|
Romanian Flag
The national flag of Romania () is a tricolour featuring three equal vertical bands colored blue (at the flagpole), yellow and red, with a width to length ratio of 2:3. The current version was adopted in 1989 in the wake of the Romanian Revolution and is defined in the Constitution of Romania as well as by organic law 75/1994, plus several later clarifications. Starting in 2023, the law provides exact color shades for print and digital purposes. The colors have seen documented use individually or in pairs on official insignia and symbols as far back as the 14th century but they were first officially used together on a flag in the 19th century. While the flag has undergone multiple variations over the years, the overall design has remained fairly consistent, using the same colors and with similar placement of the bands relative to each other. Legal framework and specifications Law no. 75/1994 specifies that the flag height is 2/3 of the width and that the color stripes are of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricolour (flag)
A triband is a Vexillology, vexillological style which consists of three stripes arranged to form a flag. These stripes may be two or three colours, and may be Charge (heraldry), charged with an emblem in the middle stripe. Not all tribands are tricolour flags, which requires three unique colours. Design Outside of the name, which requires three bands of colour, there are no other requirements for what a triband must look like, so there are many flags that look very different from each other but are all considered tribands. Some triband flags (e.g. those of Flag of Germany, Germany, Flag of Russia, Russia and Flag of the Netherlands, the Netherlands) have their stripes positioned horizontally, while others (e.g. that of Flag of Italy, Italy) position the stripes vertically. Often the stripes on a triband are of equal length and width, though this is not always the case, as can be seen in the flags of Flag of Colombia, Colombia and Flag of Canada, Canada. Symbols on tribands may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonfalon
The gonfalon, gonfanon, gonfalone (from the early Italian ''confalone'') is a type of heraldic flag or banner, often pointed, swallow-tailed, or with several streamers, and suspended from a crossbar in an identical manner to the ancient Roman vexillum. It was first adopted by Italian medieval communes, and later, by local guilds, corporations and districts. The difference between a gonfalon with long tails and a standard is that a gonfalon displays the device on the non-tailed area, and the standard displays badges down the whole length of the flag. Background A gonfalon can include a badge or coat of arms, or decoration. Today, every Italian comune (municipality) has a gonfalon sporting its coat of arms. The gonfalon has long been used for ecclesiastical ceremonies and processions. The papal " ombrellino", a symbol of the pope, is often mistakenly called "gonfalone" by the Italians because the pope's ceremonial umbrella was often depicted on the banner. Gonfalons are also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihnea III
Mihnea III Radu (; 1613 – 5 April 1660) was the prince of Wallachia from March 1658 to November 1659. His father was alleged to have been the voivode Radu Mihnea. Family Ancestry claims Radu's ancestry is uncertain. During his life, Radu claimed to be the son of Radu Mihnea, but other versions of his history give different accounts of his ancestry, such as claiming his true father was Radu Șerban or Mircea Ciobanu. Pârvu Cantacuzino claims that "Mihnea was originally a Greek money-lender. His father was called Iane the Deaf (Rom. “Surdul”), and he himself was baptized Franți. Thus, showing from a young age a propensity to follow Ishmael, Hagar's son, he ran away from his parents, went to Țarigrad, and bowed in allegiance to Kinan-pașa, telling him that he was the son of Radu-voivode and the grandson of Mihnea-voivode. And thus he spent his life with the Turks, around 40 years". However, the lack of contemporary evidence makes it hard to pinpoint his true ancestry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radu Șerban
Radu Șerban (? – 23 March 1620) was a Wallachian nobleman who reigned as the principality's ''voivode'' during two periods from 1602 to 1610 and during 1611. Biography A supposed descendant of Neagoe Basarab, he attained high office during the reign of Michael the Brave.Alexander D. Xenopol, ''History of Romanians in Dacia Traiana'', Ed. Romanian book, Bucharest, 1925, vol. VI, pp. 7-18. After ascending the throne, he continued the policy of independence of Wallachia first put forth by Michael the Brave. Having struggled with great difficulties inside and outside the country, he managed to cope successfully during a reign lasting almost ten years and successfully defeated Simion Movilă and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basarab I Of Wallachia
Basarab I (), also known as Basarab the Founder (; – 1351/1352), was a ''voivode'' and later the first independent ruler of Wallachia who lived in the first half of the . Many details of his life are uncertain. According to two popular theories, Basarab either came into power between 1304 and 1324 by dethroning or peacefully succeeding the legendary founder of Wallachia, Radu Negru, or in 1310 by succeeding his father, Thocomerius. A royal charter issued on 26 July 1324 is the first document to reference Basarab. According to the charter, he was subject to Charles I of Hungary as the ''voivode'' of Wallachia. Basarab became "disloyal to the Holy Crown of Hungary" in 1325. He seized the Banate of Severin and raided the southern regions of the Kingdom of Hungary. Basarab supported Michael Shishman of Bulgaria's attack against the Kingdom of Serbia, but their united armies were defeated in the Battle of Velbazhd on the 28th of July 1330. Soon after, Charles I of Hungary invade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
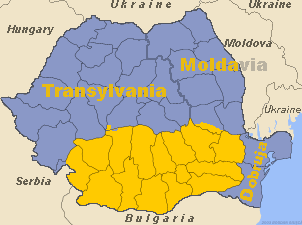
Flag And Coat Of Arms Of Transylvania
The flag and coat of arms of Transylvania were granted by Maria Theresa in 1765, when she established a Grand Principality within the Habsburg monarchy. While neither symbol has official status in present-day Romania, the coat of arms is marshalled within the national Romanian arms; it was also for decades a component of the Hungarian arms. In its upper half, it prominently includes the eagle, or more specifically the image of a Turul, a mythological bird of prey and Hungarian national symbol. Early versions of the Transylvanian charges were first designed in Habsburg Hungary at some point before 1550, and were therefore symbols of pretence. The arms were only attested as in use by the Transylvanian Principality in or after 1580. The first Prince to recognize and use them was Sigismund Báthory, who also simplified the charges. They entered the heraldic patrimony over the next few decades, and, during Ákos Barcsay's reign, were codified as representing three separate jurisd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Ghica
Alexandru Scarlat Ghica (? – after 1768) was Voivode (Prince) of Wallachia from December 1766 to October 1768. He succeeded Scarlat Ghica. References 18th-century princes of Wallachia Alexandru Alexandru is the Romanian form of the name Alexander. Common diminutives are Alecu, Alex, and Sandu. Origin Etymologically, the name is derived from the Greek "Αλέξανδρος" (Aléxandros), meaning "defending men" or "protector of m ... Year of death unknown Year of birth unknown Romanian people of Albanian descent {{Albania-noble-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihai Sturdza
Prince Mihail Sturdza (24 April 1794 – 8 May 1884), sometimes anglicized as Michael Stourdza, was prince ruler of Moldavia from 1834 to 1849. He was cousin of Princess Roxandra Sturdza and Prince Alexandru Sturdza. Early life He was born as third child and the only son of Grigore Sturdza, Lord of Cozmești, Grand Logothete (1758-1833) and his wife, Princess Maria Callimachi (1762-1822), daughter of Gregory Callimachi, reigning Prince of Moldavia. Biography A man of liberal education, he established in Iași, the Academia Mihăileană, the first University in Romania, a institution of higher education, and the precursor of the University of Iași. He brought scholars from foreign countries to act as teachers, and gave a very powerful stimulus to the educational development of the country. In 1844 he decreed the emancipation of the Gypsies, which until then had been treated as slaves and owned by the Church or by private landowners; they had been bought and sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Suțu
Alexandros Soutzos (, , '';'' 1758 – 18/19 January 1821) was a Phanariote Greek who ruled as Prince of Moldavia (July 10, 1801 – October 1, 1802 and Prince of Wallachia (July 2, 1802 – August 30, 1802; August 24, 1806 – October 15, 1806; December 1806; November 17, 1818 – January 19, 1821). Born in Constantinople, he had earlier been Grand Dragoman of the Ottoman Empire The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr .... References 1758 births 1821 deaths 19th-century princes of Wallachia Monarchs of Moldavia Greek people of the Greek War of Independence Wallachian people of the Greek War of Independence Alexandros Dragomans of the Porte Dragomans of the Fleet Constantinopolitan Greeks 19th-century Moldavian people {{Greece-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Ipsilanti
Alexandru is the Romanian form of the name Alexander. Common diminutives are Alecu, Alex, and Sandu. Origin Etymologically, the name is derived from the Greek "Αλέξανδρος" (Aléxandros), meaning "defending men" or "protector of men", a compound of the verb "ἀλέξω" (alexō), "to ward off, to avert, to defend" and the noun "ἀνδρός" (andros), genitive of "ἀνήρ" (anēr), "man". It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek (or Indo-European more generally) names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name is the Mycenaean Greek feminine noun ''a-re-ka-sa-da-ra'', (transliterated as ''Alexandra''), written in Linear B syllabic script. The name was one of the titles ("epithets") given to the Greek goddess Hera and as such is usually taken to mean "one who comes to save warriors". In the Iliad, the character Paris is known also as Alexander. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael The Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvania (1599–1600). He is considered one of Romania's greatest national heroes. Since the 19th century, Michael the Brave has been regarded by Romanian nationalism, Romanian nationalists as a symbol of Romanian unity, as his reign marked the first time in history all principalities inhabited by Romanians were under the same ruler. His rule over Wallachia began in the autumn of 1593. Two years later, Long Turkish War, war with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans began, a conflict in which the Prince fought the Battle of Călugăreni, resulting in a victory against an army nearly three times the size of the army of Michael the Brave, considered one of the most important battles of his reign. Although the Wallachians emerged victorious from the battle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ieremia Movilă
Ieremia Movilă ( ; c. 1555 – 10 July 1606) was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia between August 1595 and May 1600, and again between September 1600 and July 10, 1606. At the time, Moldavia was a vassal province of the Polish-Lituania CommonWealth. Rule A boyar of the Movilești family, Ieremia was placed on the throne in Iași by Polish Kanclerz (Chancellor) and hetman Jan Zamoyski after the ousting of Ștefan Răzvan. Zamoyski's intervention had been prompted by Răzvan's acceptance of Imperial tutelage over Moldavia, after having received backing from Transylvanian Prince Sigismund Báthory and Emperor Rudolf II. The potential conflict with the country's Ottoman overlord was defused after the Poles negotiated an agreement with Sinan Pasha, although Moldavia was invaded by the Khan of Crimea and Ottoman vassal Ğazı II Giray. Poland and the Turks signed the Treaty of Cecora after the defeat of Tatar troops in October, with the Porte agreeing to Ieremia's rule. Mold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |