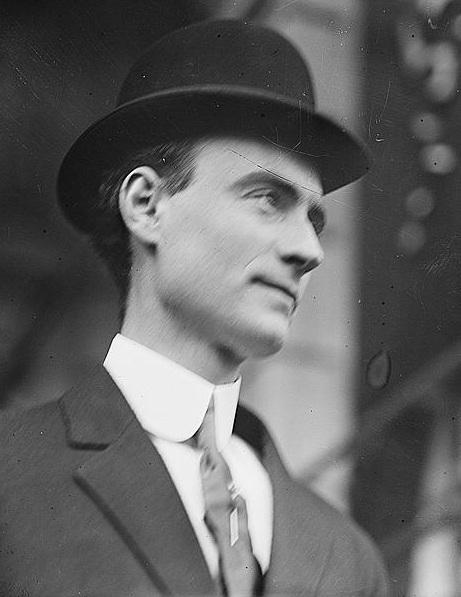|
Roosevelt Field, New York
Roosevelt Field is a former airport, located in the East Garden City, New York, East Garden City section of Uniondale, New York, Uniondale, on Long Island, New York (state), New York, United States. Originally called the Hempstead Plains Aerodrome, or sometimes Hempstead Plains field or the Garden City Aerodrome, it was a training field (Hazelhurst Field) for the Air Service, United States Army during World War I. In 1919, it was renamed in honor of President Theodore Roosevelt's son, Quentin Roosevelt, Quentin, who was killed in air combat during World War I. Roosevelt Field was the takeoff point for many historic flights in the early history of aviation, including Charles Lindbergh, Charles Lindbergh's 1927 solo transatlantic flight. It was also used by other pioneering aviators, including Amelia Earhart and Wiley Post. History The Hempstead Plains Aerodrome originally encompassed east of and abutting Clinton Road, south of and adjacent to Old Country Road, and west of Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
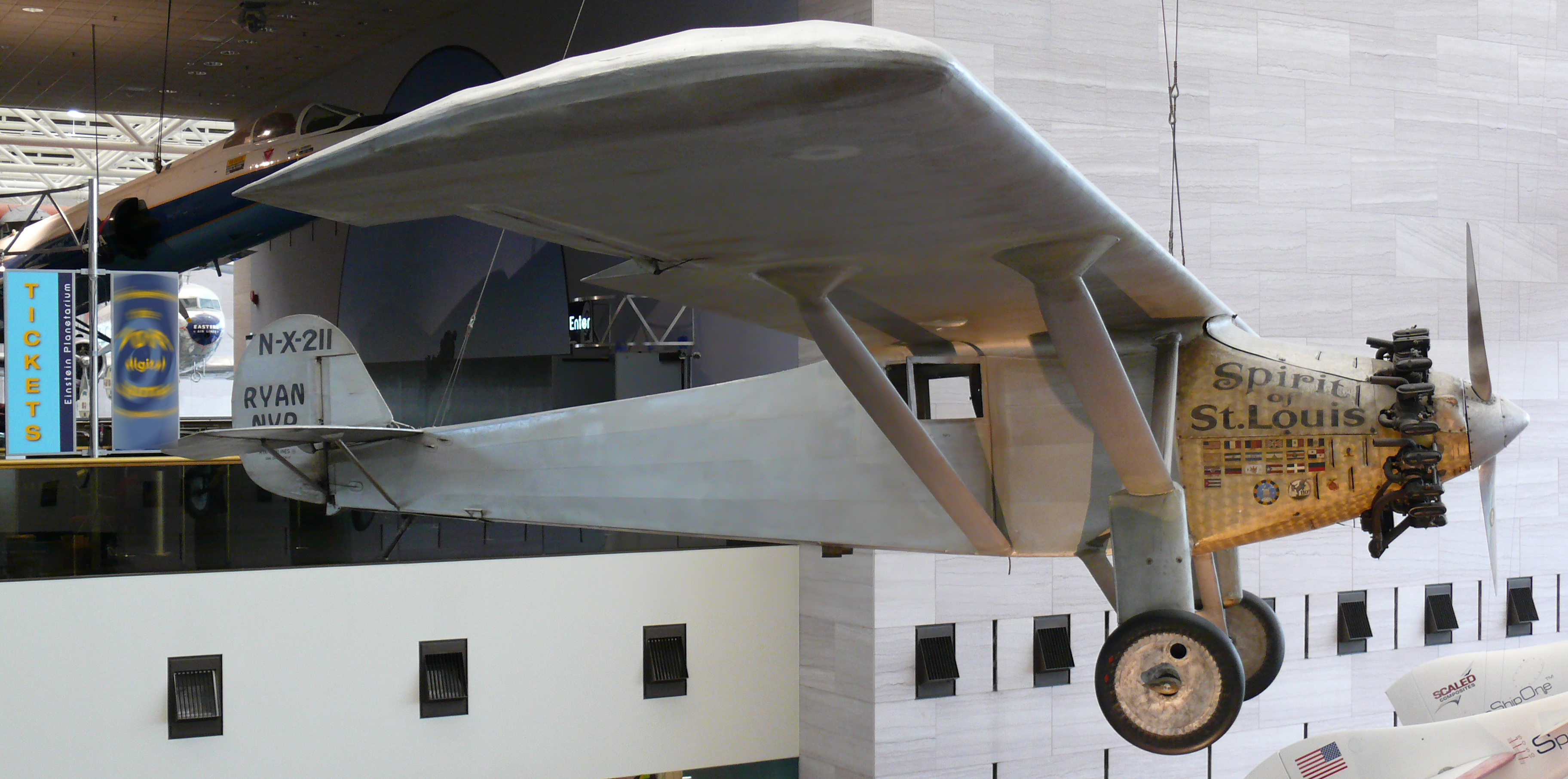
Spirit Of St
Spirit(s) commonly refers to: * Liquor, a distilled alcoholic drink * Spirit (animating force), the non-corporeal essence of living things * Spirit (supernatural entity), an incorporeal or immaterial being Spirit(s) may also refer to: Liquids * Tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol * Cologne spirit, also known as drinking alcohol * Petroleum spirit (other) ** Motor spirit, a clear petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel ** Petroleum ether, liquid hydrocarbon mixtures used chiefly as non-polar solvents ** White spirit or mineral spirits, a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating Philosophy, religion and folklore *Spirituality, pertaining to the soul or spirit *Holy Spirit, a divine force, manifestation of God in the Holy Trinity, or agent of divine action, according to Abrahamic Religions * Great Spirit, conception of a supreme being prevalent among some Native American and First Nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG) is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Army. It is simultaneously part of two different organizations: the Militia of the United States (consisting of the ARNG of each state, most territories, and Washington D.C.), as well as the federal ARNG, as part of the National Guard (United States), National Guard as a whole (which includes the Air National Guard). It is divided into subordinate units stationed in each state or insular area, responsible to their respective governors or other head-of-government. The Guard's origins are usually traced to the city of Salem, Massachusetts, in 1636. That year a regiment of militia drilled for the first time to defend a multi-community area within what is now the United States. Activation The ARNG operates under Title 10 of the United States Code when under federal control, and Title 32 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikorsky S-35
The Sikorsky S-35 was an American triple-engined sesquiplane transport later modified to use three-engines. It was designed and built by the Sikorsky Manufacturing Company for an attempt by René Fonck on a non-stop Atlantic crossing for the Orteig Prize. It was destroyed in the attempt. Design and development The S-35 was designed as a twin-engined transport with a range. During 1926 René Fonck, a French First World War fighter ace, was looking for a multi-engine aircraft to enter a competition to be the first to fly non-stop from New York to Paris. Raymond Orteig offered a prize of $25,000. Fonck had Sikorsky redesign the aircraft with three engines. The S-35 was a sesquiplane with a fixed tail-skid landing gear. It was modified to take three Gnome-Rhône Jupiter 9A radial engines and fitted with jettisonable auxiliary landing gear directly under the fuselage to support its weight at takeoff. Fuel was carried in tanks in the upper wing leading edge, the engine nacelles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Fonck
Colonel René Paul Fonck (27 March 1894 – 18 June 1953) was a French aviator who ended the First World War as the top Triple Entente, Entente fighter Flying ace, ace and, when all succeeding aerial conflicts of the 20th and 21st centuries are also considered, Fonck still holds the title of "all-time Allied Ace of Aces". He received confirmation for 75 victories (72 solo and three shared) out of 142 claims. Taking into account his probable claims, Fonck's final tally could conceivably be nearer 100 or above. He was made an Officer of the Legion of Honor in 1918 and later a Commander of the Legion of Honor after the war, and raised again to the dignity of Grand Officer. Early life Fonck was born on 27 March 1894 in the village of Saulcy-sur-Meurthe in the Vosges (department), Vosges region of north eastern France. Fonck left school when he was 13.Damien Accoulon (2018), ''René Fonck, As des As et pilote de la Grande Guerre'', Editions Privat, Toulouse. Although he had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orteig Prize
The Orteig Prize was a reward of $25,000 offered in 1919 by New York City hotel owner Raymond Orteig to the first Allies of World War I, Allied aviator, or aviators, to fly non-stop from New York City to Paris or vice versa.Bak. Pages 28 and 29. Several famous aviators made unsuccessful attempts at the New York–Paris flight before a relatively unknown American, Charles Lindbergh, won the prize in 1927 with his aircraft the ''Spirit of St. Louis''. A number of people died while competing to win the prize. Six people perished in three separate crashes, and another three were injured in a fourth crash. The Orteig Prize spurred considerable investment in aviation—sometimes far exceeding the value of the prize itself—and also advanced public interest in, and the development of, aviation technology. Background The Orteig Prize was a $25,000 reward () offered on May 22, 1919, by New York hotel owner Raymond Orteig to the first Allied aviator(s) to fly non-stop from New York City to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Island Motor Parkway
The Long Island Motor Parkway, also known as the Vanderbilt Parkway, Vanderbilt Motor Parkway, or Motor Parkway, was a limited-access parkway on Long Island, New York, United States. It was the first highway designed for automobile use only. The parkway was privately built by William Kissam Vanderbilt II with overpasses and bridges to remove most intersections. It officially opened on October 10, 1908. It closed in 1938 when it was taken over by the state of New York in lieu of back taxes. Parts of the parkway survive today, used as sections of other roads or as a bicycle trail. Origins and construction William Kissam Vanderbilt II, the great-grandson of Cornelius Vanderbilt, was an auto-racing enthusiast and created the Vanderbilt Cup, the first major road racing competition, in 1904. He ran the races on local roads in Nassau County during the first decade of the 20th century, but the deaths of two spectators and injury to many others showed the need to eliminate racing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistice With Germany
{{Short description, none This is a list of armistices signed by the German Empire (1871–1918) or Nazi Germany (1933–1945). An armistice is a temporary agreement to cease hostilities. The period of an armistice may be used to negotiate a peace treaty. * Armistice of Versailles (28 January 1871, came into effect fully by 31 January) :Signed with the Third French Republic, ended the Franco-Prussian War. A final peace, the Treaty of Frankfurt, was signed on 10 May 1871. * Armistice of Focșani (9 December 1917) :Signed by Germany and its allies—Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire—with Romania during World War I. A final peace, the Treaty of Bucharest, was signed on 7 May 1918. *Armistice between Russia and the Central Powers (15 December 1917) :Signed by Germany and its allies—Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire—with Soviet Russia after the Russian Revolution, ending the Eastern Front of World War I. The armistice came to an end on 18 February 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R34 (airship)
The R.33 class of British rigid airships were built for the Royal Naval Air Service during the First World War, but were not completed until after the end of hostilities, by which time the RNAS had become part of the Royal Air Force. The lead ship, R.33, served successfully for ten years and survived one of the most alarming and heroic incidents in airship history when she was torn from her mooring mast in a gale. She was called a "Pulham Pig" by the locals, as the blimps based there had been, and is immortalised in the village sign for Pulham St Mary. The only other airship in the class, R.34, became the first aircraft to make an east to west transatlantic flight in July 1919 and, with the return flight, made the first two-way crossing. It was decommissioned two years later, after being damaged during a storm. The crew nicknamed her "Tiny". Design and development Substantially larger than the preceding R31 class airship, R31 class, the R.33 class was in the design stage in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Air Service
The United States Army Air Service (USAAS)Craven and Cate Vol. 1, p. 9 (also known as the ''"Air Service"'', ''"U.S. Air Service"'' and before its legislative establishment in 1920, the ''"Air Service, United States Army"'') was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1918 and 1926 and a forerunner of the United States Air Force. It was established as an independent but temporary branch of the United States Department of War, U.S. War Department during World War I by two executive orders of President Woodrow Wilson: on May 24, 1918, replacing the Aviation Section, U.S. Signal Corps, Aviation Section, Signal Corps as the nation's air force; and March 19, 1919, establishing a military Director of Air Service to control all aviation activities., p. 149, Appendix 2 Redesignations of the Army Air Arm, 1907–1942. Its life was extended for another year in July 1919, during which time Congress passed the legislation necessary to make it a permanent establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Purroy Mitchel
John Purroy Mitchel (July 19, 1879 – July 6, 1918) was the 95th mayor of New York, in office from 1914 to 1917. At 34, he was the second-youngest mayor of the city, and was sometimes referred to as the "Boy Mayor of New York". Mitchel won the 1913 mayoral election in a landslide, but lost the Republican primary in 1917 and came in second place in the general election as an Independent. He is remembered for his short career as leader of anti-Tammany Hall reform politics in New York, as well as for his early death as an Army Air Service officer during a training flight in Louisiana amid World War I. Mitchel was praised by reformists in New York. Journalist Oswald Garrison Villard, the editor of ''The Nation'', called him "the ablest and best Mayor New York ever had."McClymer, p. 376. Former President Theodore Roosevelt, endorsing Mitchel's re-election bid in 1917, stated that he had "given us as nearly an ideal administration of the New York City government as I have seen in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchel Air Force Base
Mitchel Air Force Base, also known as Mitchel Field, was a United States Air Force base located on the Hempstead Plains of Long Island, New York, United States. Established in 1918 as Hazelhurst Aviation Field #2, the facility was renamed later that year as Mitchel Field in honor of former New York City Mayor John Purroy Mitchel, who was killed while training for the Air Service in Louisiana. Decommissioned in 1961, Mitchel Field became a multi-use complex that is home to the Cradle of Aviation Museum, Nassau Coliseum, Mitchel Athletic Complex, Nassau Community College, Hofstra University, and Lockheed. In 2018 the surviving buildings and facilities were recognized as a historic district and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. History Origins During the American Revolutionary War it was known as the Hempstead Plains and used as an Army enlistment center. In the War of 1812 and in the Mexican War, it was a training center for Infantry units. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Mills
Camp Albert L. Mills (Camp Mills) was a military installation on Long Island, New York (state), New York. It was located about ten miles from the eastern boundary of New York City on the Hempstead Plains within what is now the village of Garden City, New York, Garden City. In September 1917, Camp Mills was named in honor of a former Superintendent of the United States Military Academy, Superintendent of the United States Military Academy, United States Military Academy at West Point, Major general (United States), Major General Albert L. Mills, who had suddenly died the year prior in September 1916. Mills had been awarded the Medal of Honor for gallantry during the Spanish–American War. Camp Mills was one of three camps under control of the New York Port of Embarkation with a capacity for 40,000 transient troops. The facility was one of several military establishments built during World War I in the Mineola, New York, area that included the Aviation General Supply Depot and Conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |