|
Rudiments
In ''rudimental drumming'', a form of percussion music, a drum rudiment is one of a number of relatively small patterns which form the foundation for more extended and complex drumming patterns. The term "drum rudiment" is most closely associated with various forms of ''field drumming'', where the snare drum plays a prominent role. In this context "rudiment" means not only "basic", but also ''fundamental''. This tradition of drumming originates in Military drums, military drumming and it is a central component of martial music. Definition Rudimental drumming has something of a flexible definition, even within drumming societies devoted to that form of drumming. RudimentalDrumming.com defines it as "the study of coordination." The Percussive Arts Society defines it as a particular method for learning the drums—beginning with rudiments, and gradually building up speed and complexity through practicing those rudiments. ''Camp Duty Update'' defines a drum rudiment as an excer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfons Grieder
Alfons Grieder was a Swiss rudimental drummer who spread awareness of the Basel Drumming style in America during the mid to late 20th century through his traveling, teaching, and publications. Biography Grieder was born in Basel, Switzerland in 1939 and began studying Basel style snare drumming with Dr. Fritz Berger in 1949. He came to the United States in the 1950s to study classical percussion with teachers like Saul Goodman and Morris Goldenberg. Starting in 1957, Greider worked with Dutch drummer Rob Verhagen to organize Basel drumming workshops in The Netherlands. In the 1960s he visited the Deep River Drum Corps's annual muster, reportedly inspiring the corps to start a subsidiary group called the Swiss Mariners. At the muster he noticed that the ancient American Fife and Drum Corps tradition was very similar to that of his native Basel. Grieder eventually took American Ancient drumming back to Switzerland and taught Swiss drummers to play in the American style. He wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snare Drum
The snare drum (or side drum) is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used in Orchestra, orchestras, Concert band, concert bands, Marching band, marching bands, Parade, parades, drumlines, drum corps, and more. It is one of the central pieces in a drum set, a collection of percussion instruments designed to be played by a seated drummer and used in many genres of music. Because basic rhythms are very easy to learn to play on a snare drum even for children, the instrument is also suitable for the music education for young children and a rhythm band. Snare drums are usually played with drum sticks, but other beaters such as the Brush (percussion), brush or the Rute (music), rute can be used to achieve different tones. The snare drum is a versatile and expressive percussion instrument due to its sensitivity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Berger (percussionist)
Fritz Berger was a Swiss drum teacher and drum method book author. He wrote several influential books on Swiss rudimental drumming, or Basler Trommeln, that are still thought of as the authoritative sources for Swiss drumming in America. Biography Dr. Fritz Robert Berger was born in 1895 in Switzerland and is sometimes referred to as the "Drummel-Doggter". His middle name is sometimes given as Rudolf. He studied the Basel style of snare drumming, called Basler Trommeln or Basle Trommel, and published his book Das Basler Trommeln : nebst vollständigem Lehrgang und einer Sammlung aller Basler Trommelmärsche in 1928. He also published article called ''Das Basler Trommeln, Werden und Wesen'' in 1936. His books and other publications outlined the Swiss Basel rudimental system in a novel notation system that was much easier to read for drummers from outside of the Basel tradition. Previously, Basel notation had been either onomatopoetic, using syllables written out in letters to rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America. The Thirteen Colonies in their traditional groupings were: the New England Colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut); the Middle Colonies ( New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware); and the Southern Colonies (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia). These colonies were part of British America, which also included territory in The Floridas, the Caribbean, and what is today Canada. The Thirteen Colonies were separately administered under the Crown, but had similar political, constitutional, and legal systems, and each was dominated by Protestant English-speakers. The first of the colonies, Virginia, was established at Jamestown, in 1607. Maryland, Pennsylvania, and the New England Colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Stroke
In music, a drum stroke is a movement which produces a single or multiple notes on drums or other percussion instruments such as cymbals. There are several types of strokes: five basic single strokes (noted below), double strokes, and other multiple strokes such as triples, quadruples, or buzzes of indeterminate number. Basic strokes The basic strokes produce a single hit or notes while resulting in different sounds. They are produced by different movements. While the basic strokes are fundamental sequences, the basic strokes are composed of three positions: up position (maximum height of the wrist), the tap position (minimum height of the wrist), and the rest position (when the wrist is still). Each of the basic strokes are a combination of the three positions. *The ''full stroke'' begins with the tip of the drumstick up or held near vertically above the striking surface. The drummer strikes the drum and then returns the stick back up to its original position. *The ''down st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov. At the time, his name was spelled , which he romanized as Nicolas Rimsky-Korsakow; the BGN/PCGN transliteration of Russian is used for his name here; ALA-LC system: , ISO 9 system: .. (18 March 1844 – 21 June 1908) was a Russian composer, a member of the group of composers known as The Five. He was a master of orchestration. His best-known orchestral compositions—'' Capriccio Espagnol'', the '' Russian Easter Festival Overture'', and the symphonic suite '' Scheherazade''—are staples of the classical music repertoire, along with suites and excerpts from some of his fifteen operas. ''Scheherazade'' is an example of his frequent use of fairy-tale and folk subjects. Rimsky-Korsakov believed in developing a nationalistic style of classical music, as did his fellow composer Mily Balakirev and the critic Vladimir Stasov. This style employed Russian folk song and lore along with exotic harmonic, melodic and rhythmic elements in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Practice Pad With Metronome Best Practice
Practice or practise may refer to: Education and learning * Practice (learning method), a method of learning by repetition * Phantom practice, phenomenon in which a person's abilities continue to improve, even without practicing * Practice-based professional learning Medical and pharmacy * Medicine, Medical practice, providing healthcare Law * Legal practice * Practice of law Art, media, and entertainment * Practice chanter, a musical instrument used to practice the Great Highland bagpipes * ''The Practice'', a television series about a legal practice Other * Best practice * Practice theory, a family of theories in sociology * Spiritual practice * Standards and Practices, a conventional, traditional, or otherwise standardised method See also * The Practice (other) * Praxis (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top Secret Drum Corps
Top Secret Drum Corps is a drum corps based in Basel, Switzerland. With 25 drummers and colour guard section, the corps became famous for its demanding six-minute routine performed at the Royal Edinburgh Military Tattoo in 2003. With its invitation to Edinburgh, Top Secret became one of the first non-military, non-British Commonwealth acts to perform on the Esplanade at Edinburgh Castle. Since its success in 2003, Top Secret was invited to return to Edinburgh in 2006 with a new routine. They were invited a third time in 2009 and again in 2012, 2015, 2018 and 2022. Under the leadership of Erik Julliard, the band is also responsible for the founding of the Basel Tattoo, a military tattoo show similar to the Royal Edinburgh Military Tattoo, now held annually in Basel. Drumming style Top Secret was founded in 1991, with its roots in the rich drumming traditions of the band's home city, Basel, which is known for its annual carnival called '' Basler Fasnacht''. The city is sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoinot Arbeau
Thoinot Arbeau is the anagrammatic pen name of French cleric Jehan Tabourot (March 17, 1520 – July 23, 1595). Tabourot is most famous for his ''Orchésographie'', a study of late sixteenth-century French Renaissance social dance. He was born in Dijon and died in Langres. ''Orchésographie'' and other work ''Orchésographie'', first published in Langres, 1589, provides information on social ballroom behaviour and on the interaction of musicians and dancers. It is available online in facsimile and in plain text. There is an English translation by Mary Stewart Evans, edited by Julia Sutton, in print with Dover Publications. It contains numerous woodcuts of dancers and musicians and includes many dance tabulations in which extensive instructions for the steps are lined up next to the musical notes, a significant innovation in dance notation at that time. ''Orchésographie'' was partly written as a rebuttal of Calvinist treatises published at the time which argued that dance w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism in music, Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In the 1920s and 1930s Ravel was internationally regarded as France's greatest living composer. Born to a music-loving family, Ravel attended France's premier music college, the Paris Conservatoire; he was not well regarded by its conservative establishment, whose biased treatment of him caused a scandal. After leaving the conservatoire, Ravel found his own way as a composer, developing a style of great clarity and incorporating elements of modernism (music), modernism, baroque music, baroque, Neoclassicism (music), neoclassicism and, in his later works, jazz. He liked to experiment with musical form, as in his best-known work, ''Boléro'' (1928), in which repetition takes the place of development. Renowned for his abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
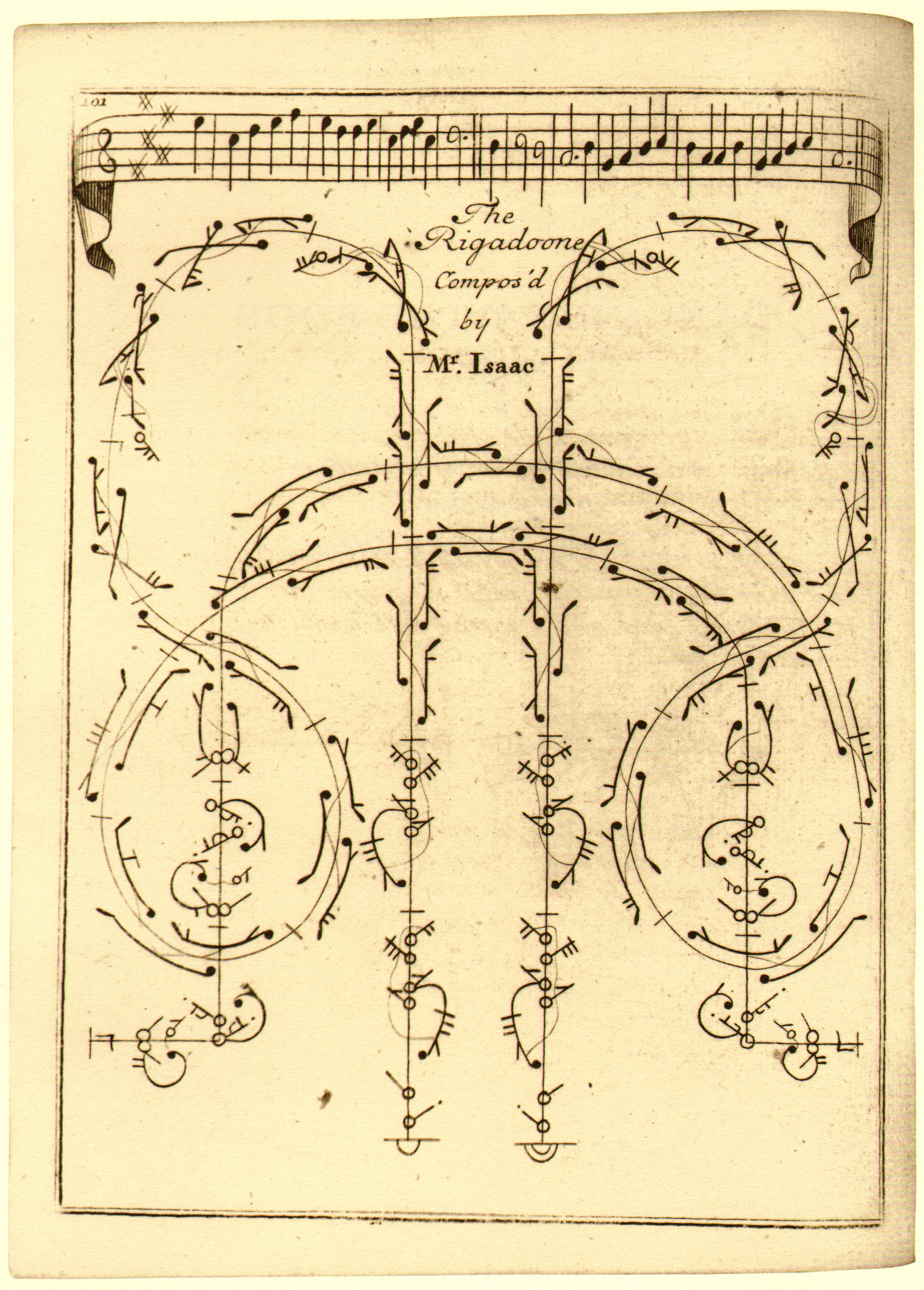
Le Rigodon
The rigaudon (, ), anglicized as rigadon or rigadoon, is a French baroque dance with a lively duple metre. The music is similar to that of a bourrée, but the rigaudon is rhythmically simpler with regular phrases (eight measure phrases are most common). It originated as a sprightly 17th-century French folk dance for couples. Traditionally, the folkdance was associated with the provinces of Vivarais, Languedoc, Dauphiné, and Provence in southern France, and it became popular as a court dance during the reign of Louis XIV. Its hopping steps were adopted by the skillful dancers of the French and English courts, where it remained fashionable through the 18th century. By the close of the 18th century, however, it had given way in popularity as a ballroom dance (along with the passepied, bourrée, and gigue) to the minuet; however, in the 20th century, Maurice Ravel would employ this baroque dance in his piano suite ''Le Tombeau de Couperin ''Le Tombeau de Couperin'' (''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |