|
Rugosa
The Rugosa or rugose corals are an extinct Class (biology), class of solitary and Colony (biology), colonial corals that were abundant in Middle Ordovician to Late Permian seas. Solitary rugosans (e.g., ''Caninia (genus), Caninia'', ''Lophophyllidium'', ''Neozaphrentis'', ''Streptelasma'') are often referred to as ''horn corals'' because of a unique horn-shaped chamber with a wrinkled, or wiktionary:rugose, rugose, wall. Some solitary rugosans reached nearly a meter (3 ft 3 in) in length. However, some species of rugose corals could form large colonies (e.g., ''Lithostrotion''). When radiating septa were present, they were usually in multiples of four, hence ''Tetracorallia'' in contrast to modern ''Hexacorallia'', colonial polyps generally with sixfold symmetry. Rugose corals have a skeleton made of calcite that is often fossilized. Like modern corals (Scleractinia), rugose corals were invariably benthic, living on the sea floor or in a reef-framework. Some symbiotic rugose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral reef, reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many cloning, genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
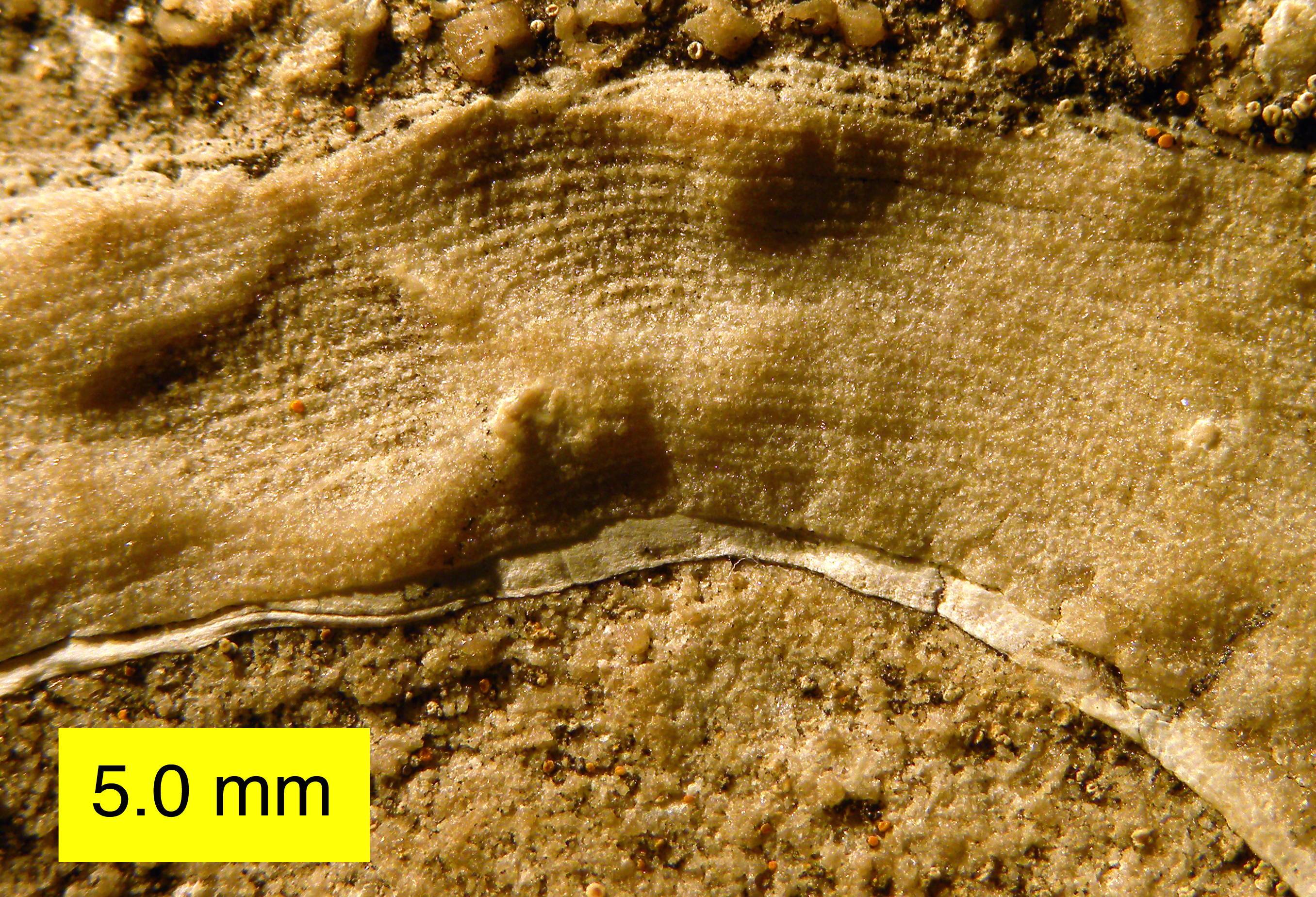
Stromatoporoidea
Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian.Stock, C.W. 2001, Stromatoporoidea, 1926–2000: ''Journal of Paleontology'', v. 75, p. 1079–1089. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking Sponge spicule, spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms. Externally, some species have raised bumps (mamelons) and star-shaped crevices (astrorhizae), which together help vent exhalant water away from the living surface. Internally, stromatoporoids have a mesh-like skeletal system combining extensive horizontal layers (laminae), vertical rods (pillars), and boxy spaces (galleries), along with other features. The most common growth forms range from laminar (flattened) to domical (dome-shaped). Spheroidal, finger-like, or tree-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grewingkia
''Grewingkia'' is a genus of extinct Paleozoic coral Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...s, found in Indiana. It contains at least one species, ''Grewingkia canadensis''. References Rugosa Prehistoric Hexacorallia genera Paleozoic life of Ontario Paleozoic life of Alberta Paleozoic life of British Columbia Paleozoic life of Manitoba Paleozoic life of the Northwest Territories Paleozoic life of Nunavut Fossil taxa described in 1862 {{paleo-invertebrate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleractinia
Scleractinia, also called stony corals or hard corals, are marine animals in the phylum Cnidaria that build themselves a hard skeleton. The individual animals are known as polyps and have a cylindrical body crowned by an oral disc in which a mouth is fringed with tentacles. Although some species are solitary, most are colonial. The founding polyp settles and starts to secrete calcium carbonate to protect its soft body. Solitary corals can be as much as across but in colonial species the polyps are usually only a few millimetres in diameter. These polyps reproduce asexually by budding, but remain attached to each other, forming a multi-polyp colony of clones with a common skeleton, which may be up to several metres in diameter or height according to species. The shape and appearance of each coral colony depends not only on the species, but also on its location, depth, the amount of water movement and other factors. Many shallow-water corals contain symbiont unicellular organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithostrotion
''Lithostrotion'' is a genus of rugose coral which is commonly found as a fossil within Carboniferous Limestone. ''Lithostrotion'' is a member of the family Lithostrotionidae. The genus ''Lithostrotion'', a common and readily recognised group of fossils, became extinct by the end of the Palaeozoic The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of ... era. Species * ''Lithostrotion affine'' Fleming, 1828 * ''Lithostrotion araneum'' (McCoy, 1844)NUDDS, J. R.: An illustrated. key to the British lithostrotionid corals. Acta Palaeont; http://app.pan.pl/archive/published/app25/app25-385.pdf. * ''Lithostrotion banffense'' Warren, 1927 * ''Lithostrotion concinum'' Lonsdale, 1845 * ''Lithostrotion decipiens'' (McCoy, 1849) * ''Lithostrotion edmondsi'' Smith, 1928 * ''Lithostrotion fascicul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caninia (genus)
''Caninia'' is an extinct genus of rugose coral. Its fossils occur worldwide from the Devonian to the Permian periods. Paleoecology It was marine in nature and known to live in lagoon-type ecosystem An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...s. Because of the shallow water in which it lived, Caninia was often affected by processes above the water level, such as storms. Distribution References {{Taxonbar, from=Q5032424 Rugosa Prehistoric Hexacorallia genera Devonian first appearances Permian genus extinctions Paleozoic life of Alberta Paleozoic life of the Northwest Territories Paleozoic life of Nunavut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexacorallia
Hexacorallia is a Class (biology), class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyp (zoology), polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are Colony (biology), colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant Order (biology), orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another class of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic Sessility (zoology), sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals. Phylogeny Hexacorallia is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugose
Rugose means "wrinkled". It may refer to: * Rugosa, an extinct order of coral, whose rugose shape earned it the name * Rugose, adjectival form of rugae Species with "rugose" in their names * ''Idiosoma nigrum'', more commonly, a black rugose trapdoor spider * Rugose spiraling whitefly {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Megaannum, Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony is composed of two or more Biological specificity#Conspecific, conspecific individuals living in close association with, or connected to, one another. This association is usually for mutual benefit such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Colonies can form in various shapes and ways depending on the organism involved. For instance, the bacterial colony is a cluster of identical cells (clones). These colonies often form and grow on the surface of (or within) a solid medium, usually derived from a single parent cell. Colonies, in the context of development, may be composed of two or more unitary (or solitary) organisms or be Modularity, modular organisms. Unitary organisms have determinate development (set life stages) from zygote to adult form and individuals or groups of individuals (colonies) are visually distinct. Modular organisms have indeterminate growth forms (life stages not set) through repeated iteration of genetically identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |