle shivaji used same tactics which Babu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
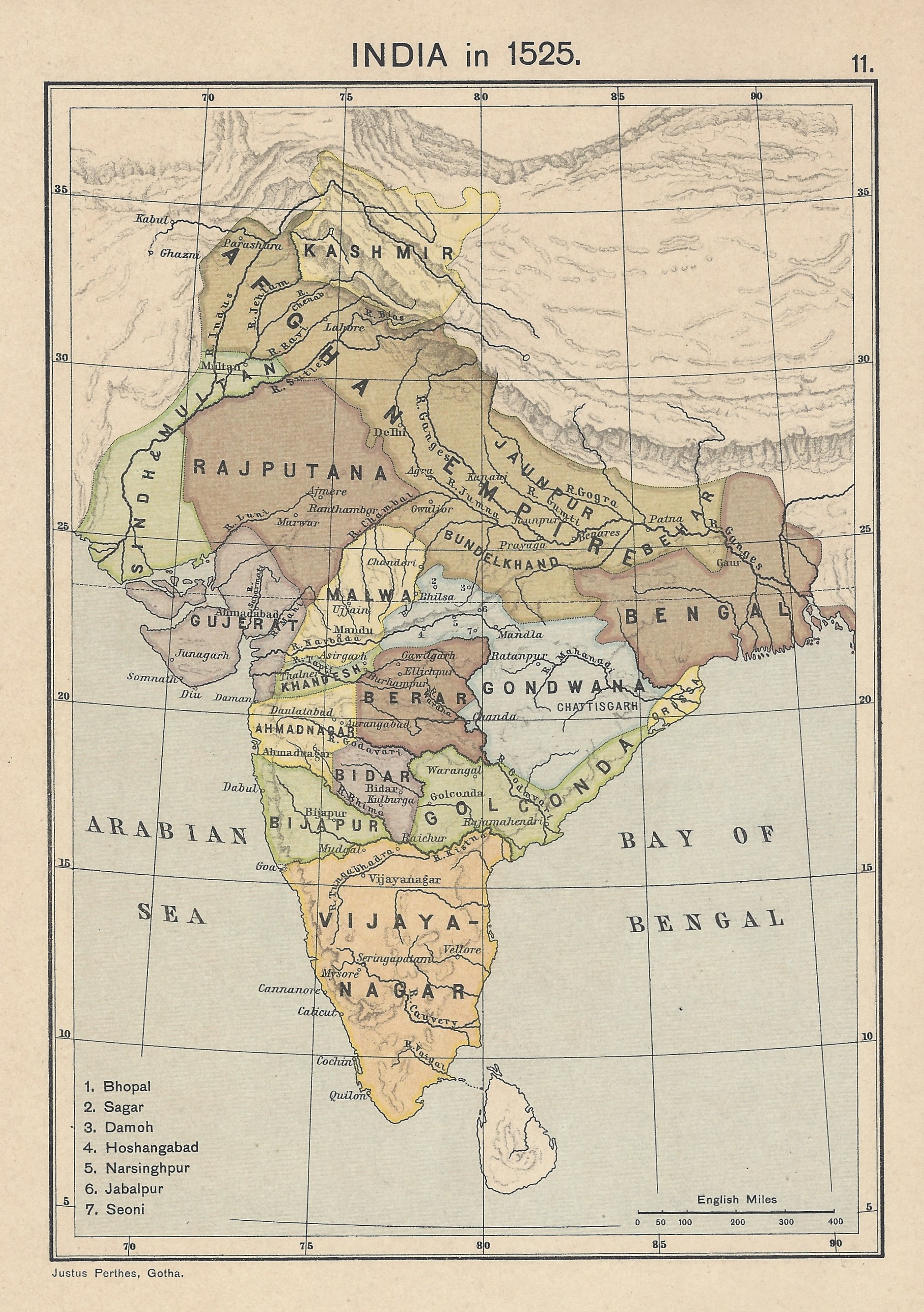
Adil Shahi
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a '' taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tanaji Malusare
Tanaji Kaloji Malusare or Subedar Tanaji Malusare was a military commander of the Maratha kingdom and a companion of Shivaji Maharaj. local poet Tulsidas, wrote a powada describing Subhedar Tanaji's heroics and sacrifice of life in the Battle of Sinhagad, which has since made him a popular figure in Indian folklore. Background According to the historian David Hardiman, Kolis were the early helpers of Shivaji in a revolt. Tanaji Malusare is one such prominent example whose name is memorizalized due to his act of capturing the fort of Singhad and handing it to Shivaji. Tanaji's father's name was Kaloji Malusare. In popular culture * Vinayak Damodar Savarkar had written a ballad on him, which was banned by the colonial British government. * ''Gad aala pan sinh gela'' (Marathi: गड आला पण सिंह गेला) () a Marathi novel by Hari Narayan Apte was written in 1903, based on his life. * In 1922 Bengali poet Jatindramohan Bagchi wrote a poem named ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indian Generals
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mewar
Mewar, also spelled as Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Mandsaur of Madhya Pradesh and some parts of Gujarat. For centuries, the region was ruled by Rajputs as Kingdom of Mewar. During the period of British East India Company, it became a princely state as Udaipur. It emerged as an administrative unit during the period governance in India and remained until the end of the British Raj era. The Mewar region lies between the Aravali Range to the northwest, Ajmer to the north, Gujarat and the Vagad region of Rajasthan to the south, the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh state to the south and the Hadoti region of Rajasthan to the east. Etymology The word "Mewar" is vernacular form of "Medapata" (IAST: Medapāṭa), the ancient name of the region. The earliest epigraph that ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (12 April 1482 – 30 January 1528), most commonly known as Rana Sanga, was the Rana of Mewar, Maharana of Mewar from 1509 to 1528. A member of the List of Ranas of Mewar, Sisodia dynasty, he controlled parts of present-day Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Sindh, and Uttar Pradesh with his capital at Chittorgarh. In his military career, Sanga achieved a series of successes against several neighbouring sultanates. Following the Battle of Gagron in 1519 against the Malwa Sultanate, Sanga Mewar-Malwa Conflict, captured much of Malwa, Eastern Malwa. He Rana Sanga's invasion of Gujarat, humbled the Sultan of Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat on various occasions. He also reduced the Khanzadas of Mewat to his submission helping him to extend his sway over modern-day Haryana. Among his great victories were the List of Mewar (Sisodiya)–Delhi conflicts#List of Battles, multiple defeats inflicted upon the Lodi dynasty of Delhi at Khatoli, Dholpur, and Ranthambore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also given the posthumous name of ''Firdaws Makani'' ('Dwelling in Paradise'). Born in Andijan in the Fergana Valley (now in Uzbekistan), Babur was the eldest son of Umar Shaikh Mirza II (1456–1494, Timurid governor of Fergana from 1469 to 1494) and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur (1336–1405). Babur ascended the throne of Fergana in its capital Akhsikath in 1494 at the age of twelve and faced rebellion. He conquered Samarkand two years later, only to lose Fergana soon after. In his attempt to reconquer Fergana, he lost control of Samarkand. In 1501, his attempt to recapture both the regions failed when the Uzbek prince Muhammad Shaybani defeated him and founded the Khanate of Bukhara. In 1504, he conquered Kabul, which was un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bijapur, Karnataka
Bijapur (officially Vijayapura) is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural importance built during the rule of the Adil Shahi dynasty. It is also well known for the popular Karnataka premier league team, the Bijapur Bulls. Bijapur is located northwest of the state capital Bangalore and about from Mumbai and north east of the city of Belgaum. The city was established in the 10th–11th centuries during the time of Kalyani Chalukyas and was known as ''Vijayapura'' (city of victory). The city was passed to Yadavas after Chalukya's demise. In 1347, the area was conquered by the Bahmani Sultanate. After the split of the Bahmani Sultanate, the Bijapur Sultanate ruled from the city. Relics of the Sultanates' rule can be found in the city, including the Bijapur Fort, Bara Kaman, Jama Masjid, and Gol Gumbaz. Bijapur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Kolhapur is one of the most significant cities in South Maharashtra and has been a hub of historical, religious, and cultural activities for centuries. It is famous for its unique food culture, including its signature Kolhapuri cuisine. The city is situated in the western part of Maharashtra and is often referred to as "Dakshin Kashi" or "Mahateerth". It boasts a rich history, which has given it various other names, including Kollagiri, Kolladigiripattan and Kollpur, all meaning "valley" Around 2 CE Kolhapur's name was 'Kuntal'. Kolhapur is known as Dakshin Kashi''' or Kashi of the South because of its spiritual history and the antiquity of its shrine Mahalaxmi, better known as Ambabai. The region is known for the production of the famous handcrafted and braided leather slippers called Kolhapuri chappal, which received the Geographical Indication designatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Afzal Khan (general)
Afzal Khan (died 20 November 1659) was a general of the Adil Shahi dynasty of Bijapur Sultanate of in Deccan Plateau, Deccan India. He played an important role in the southern expansion of the Bijapur Sultanate by subjugating the Nayaka dynasties, Nayaka chiefs who had taken control of the former Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara territory. In 1659, the Bijapur government sent Afzal Khan to subjugate Shivaji, a former vassal who had rebelled against the Bijapur government. He was killed at a truce negotiation meeting with Shivaji, and his army was defeated at the Battle of Pratapgad. Victory over the Nayakas Amid the decline of the Vijayanagara Empire, the Bijapur government campaigned against the Nayaka dynasties, Nayaka chiefs who had taken control of the former Vijayanagara territory. One of these chiefs was Virabhadra, the Nayakas of Keladi, Nayaka of Ikkeri. Kenge Nayaka (or Keng Nayak), the chief of Basavapattana and a discontented tributary of Virabhadra, helped the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adilshah
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a ''taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marathas
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Maratha states under the nominal leadership of the former. The Marathas were a Marathi language, Marathi-speaking peasantry group from the western Deccan Plateau (present-day Maharashtra) that rose to prominence under leadership of Shivaji (17th century), who revolted against the Bijapur Sultanate and the Mughal Empire for establishing "Hindavi Swarajya" (). The religious attitude of Aurangzeb, Emperor Aurangzeb estranged Kafir, non-Muslims, and the Deccan wars, Maratha insurgency came at a great cost for his men and treasury. The Maratha government also included warriors, administrators, and other nobles from other Marathi people, Marathi groups. Shivaji's monarchy, referred to as the Maratha Kingdom, expanded into a large realm in the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shahaji
Shahaji Bhonsale (; 18 March 1594 – 23 January 1664) was a 17th century Indian military leader who served the Ahmadnagar Sultanate, the Bijapur Sultanate, and the Mughal Empire at various points in his career. As a member of the Bhonsle dynasty, Shahaji inherited the Pune and Supe jagirs (fiefs) from his father Maloji, who previously served the Ahmadnagar Sultanate. During the Mughal invasion of the Deccan, Shahaji joined the Mughal forces and served under Emperor Shah Jahan for a short period. After being deprived of his jagirs, he defected to the Bijapur Sultanate in 1632 and regained control over Pune and Supe. In 1638, he received the jagir of Bangalore after Bijapur's invasion of Kempe Gowda III's territories. Afterwards, he became the chief general of Bijapur and oversaw its expansion. He was the father of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Kingdom. Early life Shahaji was the son of Maloji Bhosale, a Maratha warrior and nobleman who had been awarded the jagirs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |