|
Royal Westminster Militia
The Royal Westminster Militia, later the 5th (Reserve) Battalion, Royal Fusiliers, was an auxiliary regiment raised in the City of Westminster in the suburbs of London. Descended from the Westminster Trained Bands, which were on duty during the Armada campaign of 1588 and saw considerable service during the English Civil War, the regiment underwent reorganisation in 1760 as part of the Middlesex Militia. From 1778 until 1918 the regiment served in home and colonial defence in all of Britain's major wars, and supplied thousands of reinforcements to the Royal Fusiliers during World War I. After a shadowy postwar existence the unit was finally disbanded in 1953. Background The universal obligation to military service in the Shire levy was long established in England and its legal basis was updated by two acts of 1557 ( 4 & 5 Ph. & M. cc. 2 and 3), which placed the militia under the command of county Lords Lieutenant appointed by the monarch. This is seen as the starting date for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Royal Fusiliers
The Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in continuous existence for 283 years. It was known as the 7th Regiment of Foot until the Childers Reforms of 1881. The regiment served in many wars and conflicts throughout its long existence, including the Second Boer War, the First World War and the Second World War. In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the other regiments of the Fusilier Brigade – the Royal Northumberland Fusiliers, the Royal Warwickshire Fusiliers and the Lancashire Fusiliers – to form a new large regiment, the Royal Regiment of Fusiliers. The Royal Fusiliers War Memorial, a monument dedicated to the almost 22,000 Royal Fusiliers who died during the First World War, stands on Holborn in the City of London. History Formation It was formed as a fusilier regiment in 1685 by George Legge, 1st Baron Dartmouth, from two companies of the Tower of London guard, and was originally called the Ordnance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middlesex Militia
The Middlesex Militia was an auxiliary military force in the county of Middlesex in South East England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands, in 1572 and their service during the Armada Crisis and in the English Civil War, the Militia regiments of Middlesex served during times of international tension and all of Britain's major wars. By 1853 there were five regiments in the county. They provided internal security and home defence but sometimes operated further afield, including France and the Mediterranean, relieving regular troops from routine garrison duties, and acting as a source of trained officers and men for the Regular Army. Some of the infantry battalions went on active service during the Second Boer War and all served as Special Reserve training units in World War I. After 1921 the militia had only a shadowy existence until its final abolition in 1953. Early history The English militia was descended from the Anglo-Saxon ''Fyrd'', the military force raised fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
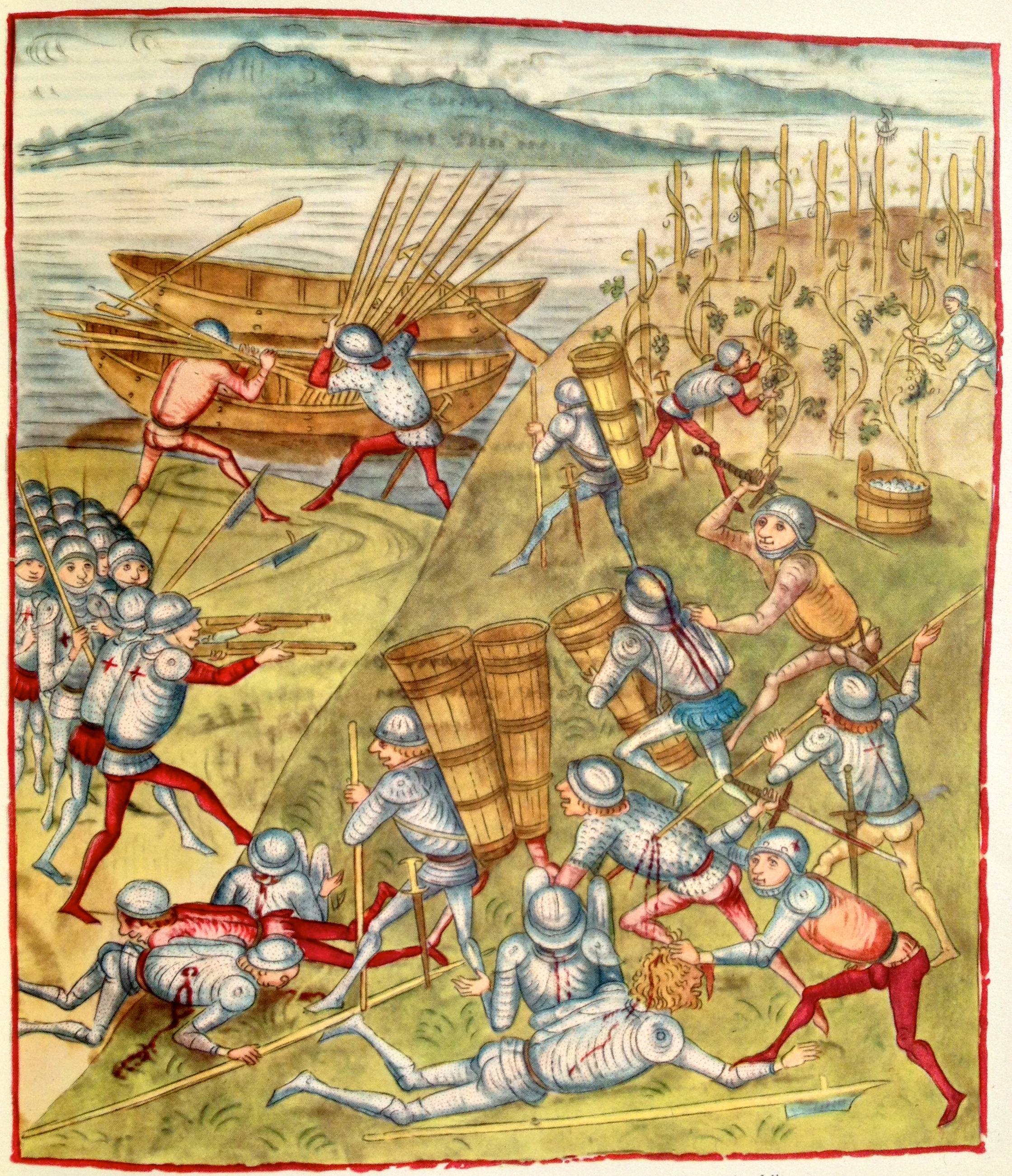
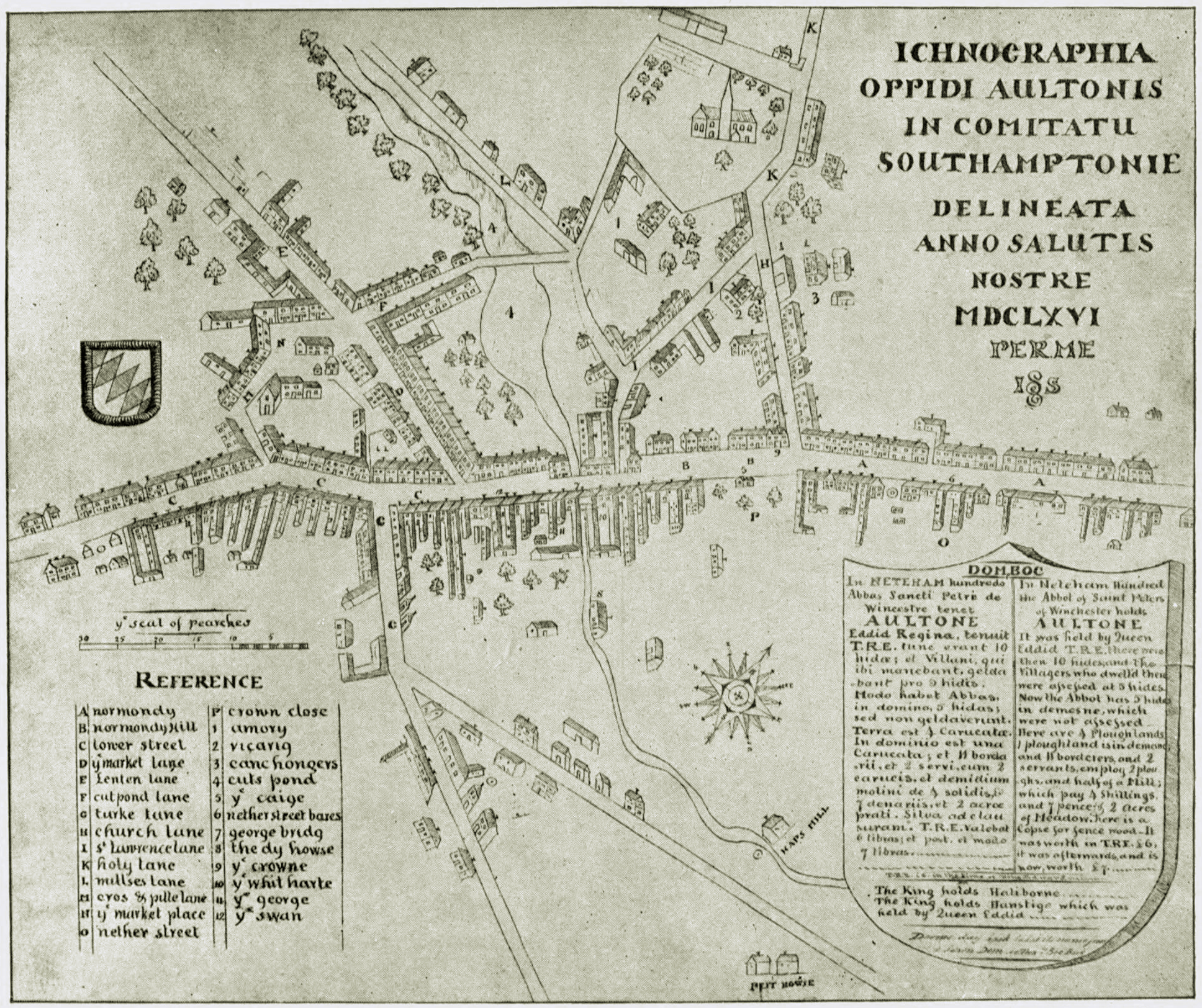
Battle Of Alton
The Battle of Alton (also known as the Storming of Alton), of the First English Civil War, took place on 13 December 1643 in the town of Alton, Hampshire, England. There, Roundheads, Parliamentary forces serving under Sir William Waller led a successful surprise attack on a winter garrison of Cavalier, Royalist infantry and cavalry serving under the Ludovic Lindsay, 16th Earl of Crawford, Earl of Crawford. The Battle of Alton was the first decisive defeat of Ralph Hopton, 1st Baron Hopton, Sir Ralph Hopton, leader of Royalist forces in the south, and the event had a significant psychological effect on him as commander. More important to Hopton was the loss of men, however, as he was already short-handed in much-needed infantry. The successful Parliamentarians were able, after their victory, to attack and successfully Siege of Arundel, besiege Arundel, a larger and more formidable Royalist outpost to the south-east of Alton. At dawn on 13 December, as Waller's army approa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Basing House
The siege of Basing House near Basingstoke in Hampshire, was a Parliamentarian victory late in the First English Civil War. Whereas the title of the event may suggest a single siege, there were in fact three major engagements. John Paulet, 5th Marquess of Winchester owned the House and as a committed Royalist garrisoned it in support of King Charles I, as it commanded the road from London to the west through Salisbury. The first engagement was in November 1643, when Sir William Waller at the head of an army of about 7,000 attempted to take Basing House by direct assault. After three failed attempts it became obvious to him that his troops lacked the necessary resolve, and with winter fast approaching Waller retreated back to a more friendly location. Early in 1644 the Parliamentarians attempted to arrange the secret surrender of Basing House with Lord Edward Paulet, the Marquess of Winchester's younger brother, but the plot was discovered. Parliamentary forces conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
London Trained Bands
The London Trained Bands (LTBs) were a part-time military force in the City of London from 1559 until they were reconstituted as conventional Militia regiments in 1794. They were periodically embodied for home defence, for example in the army mustered at Tilbury during the Armada Campaign of 1588. They saw a great deal of active service during the English Civil War, including the First and Second Battles of Newbury, and the battles of Alton, Cheriton, Cropredy Bridge and Lostwithiel. Throughout their history they were used to suppress civil disorder and insurrection around the capital. Early history The English militia was descended from the Anglo-Saxon ''Fyrd'', the military force raised from the freemen of the shires under command of their Sheriff. It continued under the Norman kings, notably at the Battle of the Standard (1138). The force was reorganised under the Assizes of Arms of 1181 and 1252, and again by King Edward I's Statute of Winchester of 1285.Holmes, pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caliver
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier. The term ''arquebus'' was applied to many different forms of firearms from the 15th to 17th centuries, but it originally referred to "a hand-gun with a hook-like projection or lug on its under surface, useful for steadying it against battlements or other objects when firing". These "hook guns" were in their earliest forms defensive weapons mounted on German city walls in the early 15th century. The addition of a shoulder stock, priming pan, and matchlock mechanism in the late 15th century turned the arquebus into a handheld firearm and also the first firearm equipped with a trigger. The exact dating of the matchlock's appearance is disputed. It could have appeared in the Ottoman Empire as early as 1465 and in Europe a little before 1475. The heavy arquebus, which was then called a musket, was developed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pike (weapon)
A pike is a long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the early modern warfare, early modern period, and wielded by infantry, foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well known as the primary weapon of Spanish tercios, Swiss mercenary, German Landsknecht units and French sans-culottes. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in classical antiquity, antiquity by Alexander the Great's Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian phalanx infantry. Design The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th-century military writer John Smith (High Sheriff of Kent), Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
St Martin-in-the-Fields (parish)
St Martin in the Fields was a civil parish in the county of Middlesex, later part of the new County of London, England. It took its name from the Church of St Martin-in-the-Fields and was within the Liberty of Westminster. Within its boundaries were the former extra-parochial areas of Buckingham Palace and St James's Palace. Geography St Martin in the Fields was an ancient parish. In 1542, it gained the "lands between the church of St Clement Danes and the Palace of Westminster" from the parish of Westminster St Margaret. The parish originally included a number of areas that were carved out between 1645 and 1724 to create new parishes: The vestry In 1855, the parish vestry became a local authority within the area of responsibility of the Metropolitan Board of Works. Under the Metropolis Management Act 1855, any parish that exceeded 2,000 ratepayers was to be divided into wards; as such, the incorporated vestry of St Martin in the Fields was divided into three wards (electi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
St Giles, London
St Giles is an area in London, England and is located in the London Borough of Camden. It is in Central London and part of the West End of London, West End. The area gets its name from the parish church of St Giles in the Fields. The combined parishes of St Giles in the Fields and Bloomsbury, St George Bloomsbury (which was carved out of the former) were administered jointly for many centuries, leading to the conflation of the two, with much or all of St Giles usually taken to be a part of Bloomsbury. Points of interest include the church of St Giles in the Fields, Seven Dials, London, Seven Dials, the Phoenix Garden, and St Giles Circus. History There has been a church at St Giles since Saxon times, located beside a major highway.''London: A Biography'' (2000) Ackroyd, Peter Chatto and Windus p131-140 St Giles in the Fields, The hospital of St Giles, recorded as ''Hospitali Sancti Egidii extra Londonium'' was founded, together with a monastery and a chapel, by Matilda of Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, former county in South East England, now mainly within Greater London. Its boundaries largely followed three rivers: the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Lea to the east and the River Colne, Hertfordshire, Colne to the west. A line of hills formed its northern boundary with Hertfordshire. The county was the List of counties of England by area in 1831, second smallest of the historic counties of England, after Rutland. The name of the county derives from its origin as a homeland for the Middle Saxons in the early Middle Ages, with the county subsequently part of that territory in the ninth or tenth century. The City of London, formerly part of the county, became a self governing county corporate in the twelfth century; the City was still able to exert influence as the sheriffs of London maintained their jurisdiction in Middlesex, though the county otherwise remained separate. To the east of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Militia (English)
The English Militia was the principal military reserve force of the Kingdom of England. Militia units were repeatedly raised in England from the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period onwards for internal security duties and to defend against external invasions. One of the first militia units in England were the ''fyrd'', which were raised from Estates of the realm, freemen to defend the estate of their local Shire's lord or accompany the housecarls on offensive expeditions. During the Middle Ages, English militia units continued to be raised for service in various conflicts such as the Wars of Scottish Independence, the Hundred Years' War and the Wars of the Roses. Militia troops continued to see service in Tudor period, Tudor and Stuart periods, most prominently in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Following the Acts of Union 1707, the English Militia was transformed into the Militia (Great Britain), British Militia. Origins The origins of military obligation in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lord Lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility over the local militia was removed. However, it was not until 1921 that they formally lost the right to call upon able-bodied men to fight when needed. Lord-lieutenant is now an honorary titular position usually awarded to a notable person in the county, and despite the name, may be either male or female, peer or not. Origins England and Wales Lieutenants were first appointed to a number of Historic counties of England, English counties by King Henry VIII in the 1540s, when the military functions of the sheriffs were handed over to them. Each lieutenant raised and was responsible for the efficiency of the local militia units of his county, and afterwards of the yeomanry and volunteers. He was commander of these forces, whose officers he a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |